Uber Data Scientist Interview Guide: Process, Questions & Preparation Tips (2026)
Introduction
Data science remains one of the fastest-growing roles in technology, with the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting more than 35 percent growth in data-focused jobs through the next decade. At marketplace-driven companies like Uber, this growth is even more concentrated. Uber data scientists work at the intersection of real-time demand, pricing, incentives, and logistics, using data to influence millions of daily decisions across riders, drivers, and couriers. Because of that impact, the hiring bar is high. Fewer than 15 percent of applicants typically advance past early interview stages, as Uber looks for candidates who can reason clearly about messy data and high-stakes trade-offs.
What makes the Uber data scientist interview challenging is not just technical difficulty, but context. You are evaluated on how well you think in Uber’s world: designing experiments with real economic consequences, defining metrics that actually guide product decisions, and communicating insights to non-technical partners. This guide is built to help you prepare with that lens. It walks through the full Uber data scientist interview process, the most common Uber-specific data science questions, and the preparation strategies that experienced Uber data scientists rely on to stand out.
Uber Data Scientist Interview Process
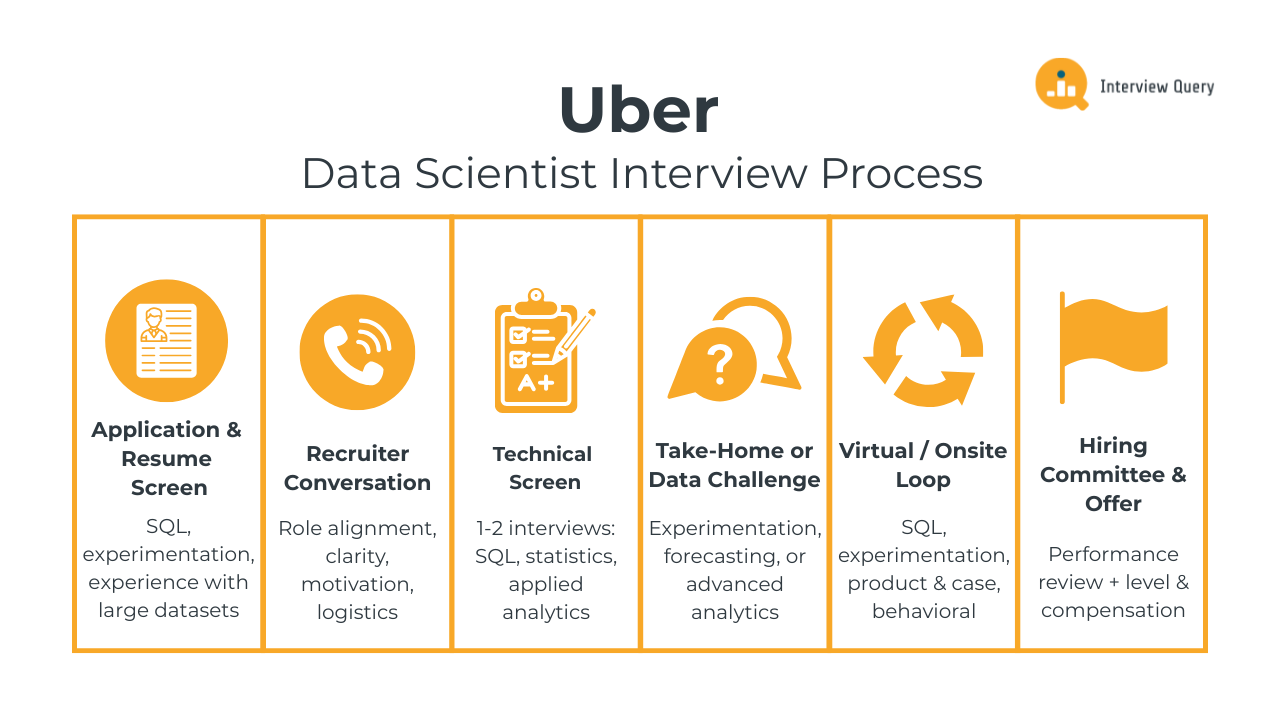
The Uber data scientist interview process is designed to evaluate how well you analyze complex marketplace data, reason through ambiguous product problems, and translate insights into decisions that scale globally. Beyond SQL and modeling fundamentals, Uber places heavy emphasis on experimentation judgment, metric design, and cross-functional communication. Most candidates complete the full Uber interview loop within three to six weeks, depending on team needs and seniority.
Below is a breakdown of each stage and what interviewers at Uber consistently look for throughout the process.
Application and Resume Screen
During the application review, Uber recruiters look for strong analytical foundations paired with clear evidence of business impact. Resumes that stand out typically show deep SQL ownership, experience working with large event datasets, and familiarity with experimentation or causal analysis. Marketplace experience, such as pricing, incentives, logistics, or growth analytics, is highly relevant, but not required if your past work demonstrates strong decision-making under uncertainty.
Tip: Quantify outcomes in terms Uber cares about, such as changes in wait time, conversion, retention, or supply efficiency. This signals that you understand how analysis translates into real marketplace outcomes.
Initial Recruiter Conversation
The recruiter call focuses on role alignment, communication clarity, and motivation for Uber. You will discuss your background, the types of problems you have worked on, and why Uber’s marketplace problems interest you. Recruiters also confirm logistical details like location, team fit, interview timeline, and compensation expectations. This round is non-technical, but it sets the tone for how clearly you can articulate your experience.
Tip: Frame your experience around decision-making, not tools. Recruiters respond strongly to candidates who explain how their work influenced product or operational choices.
Technical Screen
The technical screen usually consists of one or two interviews focused on SQL, statistics, and applied analytics. You may be asked to write complex queries with joins and window functions, define or critique metrics, or analyze a scenario such as declining conversion or rising cancellations. Interviewers care as much about your reasoning and assumptions as your final answer.
Tip: Narrate your thinking as you work. Clear reasoning shows analytical maturity and reduces the risk of solving the wrong problem, which matters more than perfect syntax at Uber.
Take Home Assignment or Data Challenge
Some Uber teams include a take-home assignment, particularly for roles focused on experimentation, forecasting, or advanced analytics. These exercises often involve exploring a dataset, identifying key patterns, and making recommendations. Submissions are evaluated on structure, clarity, and decision logic, not just technical correctness.
Tip: Treat the write-up like an internal Uber doc. Explicitly call out assumptions, trade-offs, and what you would test next. This demonstrates ownership and practical judgment.
Virtual or Onsite Interview Loop
The final interview loop is the most in-depth part of the Uber data scientist interview process. It typically includes four to five interviews, each lasting 45 to 60 minutes. These rounds simulate the types of decisions Uber data scientists make daily and assess how you operate in ambiguous, high-impact environments.
SQL and data analysis round: You will work with realistic, messy datasets and answer questions involving aggregation, segmentation, and trend analysis. Examples include diagnosing changes in trip completion, comparing city-level performance, or computing cohort retention. Interviewers evaluate how cleanly you structure queries and how effectively you extract insight from data.
Tip: State your assumptions before writing SQL. This shows analytical discipline and reduces ambiguity, a skill Uber values in production decision-making.
Experimentation and causal reasoning round: This round focuses on experiment design and interpretation. You may be asked to design an A/B test for pricing changes, driver incentives, or app features, or to critique an experiment with flawed assumptions. Interviewers look for strong metric selection, awareness of interference, and thoughtful trade-offs.
Tip: Emphasize how you would protect experiment validity in a live marketplace. This signals strong causal reasoning and real-world awareness.
Product and marketplace case round: You will tackle an open-ended problem such as reducing rider wait times, improving courier reliability, or understanding a drop in engagement. The goal is not a perfect answer, but a structured approach that connects data to product decisions.
Tip: Anchor your analysis to a single primary metric before expanding. This shows prioritization skills and product clarity.
Behavioral and collaboration round: This interview assesses how you work with product managers, engineers, and operations partners. Expect questions about handling disagreement, navigating ambiguity, and owning outcomes. Uber values data scientists who can influence without authority.
Tip: Highlight moments where you changed a decision or direction through data. This demonstrates impact, communication strength, and leadership.
Hiring Committee and Offer
After the final loop, interviewers submit independent written feedback. A hiring committee reviews your performance across all rounds, weighing analytical strength, judgment, communication, and role fit. If approved, Uber determines level and compensation and may align you with a specific team based on feedback and business needs.
Tip: If you have strong preferences for product areas like pricing, growth, or logistics, share them early. Clear signals help Uber match you to teams where you can have the most impact.
Want realistic practice without scheduling or pressure? Use Interview Query’s AI Interviewer to simulate Uber data scientist interviews and get instant feedback on your SQL, experimentation, and marketplace reasoning before the real interview.
Uber Data Scientist Interview Questions
The Uber data scientist interview includes a mix of SQL, analytics, experimentation, product reasoning, and applied modeling. These questions are designed to evaluate how well you work with noisy, real-world marketplace data, reason about trade-offs between riders and drivers, and turn analysis into decisions that scale globally. At Uber, interviewers care about how you structure problems, validate assumptions, and communicate insights in ambiguous situations.
Read more: Top 110 Data Science Interview Questions
SQL and Analytics Interview Questions
Uber relies heavily on SQL-driven analysis to monitor marketplace health, evaluate product changes, and diagnose performance issues. SQL questions often involve large event tables, time-based analysis, segmentation, and window functions. Interviewers are looking for clean query structure, correct logic, and an ability to reason about data quality and edge cases that naturally arise in real-time systems.
How would you calculate rider retention by cohort over the first 90 days?
Uber asks this because retention is a core signal of product value, and cohorts let you separate real behavior change from shifts in acquisition mix. You should explain that you would define cohorts by each rider’s first completed trip date, then join subsequent trips and compute retention at standard intervals like day 7, day 28, and day 90. In SQL, you typically build a cohort table, calculate
days_since_first_trip, bucket it, and aggregate unique riders per bucket divided by cohort size, while accounting for delayed events and late-arriving trips.Tip: Call out how you would handle reactivations versus true retention. That shows strong metric judgment, which is exactly what Uber interviewers look for in product analytics roles.
-
Uber asks this because it mirrors real marketplace telemetry: event tracking, clean schema design, and turning raw logs into operational insights. You should propose an
entriestable keyed bycrossing_idwithvehicle_id,car_model,entry_time,exit_time, and a date partition. Then explain you would compute crossing duration asexit_time - entry_time, filter to “today,” and select the minimum duration for fastest crossing. For fastest average by model, group bycar_modeland order byAVG(duration)ascending, watching for missing exits.Tip: Mention guardrails like filtering out negative or implausible durations and handling vehicles without exit events. That signals production readiness, which Uber values as much as correctness.
-
Uber asks this because dispatch and matching are marketplace-critical, and data scientists need to reason about fairness, incentives, and selection bias. You should describe a weighted random sample where drivers with higher weights are more likely to be chosen. Practically, you can compute a cumulative distribution by ordering drivers, summing weights with a window function, generate a random number between 0 and total weight, and pick the first driver whose cumulative weight exceeds that value. You should also explain why weights must be normalized and how you would ensure eligible drivers only.
Tip: Say how you would test for unintended bias across driver segments after introducing weighting. This shows marketplace judgment and responsible decision-making, which stands out strongly at Uber.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber-specific data scientist interview questions in one place. Work through SQL, experimentation, marketplace cases, and behavioral questions with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback to prepare for the exact mix of technical depth and product judgment Uber interviews require.
-
Uber asks this because it reflects core analytics work: deriving behavioral metrics from trip data and making them decision-ready for product or ops partners. You should explain you would join
userstoridesonuser_id, sum distance per user across rides, and rank users using a window function likeDENSE_RANK()ordered by total distance descending. In SQL terms:GROUP BY user_idwithSUM(ride_distance)and then rank in an outer query. You should also mention filtering to completed rides and handling unit consistency.Tip: Add how you would sanity-check for outliers like impossible distances or duplicated rides. That demonstrates data validation instincts, a key trait for Uber data scientists working with messy event data.
How would you detect duplicate trip events in the data?
Uber asks this because event duplication happens in real systems, and bad instrumentation can quietly break marketplace metrics and experiments. You should explain you would define what “duplicate” means first, usually same
trip_idemitted multiple times or near-identical events for the same rider-driver pair within a short time window. Then you can useCOUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY trip_id, event_type)to flag repeats, or useROW_NUMBER()to keep the first event and mark the rest. For near-duplicates, you can compare adjacent timestamps withLAG()and threshold by seconds.Tip: Explain how you would quantify the impact on key metrics before “fixing” it. That shows ownership and prioritization, which Uber interviewers associate with senior-level judgment.
If you want to master SQL interview questions, join Interview Query to access our 14-Day SQL Study Plan, a structured two-week roadmap that helps you build SQL mastery through daily hands-on exercises, real interview problems, and guided solutions. It’s designed to strengthen your query logic, boost analytical thinking, and get you fully prepared for your next data science interview.
A/B Testing and Experimentation Interview Questions
Uber’s experimentation questions focus on whether you can design tests that hold up inside a live marketplace. You are evaluated on how you choose metrics, protect user experience, and interpret results when interference, limited data, or uneven regional effects are unavoidable. The goal is to see if you can make safe, scalable decisions, not just run statistically clean tests.
How would you design an experiment to test a new driver incentive program?
Uber asks this because incentives directly affect supply, earnings, and rider experience. You should explain that you would randomize at a city or zone level to limit spillovers, choose a primary metric like incremental supply hours or acceptance rate, and set guardrails such as rider wait time, cancellations, and churn. You should also discuss ramping gradually and monitoring real-time metrics since incentives can shift behavior quickly.
Tip: Call out how you would cap downside risk during early rollout. This signals strong ownership and marketplace judgment, not just experimentation knowledge.
-
This tests whether you can adapt experimentation methods to real constraints Uber often faces in smaller markets or fleet pilots. You should explain that instead of relying on normality assumptions, you might use non-parametric tests, bootstrapping, or Bayesian methods to compare variants. You should also discuss focusing on effect size and confidence intervals rather than p-values alone, especially when sample sizes are small.
Tip: Explain how you would combine statistical evidence with operational intuition. This shows practical decision-making under uncertainty, which Uber values highly.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber-specific data scientist interview questions in one place. Work through SQL, experimentation, marketplace cases, and behavioral questions with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback to prepare for the exact mix of technical depth and product judgment Uber interviews require.
-
Uber asks this because cancellation fees affect multiple stakeholders simultaneously. You should explain that you would randomize riders into fee tiers, track primary metrics like cancellation rate and completed trips, and include guardrails such as rider retention and driver idle time. A strong answer also discusses elasticity and whether higher fees reduce bad behavior or suppress demand too aggressively.
Tip: Tie your recommendation to long-term behavior change, not short-term revenue. This demonstrates product maturity and systems thinking.
How would you interpret an experiment that shows positive results overall but negative impact in certain cities?
This question evaluates your ability to reason about heterogeneous effects in a global marketplace. You should explain that you would segment by city characteristics such as density, supply balance, or rider mix, then compare confidence intervals to assess whether differences are meaningful. Based on findings, you might recommend targeted rollouts or follow-up experiments rather than a global launch.
Tip: Emphasize learning before scaling. This signals responsible experimentation and strong causal reasoning.
-
Uber asks this to assess whether you can connect experimentation, modeling, and production systems. You should describe a pipeline with offline training on historical trip data, real-time inference using current context, and monitoring for feature drift and performance decay. A strong answer explains how experiments validate model changes before full deployment and how alerts trigger retraining or rollback.
Tip: Highlight how you would protect rider experience during model updates. This shows engineering judgment and accountability, not just technical depth.
Watch next: Top Statistics Questions in 2025 for Data Scientists
In this statistics-focused deep dive, Jay, the founder of Interview Query, breaks down the recurring patterns behind statistics questions asked at top companies like Google, Netflix, and Wall Street firms, and shows how to approach each with confidence. This breakdown is especially valuable for Uber data scientist candidates, as it sharpens intuition around hypothesis testing, variance, and experiment interpretation, all of which are critical when evaluating marketplace metrics, pricing tests, and incentive experiments at Uber.
Product and Marketplace Case Interview Questions
These case-style questions test how you reason about Uber’s marketplace as a system. Interviewers evaluate how you structure ambiguous problems, prioritize signals, and connect data to decisions that balance rider experience, driver outcomes, and platform health. Clear framing and trade-off awareness matter more than arriving at a single “right” answer.
Rider wait times increased last month. How would you investigate?
Uber asks this to see how you decompose a marketplace problem before diving into data. You should start by framing wait time as a function of supply, demand, and matching efficiency, then examine changes in trip requests, active drivers, acceptance rates, pricing, and operational constraints by city and time of day. From there, you would isolate whether the issue is demand spikes, supply drops, or system inefficiencies and validate with supporting metrics.
Tip: Explicitly state the order you would investigate signals and why. This shows prioritization and marketplace intuition, not just analytical ability.
To improve customer experience on Uber Eats, what key parameters would you focus on improving?
This question tests whether you understand the Uber Eats marketplace beyond surface-level metrics. A strong answer explains that you would focus on delivery time reliability, order accuracy, merchant preparation time, courier availability, and cancellation rates. You should also discuss trade-offs, such as faster delivery versus higher courier wait times, and how improvements affect retention rather than just one-off satisfaction.
Tip: Tie each parameter back to a specific customer pain point. This demonstrates product thinking grounded in user experience, which Uber values highly.
-
Uber asks this to assess your ability to blend modeling with business context. You should explain how you would define driver lifetime using churn or inactivity thresholds, model survival probability using early engagement signals, and estimate lifetime value by combining expected active duration with average earnings contribution. A strong answer also calls out uncertainty and how estimates improve as more data becomes available.
Tip: Emphasize how early signals guide intervention strategies, not just forecasting. This shows you think about analytics as a decision tool, not an academic exercise.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber-specific data scientist interview questions in one place. Work through SQL, experimentation, marketplace cases, and behavioral questions with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback to prepare for the exact mix of technical depth and product judgment Uber interviews require.
How would you prioritize cities for expansion or investment?
This question evaluates how you balance quantitative analysis with strategic judgment. You should explain that you would compare cities using demand forecasts, supply availability, unit economics, regulatory complexity, and competitive landscape. Strong answers also discuss constraints like onboarding capacity and local operational readiness, rather than ranking cities on a single metric.
Tip: Clearly explain what you would deprioritize and why. This signals comfort making trade-offs under ambiguity, a key skill for Uber data scientists.
-
Uber asks this to see whether you can design metrics that operate in real time. You should explain defining demand through incoming requests per minute, supply through available drivers, and imbalance through ratios like requests per active driver. You would then set thresholds based on historical distributions and trigger actions such as pricing adjustments or incentives when limits are crossed.
Tip: Mention how you would tune thresholds differently by city and time of day. This shows operational awareness and avoids one-size-fits-all thinking.
Need personalized guidance on your interview strategy? Explore Interview Query’s Coaching Program that pairs you with mentors to refine your prep and build confidence.
Behavioral Interview Questions
Behavioral interviews at Uber assess how you operate in ambiguous, cross-functional environments where influence matters more than authority. Interviewers look for ownership, sound judgment, and the ability to move decisions forward using data while maintaining trust with product, engineering, and operations partners.
Tell me about a time your analysis changed a product decision.
This question evaluates your ability to influence outcomes with data, not just produce analysis. Uber wants to see that you can connect insights to action in a high-stakes product environment.
Sample answer: In my previous role, a team planned to roll out a pricing change globally based on early metrics. I analyzed city-level data and found a 6 percent conversion drop in dense urban areas tied to longer ETAs. I presented a segmented view, recommended a phased rollout, and proposed a targeted experiment instead. As a result, the team delayed the launch, ran a follow-up test, and avoided an estimated 4 percent revenue loss in key markets.
Tip: Quantify both the insight and the decision impact. This shows product influence and business judgment, which Uber prioritizes in senior data scientists.
What makes you a good fit for an Uber data scientist position?
This question tests self-awareness and alignment with Uber’s operating model. Interviewers want to hear how your strengths map to real marketplace problems.
Sample answer: My background centers on marketplace analytics and experimentation, where I routinely worked with noisy event data and competing stakeholder goals. In my last role, I owned metrics tied to supply efficiency and reduced wait times by 8 percent through targeted experimentation. I enjoy working in ambiguous environments and translating data into decisions, which aligns closely with how Uber data scientists operate day to day.
Tip: Anchor your answer in Uber-style problems, not generic skills. This signals genuine role fit and informed motivation.
Describe a time you disagreed with a stakeholder. How did you handle it?
This question assesses collaboration and conflict resolution. Uber values respectful disagreement backed by evidence.
Sample answer: A product manager wanted to launch a feature based on early engagement gains, but my analysis showed a 12 percent increase in downstream cancellations. I scheduled a working session, walked through the data assumptions, and proposed an alternative metric aligned with long-term retention. We agreed to delay the launch and run a refined experiment, which later showed neutral engagement but improved retention by 5 percent.
Tip: Emphasize alignment and shared goals. Uber looks for data scientists who de-escalate tension and guide decisions collaboratively.
How would you convey insights and the methods you use to a non-technical audience?
This question tests communication clarity and decision enablement. Uber data scientists frequently brief non-technical partners.
Sample answer: When presenting to operations leaders, I focus on the decision first, then support it with one or two key metrics. In one case, I replaced a technical model explanation with a simple scenario comparison and visual trend, which helped leadership quickly decide on a policy change that reduced driver idle time by 7 percent.
Tip: Lead with outcomes, not methodology. This shows you understand how to make data usable in fast-moving environments.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber-specific data scientist interview questions in one place. Work through SQL, experimentation, marketplace cases, and behavioral questions with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback to prepare for the exact mix of technical depth and product judgment Uber interviews require.
Tell me about a failed analysis or experiment. What did you learn?
This question evaluates resilience and learning mindset. Uber expects thoughtful iteration, not perfection.
Sample answer: I once ran an experiment that showed no significant lift, later discovering that traffic was unevenly distributed due to a logging issue. I documented the failure, worked with engineers to fix instrumentation, and redesigned the experiment. The follow-up test produced a clear 5 percent improvement, and the learnings became a standard checklist for future experiments.
Tip: Focus on what you changed after the failure. Uber values accountability and continuous improvement over defensiveness.
Struggling with take-home assignments? Get structured practice with Interview Query’s Take-Home Test Prep and learn how to ace real case studies.
What Does an Uber Data Scientist Do?
An Uber data scientist turns large-scale marketplace data into decisions that directly affect pricing, supply, growth, and user experience across rides, delivery, and logistics. The role sits at the intersection of product analytics, experimentation, and applied modeling, where insights are expected to move quickly from analysis to action. At Uber, data scientists partner closely with product managers and engineers to define metrics, design experiments, and evaluate trade-offs in a live, highly dynamic system where small changes can have outsized real-world impact.
How Uber Data Scientists Turn Work into Impact
| What They Work On | Core Skills Used | Tools And Methods | Why It Matters At Uber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketplace supply and demand | SQL, causal reasoning, time series analysis | Cohort analysis, regression, experimentation | Keeps rider wait times low while ensuring healthy driver earnings |
| Pricing and incentives | Experiment design, metric selection, elasticity analysis | A/B tests, holdouts, quasi-experiments | Balances growth, efficiency, and marketplace stability |
| Product performance metrics | Analytical thinking, metric governance | Dashboards, deep-dive analyses | Ensures teams optimize the right outcomes, not vanity metrics |
| User behavior analysis | Segmentation, funnel analysis | Event data modeling, retention analysis | Improves rider and driver experience across journeys |
| Forecasting and planning | Statistical modeling, uncertainty estimation | Forecast models, scenario analysis | Supports city launches, promotions, and capacity planning |
Tip: At Uber, strong data scientists show they understand marketplace trade-offs. In interviews, explain not just what metric you chose, but why it aligns rider experience, driver incentives, and long-term platform health. This signals product judgment, not just technical ability.
How to Prepare for an Uber Data Scientist Interview
Preparing for the Uber data scientist interview goes beyond practicing SQL queries or reviewing statistical formulas. You are preparing for a role that operates inside a live marketplace, where data decisions affect pricing, supply balance, and user trust in real time. Success depends on how well you think through trade-offs, structure ambiguous problems, and communicate recommendations that product and operations teams can act on immediately. At Uber, strong preparation is less about memorization and more about building judgment that holds up under real-world constraints.
Read more: How to Prepare for Data Science Interviews
Below is a focused preparation plan that reflects how experienced Uber data scientists actually approach interviews.
Build intuition for marketplace dynamics, not just metrics: Uber interviews reward candidates who understand how rider demand, driver supply, pricing, and incentives interact. Practice explaining how a change in one part of the system creates second-order effects elsewhere, even before looking at data.
Tip: When discussing any metric, explicitly state who it benefits and who it might hurt. This demonstrates marketplace awareness and product judgment, not just analytical skill.
Practice turning ambiguous questions into clear analytical plans: Many Uber questions start vague by design. Get comfortable clarifying objectives, identifying constraints, and proposing a step-by-step analysis before touching data. This mirrors how real decisions are made internally.
Tip: Start answers by restating the problem and your assumptions out loud. This signals structured thinking and reduces misalignment with interviewers.
Strengthen your ability to reason about data quality and bias: Uber data is noisy, delayed, and sometimes incomplete. Prepare to discuss how you would validate metrics, handle missing events, and detect instrumentation issues before drawing conclusions.
Tip: Call out potential data pitfalls proactively. Interviewers see this as a sign of ownership and production readiness.
Refine how you communicate insights to non-technical partners: Data scientists at Uber spend significant time influencing product managers and operations teams. Practice explaining analyses in plain language, focusing on decisions and trade-offs rather than technical details.
Tip: Frame insights as recommendations with clear next steps. This shows you can move teams forward, not just analyze data.
Rehearse full interview loops under realistic conditions: Simulate an Uber-style loop via mock interview sessions by practicing one SQL round, one experimentation or case round, and one behavioral session back to back. Pay attention to pacing, clarity, and how often you pause to think.
Tip: After each mock, note where your explanations felt unclear or overly detailed. Tightening those moments often makes the biggest difference in final interview performance.
Looking for hands-on problem-solving? Test your skills with real-world challenges from top companies. Ideal for sharpening your thinking before interviews and showcasing your problem solving ability.
Uber Data Scientist Salary
Uber’s compensation framework is built to reward data scientists who can drive measurable marketplace impact, design reliable experiments, and influence high-stakes product decisions. Data scientists at Uber receive competitive base pay, annual performance bonuses, and meaningful equity through restricted stock units. Your total compensation depends heavily on level, location, and scope of ownership, with most candidates interviewing at the mid-level or senior bands due to the company’s emphasis on prior product and experimentation experience.
Read more: Data Scientist Salary
Tip: Clarify your target level with the recruiter early. At Uber, level alignment directly affects compensation bands and role expectations, and late corrections are difficult.
Uber Data Scientist Compensation Overview (2026)
| Level | Role Title | Total Compensation (USD) | Base Salary | Bonus | Equity (RSUs) | Signing / Relocation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS I | Data Scientist I | $135K – $175K | $115K–$140K | Performance based | Standard RSUs | Rare, role dependent |
| DS II | Data Scientist II / Mid Level | $165K – $220K | $130K–$160K | Performance based | RSUs included | Offered selectively |
| Senior DS | Senior Data Scientist | $195K – $275K | $150K–$185K | Above target possible | Larger RSU grants | Common for strong candidates |
| Staff / Lead DS | Staff or Lead Data Scientist | $240K – $330K+ | $170K–$210K | High performer bonuses | Large RSUs + refreshers | Frequently offered |
Note: These estimates are aggregated from data on Levels.fyi, Glassdoor, TeamBlind, public job postings, and Interview Query’s internal salary database.
Tip: Focus on total compensation, not just base salary. At Uber, equity appreciation and refresher grants meaningfully affect long-term earnings, especially at senior levels.
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Negotiation Tips that Work for Uber
Negotiating compensation at Uber is most effective when you combine market benchmarks with a clear narrative around scope and impact. Recruiters respond best to candidates who are informed, realistic, and precise.
- Confirm your level before negotiating numbers: Uber’s leveling from DS II to Senior or Staff can shift offers by tens of thousands. Always confirm level alignment before discussing compensation details.
- Anchor discussions with real market data: Use verified benchmarks from Levels.fyi, Glassdoor, and Interview Query salaries. Frame your value through marketplace impact, such as improving conversion, reducing wait times, or increasing supply efficiency.
- Account for location-based differences: Compensation varies significantly across San Francisco, Seattle, New York, and remote roles. Ask for location-specific bands so you can evaluate offers accurately.
Tip: Request a full compensation breakdown including base, bonus target, equity amount, vesting schedule, and refresher policy. This signals senior-level professionalism and helps you negotiate from a well-informed position.
FAQs
How long does the Uber data scientist interview process take?
Most candidates complete the process within three to six weeks. Timelines vary based on team matching, interview availability, and level calibration. Recruiters typically share clear next steps after each round and keep candidates informed if timelines shift.
Does Uber use online assessments or take-home tests?
Some teams include a short take-home assignment or data exercise, especially for experimentation-heavy roles. Many mid-level and senior candidates move directly to live technical screens. The format depends on the team and problem area.
How important is prior marketplace experience for Uber?
Marketplace experience is helpful but not required. Uber looks for strong analytical judgment, experimentation thinking, and comfort with ambiguity. Candidates from e-commerce, logistics, or consumer product backgrounds often ramp quickly.
What level of SQL difficulty should I expect at Uber?
Uber’s SQL questions are moderately to highly challenging and focus on real event data. Expect multi-join queries, window functions, time-based analysis, and metric validation. Clear logic and assumptions matter as much as syntax.
Does Uber test machine learning knowledge for data scientists?
Machine learning depth varies by team. Many roles emphasize experimentation, metrics, and causal reasoning over model building. You should be prepared to explain modeling trade-offs, evaluation, and when simpler approaches are better.
How product-focused are Uber data scientist interviews?
Very product-focused. Interviewers expect you to connect analysis to decisions affecting riders, drivers, or couriers. Strong candidates consistently tie metrics and experiments back to user experience and marketplace health.
What behavioral traits does Uber value most in data scientists?
Uber values ownership, clarity, and influence. Data scientists are expected to drive decisions without authority, communicate trade-offs clearly, and take responsibility for outcomes in ambiguous environments.
Can candidates be considered for multiple teams at Uber?
Yes. Many candidates are evaluated for multiple teams during the process. Communicating your interests early helps recruiters and hiring managers align you with teams where your strengths and interests fit best.
Become an Uber Data Scientist with Interview Query
Preparing for the Uber data scientist interview means developing strong analytical judgment, deep SQL fluency, and the ability to reason through marketplace trade-offs that affect millions of users in real time. By understanding Uber’s interview structure, practicing real-world SQL, experimentation, and product case scenarios, and refining how you communicate insights, you can approach each stage with confidence. For targeted practice, explore the full Interview Query question bank, train with the AI Interviewer, or work directly with experienced mentors through Interview Query’s Coaching Program to sharpen your thinking and stand out in Uber’s highly competitive data science hiring process.


