Uber Machine Learning Engineer Interview Guide (2026): Process, Questions & Prep
Introduction
The Uber machine learning engineer interview reflects how the company builds and ships machine learning in the real world. Uber’s platform operates at massive global scale, making real-time decisions across pricing, estimated time of arrival predictions, fraud detection, marketplace balance, and routing. Machine learning engineers at Uber are not evaluated on theoretical depth alone. They are assessed on how well they design systems that work reliably under latency constraints, data imperfections, and constantly shifting demand patterns.
Interviewers want to see how you reason about trade-offs, deploy models into production, monitor performance, and collaborate with product and platform teams to drive measurable business impact. This guide is built around those realities. It walks through the Uber machine learning engineer interview process step by step, explains what each stage evaluates, and breaks down the most common Uber specific question types candidates face across modeling, system design, coding, and behavioral rounds. The goal is not just to help you pass interviews, but to prepare you to think like a machine learning engineer who can succeed inside Uber’s fast-moving marketplace environment.
Uber Machine Learning Engineer Interview Process
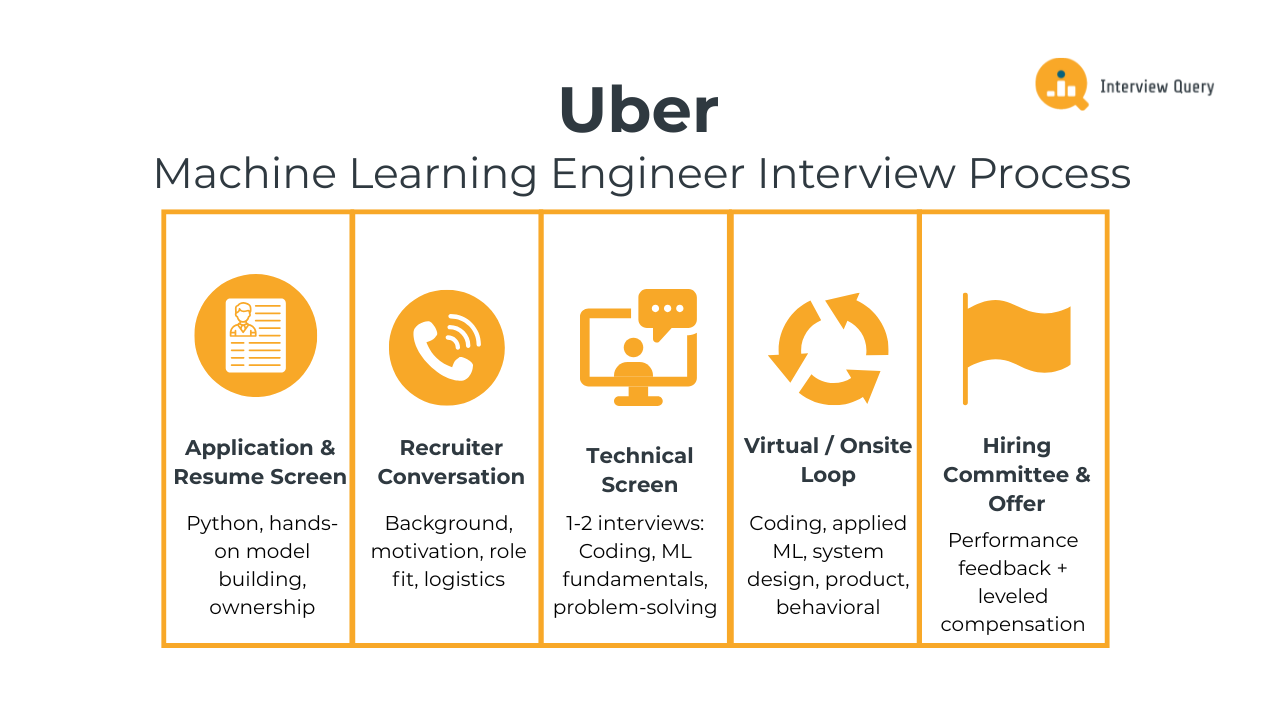
The Uber machine learning engineer interview process is designed to evaluate how well you build, deploy, and operate machine learning systems in production. Uber focuses on applied machine learning that supports real-time marketplace decisions, so the interview loop emphasizes ML system thinking, trade-off analysis, and collaboration just as much as modeling skill. Most candidates move through the full process in three to six weeks, depending on role level and team alignment.
Below is a breakdown of each stage and what Uber interviewers consistently evaluate throughout the loop.
Application and Resume Screen
During the application review, Uber recruiters look for hands-on experience building machine learning systems that operate at scale. Strong resumes highlight Python proficiency, experience with production pipelines, and direct ownership of model outcomes. Projects involving real-time inference, experimentation, marketplace optimization, or monitoring tend to stand out. Clear evidence of cross-functional work with product or platform teams is also a strong signal.
Tip: Quantify the impact of your models using metrics like latency reduction, revenue lift, or accuracy gains in live systems. This shows production ownership and signals that you understand how ML drives business outcomes at Uber.
Initial Recruiter Conversation
The recruiter call is a non-technical conversation focused on your background, motivation for Uber, and overall role fit. Recruiters validate your experience with applied machine learning, discuss past projects at a high level, and confirm logistics such as location preferences and compensation expectations. This call also helps determine which Uber teams may be the best fit based on your experience.
Tip: Clearly articulate why you enjoy working on production machine learning systems. Uber values engineers who are motivated by real-world impact rather than offline modeling alone.
Technical Screen
The technical screen usually includes one or two interviews focused on coding, machine learning fundamentals, and problem-solving. You may be asked to write Python code, reason through a modeling approach, or walk through the design of a system you previously built. Questions often involve practical scenarios such as improving model latency, handling noisy data, or debugging performance regressions.
Tip: Talk through your assumptions and trade-offs as you solve problems. Interviewers are evaluating how you think under constraints, which mirrors how decisions are made on Uber’s ML teams.
Virtual or Onsite Loop
The virtual or onsite loop is the most in-depth stage of the Uber machine learning engineer interview process. It typically consists of four to five interviews, each lasting 45 to 60 minutes. These rounds assess your ability to design, implement, and operate machine learning systems that scale reliably in production environments.
Coding and data round: You will solve ML problems using Python and may work with data manipulation or algorithmic tasks relevant to Uber’s systems. Interviewers look for clean code, correct logic, and the ability to reason through edge cases. Performance considerations such as time complexity and memory usage are often discussed.
Tip: Explain your approach before coding and narrate key decisions as you go. This demonstrates structured thinking and strong communication, both critical for collaborative engineering at Uber.
Applied machine learning round: This interview focuses on end-to-end modeling. You may be asked to design a prediction system, select features, choose evaluation metrics, or explain how you would monitor and retrain a model over time. Expect questions about bias, drift, and trade-offs between accuracy and system reliability.
Tip: Ground your answers in production experience. Discuss how you validated models after deployment and responded to real-world failures to show strong ownership.
Machine learning system design round: You will design a scalable ML system for a realistic Uber use case, such as ETA prediction or fraud detection. Interviewers assess how you structure components, manage data flow, and handle failure scenarios. Latency, scalability, and observability are key themes.
Tip: Think in terms of modular systems and explain how each component would be monitored. This shows you understand how Uber maintains reliability at scale.
Product and collaboration round: This round evaluates how you work with product managers, engineers, and data scientists. You may discuss how to prioritize model improvements, align with product goals, or make trade-offs when constraints conflict. Clear communication and stakeholder awareness are critical.
Tip: Tie technical decisions back to user and marketplace impact. Uber values engineers who connect ML choices to rider and driver experience.
Behavioral round: Interviewers explore how you handle setbacks, disagreements, and long-term ownership. Questions focus on decision-making under pressure, learning from failures, and mentoring others. Authentic reflection and accountability matter here.
Tip: Be specific about challenges you faced and what you changed afterward. This demonstrates maturity and a growth mindset that aligns with Uber’s engineering culture.
Hiring Committee and Offer
After the loop, interviewers submit independent feedback that is reviewed by a hiring committee. This group evaluates your performance across technical depth, system thinking, communication, and cultural alignment. If approved, Uber determines level and compensation based on scope, impact, and experience, followed by team matching where possible.
Tip: If you have preferences for certain problem domains or teams, communicate them early. Uber often considers alignment during the final decision stage, and clarity can help ensure a strong long-term fit.
Want to master the entire ML pipeline? Explore our ML Engineering 50 learning path to practice a curated set of machine learning questions designed to strengthen your modeling, coding, and system design skills.
Uber Machine Learning Engineer Interview Questions
The Uber machine learning engineer interview focuses on applied problem solving across modeling, systems, data, and decision-making. Questions are grounded in real production challenges such as real-time predictions, marketplace optimization, noisy data, and system reliability at scale. Interviewers are evaluating not only whether you know machine learning concepts, but whether you can apply them under real constraints, explain trade-offs clearly, and make sound engineering decisions that hold up in production.
Read more: Top 9 Machine Learning Algorithm Interview Questions
Machine Learning and Modeling Interview Questions
These questions focus on how you apply machine learning under real marketplace constraints. Uber uses them to assess whether you can design models that scale, remain reliable in dynamic environments, and drive business outcomes beyond offline accuracy. Interviewers listen closely for how you reason about trade-offs, feedback loops, and production behavior once models are live.
How would you design a model to predict ride demand in real time?
This question tests whether you can think end to end about modeling in a live marketplace. At Uber, demand predictions directly influence pricing, driver incentives, and rider experience, so interviewers care about how you choose features, handle seasonality and local events, and operate under latency constraints. A strong answer explains how predictions feed downstream systems, how you evaluate performance beyond offline accuracy, and how you adapt when demand patterns shift in real time.
Tip: Talk through how prediction errors affect surge pricing or driver wait times. This shows you understand how modeling decisions translate into real marketplace outcomes, not just metrics.
-
This question tests your ability to reason about causal impact in a two-sided marketplace. Uber asks it to see whether you can balance growth metrics with marketplace health, such as supply retention, rider conversion, and long-term equilibrium. A strong answer discusses defining success metrics, running controlled experiments, segmenting by market conditions, and watching for unintended effects like driver churn or increased wait times.
Tip: Frame your answer around short-term growth versus long-term marketplace stability. This signals strong product judgment, which Uber values highly in machine learning engineers.
-
Uber frequently deals with rare events such as fraud, safety incidents, or extreme delays, making imbalance a real production concern. This question evaluates how you reason about sampling strategies, label quality, and evaluation metrics when positive cases are scarce. A strong answer explains trade-offs between resampling, weighting, threshold tuning, and how business costs influence modeling choices.
Tip: Tie imbalance handling to operational cost, like false positives affecting drivers or riders. This shows you think beyond model performance and into real-world impact.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber machine learning engineer–specific interview questions in one place. You can work through applied machine learning scenarios, ML system design cases, coding challenges, and behavioral prompts with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback, making it easier to prepare for your next Uber interview.
-
This question tests your understanding of modeling variability and experimentation discipline. Uber asks it to see whether you recognize factors like data splits, feature leakage, randomness, hyperparameter choices, and evaluation methodology. A good answer explains why reproducibility matters in production and how you control variance when comparing models.
Tip: Mention practices like fixed seeds and consistent validation pipelines. This demonstrates engineering rigor and reliability, both critical in Uber’s ML workflows.
How do you detect and respond to model drift in production?
This question assesses whether you can operate models after launch. Uber models run in dynamic environments where rider behavior, traffic patterns, and supply conditions change constantly. A strong answer covers monitoring input distributions, prediction behavior, and business metrics together, then explains how you decide between retraining, feature fixes, or rollback.
Tip: Explain how you design alerts that trigger investigation, not panic. This shows you can own production systems calmly and responsibly at Uber scale.
Watch Next: How to Ace a Machine Learning Mock Interview - Design a recommendation engine
In this mock interview session, Ved, a PhD student and machine learning research scientist intern at LinkedIn, walks through a realistic applied machine learning prompt that closely mirrors how Uber machine learning engineer interviews evaluate candidates. He demonstrates how to break an ambiguous, real-world problem into well-defined features, choose modeling approaches that balance performance with reliability, select metrics aligned with business risk, and communicate results clearly. This walkthrough provides an interview-ready framework you can directly apply when preparing for Uber machine learning engineer interviews, where structured thinking, sound judgment, and clarity of explanation matter just as much as technical depth.
Machine Learning System Design Interview Questions
Uber’s system design interviews evaluate how you architect machine learning systems that operate reliably in real time, handle massive scale, and remain observable as conditions change. These questions focus on production readiness, failure handling, and how ML systems integrate with core marketplace workflows like dispatch, pricing, and ETA prediction.
-
This question tests whether you understand that model performance at Uber cannot be judged by offline metrics alone. Interviewers want to see how you combine prediction accuracy, latency, data freshness, and downstream business metrics such as rider wait times or trip cancellations. A strong answer explains layered monitoring, including input distribution checks, prediction error tracking, real-time latency dashboards, and post-trip outcome validation, along with clear thresholds for investigation or rollback.
Tip: Talk about tying model metrics to rider experience, like pickup delays or cancellations. This shows you understand how Uber evaluates success beyond model accuracy.
-
This question evaluates your ability to reason about data sufficiency, not just dataset size. Uber asks it to see whether you consider coverage across routes, times of day, weather conditions, and traffic regimes rather than relying on raw volume. A strong answer explains analyzing feature diversity, temporal coverage, and error stability, and how you would validate whether additional data would meaningfully reduce uncertainty.
Tip: Explain how you would break the data down by segments like peak hours or rare conditions. This shows strong judgment about data quality, not just quantity.
-
This question tests end-to-end system thinking around a core marketplace decision. Interviewers want to see how you choose features tied to driver incentives, trip characteristics, and context, while balancing interpretability, latency, and accuracy. A strong answer discusses feature freshness, model simplicity versus performance, and how acceptance predictions feed into dispatch logic without introducing bias or instability.
Tip: Discuss how false positives affect driver trust and system efficiency. This shows you understand the human and marketplace impact of modeling decisions.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber machine learning engineer–specific interview questions in one place. You can work through applied machine learning scenarios, ML system design cases, coding challenges, and behavioral prompts with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback, making it easier to prepare for your next Uber interview.
How would you support frequent model updates without service disruption?
This question evaluates your deployment and reliability instincts. Uber operates continuously, so interviewers want to see how you minimize risk while iterating quickly. A strong answer explains techniques like shadow testing, gradual rollouts, versioned models, and automated rollback based on both system and business signals, not just model metrics.
Tip: Emphasize monitoring during rollout windows, not just before and after. This demonstrates production discipline and calm ownership under real traffic.
Design an experimentation framework for ML models.
This question tests whether you can run experiments safely in a two-sided marketplace. Uber looks for candidates who understand randomization units, guardrail metrics, and how model experiments can interfere with each other. A strong answer explains how you isolate experiments, measure both short-term and long-term impact, and prevent cross-experiment contamination that could distort results.
Tip: Explain how you would protect marketplace balance during experiments. This signals advanced experimentation judgment and strong product awareness.
Looking for hands-on problem-solving? Test your skills with real-world challenges from top companies. Ideal for sharpening your thinking before interviews and showcasing your problem solving ability.
Coding And Applied Problem Solving Interview Questions
Uber’s coding interviews test your ability to write clean, efficient code and reason about performance under constraints. These questions test how you think through edge cases, choose data structures, and translate messy inputs into reliable outputs, the same skills you use when building production ML pipelines and marketplace services.
Write Python code to compute rolling performance metrics efficiently.
This question tests whether you can compute time-based metrics at scale without turning it into an inefficient loop. At Uber, rolling metrics show up everywhere, from model health monitoring to marketplace dashboards, so interviewers watch how you structure the computation, handle missing days, and keep time complexity tight. A strong answer describes the window definition, uses prefix sums or a deque depending on the metric, and validates behavior on boundary cases before optimizing.
Tip: Call out how you would handle late or missing events in the time series. That signals production data maturity and shows you can build metrics that hold up in real pipelines.
-
This question tests graph thinking and whether you can choose the right approach under time constraints. Uber asks questions like this to evaluate your ability to model problems as state transitions, which comes up in routing, matching, and other optimization systems. The best solution frames words as nodes and uses breadth-first search to guarantee the shortest path, with preprocessing to map wildcard patterns to neighbors so you avoid an O(n²) comparison scan.
Tip: Explain how you cut the neighbor lookup cost with pattern indexing. That demonstrates algorithmic efficiency and the ability to engineer scalable solutions, not just pass toy examples.
Implement logic to detect near-duplicate marketplace events.
This question evaluates how you reason about noisy event streams where perfect identifiers do not exist. Uber cares because deduplication affects everything from metrics accuracy to downstream model features. A strong answer defines what “near-duplicate” means using time windows and key fields, sorts or partitions events, and compares only plausible neighbors using hashing or windowed buffers to keep it fast. You should also explain how you would tune thresholds to reduce false positives.
Tip: Describe how you would tune and validate the thresholds using real event distributions. That shows strong data intuition and good judgment, which is exactly what Uber looks for in production engineers.
-
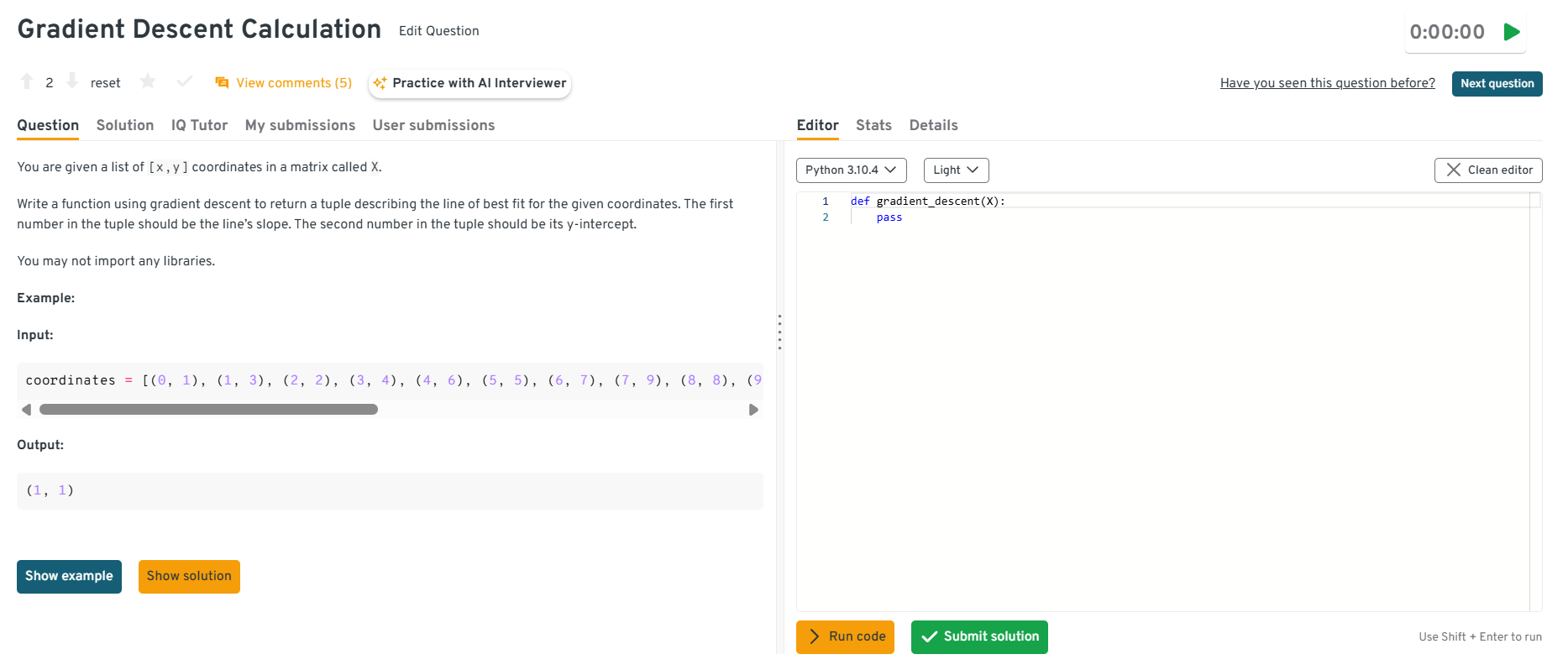
This question tests whether you truly understand optimization, not whether you can call a library. Uber uses it to gauge your modeling fundamentals and your ability to reason about convergence when training models in practice. A strong answer defines the mean squared error loss, derives gradients for slope and intercept, iteratively updates parameters with a learning rate, and includes stopping criteria like max iterations or a small change in loss. You should also mention feature scaling and learning rate sensitivity.
Tip: Mention how you would detect divergence and adjust the learning rate. That shows training stability instincts and demonstrates you can debug model behavior like an engineer, not just implement formulas.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber machine learning engineer–specific interview questions in one place. You can work through applied machine learning scenarios, ML system design cases, coding challenges, and behavioral prompts with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback, making it easier to prepare for your next Uber interview.
-
This question tests whether you can translate evaluation definitions into correct, defensive code. Uber cares because classification metrics are central to fraud, safety, and risk models where false positives and false negatives have different real costs. A strong answer correctly extracts true positives, false positives, and false negatives from the matrix, computes precision and recall with careful handling of division-by-zero, and explains what the metrics mean in an Uber context, like blocking good users versus missing bad actors.
Tip: Tie the metric choice to operational cost, for example false positives hurting driver trust. This signals business-aware evaluation judgment, which helps you stand out in Uber’s ML interviews.
Struggling with take-home assignments? Get structured practice with Interview Query’s Take-Home Test Prep and learn how to ace real case studies.
Behavioral Interview Questions
Uber’s behavioral interviews focus on ownership, collaboration, and judgment in high-impact environments. Interviewers look for engineers who take responsibility for outcomes, communicate clearly under pressure, and make decisions that balance technical quality with marketplace impact.
Tell me about a time your model caused an issue in production.
This question evaluates accountability and how you respond when systems fail at scale. Uber asks it to understand whether you can diagnose issues quickly, protect users, and implement durable fixes.
Sample answer: I deployed a pricing-related model that improved offline accuracy by 6 percent but increased p95 latency by 120 milliseconds during peak hours, leading to higher trip timeouts. I rolled back within 15 minutes, added latency alerts tied to traffic spikes, simplified two high-cost features, and re-launched via a canary. Latency returned to baseline and cancellation rate dropped by 3 percent the same week.
Tip: Emphasize the permanent changes you made to monitoring or rollout. That shows ownership and reliability thinking Uber values.
Describe a disagreement with a product manager about model trade-offs.
This tests cross-functional influence and decision-making under competing goals. Uber wants engineers who align teams with data, not opinions.
Sample answer: A PM pushed for maximum accuracy on a driver acceptance model, but I flagged latency risk. I proposed a one-week experiment comparing a lighter model with 1.5 percent lower accuracy but 40 percent faster inference. The results showed no measurable impact on acceptance while improving dispatch speed, and we aligned on shipping the faster model.
Tip: Show how you used experiments to resolve conflict. Uber rewards engineers who turn disagreement into measurable decisions.
How do you prioritize technical debt versus new features?
This question assesses long-term ownership and risk management. Uber asks it to see whether you protect system health while delivering value.
Sample answer: I prioritize debt based on incident risk and iteration cost. For a core ETA service, I scheduled incremental refactors alongside feature work, reducing on-call alerts by 25 percent while still shipping a new model version on time. I track debt with clear owners and timelines so it does not get deferred indefinitely.
Tip: Tie debt reduction to reliability or delivery speed. This signals senior-level judgment and sustained ownership.
What makes you a good fit for an Uber machine learning engineer position?
This evaluates motivation and role alignment. Uber looks for engineers who are excited by real-time systems and marketplace complexity.
Sample answer: I enjoy owning models end to end in production. In my last role, I led a real-time ranking system used by millions, improved p99 latency by 35 percent, and partnered closely with product to balance user experience with system constraints. That combination of applied ML, scale, and impact is exactly why Uber’s marketplace problems resonate with me.
Tip: Connect your experience to Uber’s real-time, two-sided marketplace. Specific alignment stands out more than generic enthusiasm.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice Uber machine learning engineer–specific interview questions in one place. You can work through applied machine learning scenarios, ML system design cases, coding challenges, and behavioral prompts with built-in code execution and AI-guided feedback, making it easier to prepare for your next Uber interview.
How do you mentor junior engineers?
This question assesses leadership and knowledge transfer. Uber values engineers who raise the team’s bar, not just their own output.
Sample answer: I mentor through design reviews and post-incident walkthroughs. On a recent project, I paired with a junior engineer to reason through feature trade-offs and rollout risks, which helped them independently lead the next release. Their service later shipped with zero incidents over a high-traffic weekend.
Tip: Highlight how you teach judgment and decision-making. Uber looks for mentors who scale impact through others.
Want realistic ML interview practice without scheduling or pressure? Try Interview Query’s AI Interviewer to simulate Uber style coding, modeling, and system design questions and get instant, targeted feedback.
What Does an Uber Machine Learning Engineer Do?
An Uber machine learning engineer builds and operates the models that drive real-time decisions across Uber’s marketplace. This role sits at the intersection of large-scale data, low-latency inference, and complex optimization problems, supporting systems like dynamic pricing, estimated time of arrival predictions, fraud detection, and dispatch efficiency. Machine learning engineers at Uber work end to end, taking models from problem formulation and feature design through deployment, monitoring, and iteration in production environments where performance and reliability directly affect riders, drivers, and revenue.
How Uber Machine Learning Engineers Turn Work into Impact
| What They Work On | Core Skills Used | Tools And Methods | Why It Matters At Uber |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marketplace pricing and incentives | Regression, optimization, causal reasoning | Offline evaluation, online experiments | Balances rider demand and driver supply in real time |
| ETA and routing prediction | Time series modeling, feature engineering | Real-time inference, monitoring pipelines | Improves trip accuracy and user trust at global scale |
| Fraud and risk detection | Classification, imbalance handling | Threshold tuning, alerting, staged rollouts | Protects users and reduces financial loss |
| Search and dispatch ranking | Ranking models, evaluation metrics | Feature stores, lightweight serving models | Determines which drivers and trips are matched |
| ML infrastructure and reliability | System design, scalability, debugging | Model serving, retraining pipelines, observability | Keeps predictions fast and stable under traffic spikes |
Tip: Uber interviewers look for engineers who think in systems, not isolated models. When discussing your work, explain how you handled latency, failure modes, and monitoring in production, since that demonstrates strong engineering judgment and ownership at Uber scale.
How to Prepare for an Uber Machine Learning Engineer Interview
Succeeding in the Uber machine learning engineer interview requires preparing for production ownership, not just algorithm recall. Uber’s teams build systems that make real-time decisions across pricing, routing, fraud, and marketplace balance, often under tight latency and reliability constraints. Strong candidates demonstrate sound engineering judgment, clear communication, and an ability to reason through trade-offs that affect riders, drivers, and the broader marketplace. The guide below focuses on preparation areas that consistently differentiate top performers.
Build intuition for marketplace-driven machine learning decisions: Uber’s models influence two-sided markets where changes affect both supply and demand. Study how prediction errors, threshold shifts, or delayed feedback loops can destabilize a marketplace. Focus on reasoning about incentives, fairness, and downstream effects rather than isolated model metrics.
Tip: Practice explaining how a small model change could impact driver earnings or rider wait times. This shows marketplace awareness, a critical signal Uber interviewers value.
Practice reasoning under latency and reliability constraints: Many Uber systems operate in near real time. Review how feature availability, caching, and fallback logic influence model design. Be prepared to discuss what happens when data is delayed, incomplete, or incorrect.
Tip: Walk through how your system degrades gracefully during partial outages. This demonstrates operational maturity and production readiness.
Develop strong mental models for ML observability: Uber expects engineers to own models after launch. Review approaches to monitoring inputs, predictions, and business metrics together. Understand how to distinguish data issues from model issues and when to retrain versus roll back.
Tip: Explain how you would design alerts that are actionable rather than noisy. This highlights your ability to run systems sustainably at scale.
Refine how you communicate trade-offs to non-ML partners: Machine learning engineers at Uber work closely with product managers and engineers. Practice translating model behavior into clear, non-technical implications that support decision-making.
Tip: Rehearse explaining a modeling compromise in plain language. This shows collaboration strength and leadership potential.
Recreate the interview flow with realistic practice: Simulate a full loop by practicing a coding exercise, an ML system design discussion, and a behavioral conversation back to back. This helps identify where explanations break down under time pressure.
Use Interview Query’s mock interviews and coaching program to practice Uber-style scenarios with targeted feedback.
Tip: After each mock, note where you over-explained or hesitated. Reducing these moments signals clarity and confidence, traits Uber engineers consistently look for.
Want to build up your machine learning interview skills? Practice real hands-on problems on the Interview Query Dashboard and start getting interview ready today.
Uber Machine Learning Engineer Salary
Uber’s compensation framework is built to reward machine learning engineers who can ship production-ready models, maintain system reliability, and support real-time marketplace decisions at global scale. Machine learning engineers at Uber typically receive a competitive base salary, annual performance bonus, and meaningful equity grants. Total compensation varies based on level, location, technical scope, and the criticality of the systems you own. Most candidates interviewing for machine learning engineer roles fall into mid-level or senior bands, especially if they have experience with real-time inference, large-scale experimentation, or ML system design.
Read more: Machine Learning Engineer Salary
Tip: Confirm your target level with your recruiter early, since Uber’s leveling directly determines compensation range and the expectations tied to your role.
Uber Machine Learning Engineer Compensation Overview (2026)
| Level | Role Title | Total Compensation (USD) | Base Salary | Bonus | Equity (RSUs) | Signing / Relocation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLE I | Machine Learning Engineer I | $180K – $215K | $140K–$160K | Performance based | Standard RSUs | Occasional |
| MLE II | Machine Learning Engineer II | $215K – $260K | $155K–$175K | Performance based | RSUs included | Offered case-by-case |
| Senior MLE | Senior Machine Learning Engineer | $260K – $320K | $175K–$195K | Above target possible | Larger RSU grants | More common |
| Staff MLE | Staff Machine Learning Engineer | $320K – $400K+ | $195K–$220K | High performer bonuses | High RSUs + refreshers | Frequently offered |
Note: These estimates are aggregated from data on Levels.fyi, Glassdoor, TeamBlind, public job postings, and Interview Query’s internal salary database.
Tip: Equity refreshers become a meaningful part of compensation after your first year, especially for senior and staff engineers who own long-lived production systems.
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Negotiation Tips That Work For Uber
Negotiating compensation at Uber is most effective when you understand market benchmarks and communicate your value clearly. Recruiters expect candidates to be informed, realistic, and data-driven.
- Confirm your level early: Uber’s leveling system (MLE I → MLE II → Senior → Staff) drives base salary, bonus targets, and equity ranges. A one-level difference can shift total compensation by tens of thousands.
- Anchor with verified benchmarks: Use sources like Levels.fyi, Glassdoor, and Interview Query salaries. Frame your value using concrete impact such as latency reductions, marketplace efficiency gains, or model reliability improvements.
- Account for geographic variation: Compensation differs meaningfully across San Francisco, New York, Seattle, and remote roles. Always request location-specific bands to evaluate offers accurately.
Tip: Ask for a full compensation breakdown including base salary, bonus target, equity vesting schedule, refreshers, and any signing incentives so you can compare offers clearly and negotiate from an informed position.
FAQs
How long does the Uber machine learning engineer interview process take?
Most candidates complete the Uber machine learning engineer interview process within three to six weeks. Timelines can extend if multiple teams are reviewing your profile or if scheduling onsite interviews takes longer. Recruiters usually share clear next steps after each round.
Does Uber test theoretical machine learning or mostly applied skills?
Uber focuses heavily on applied machine learning. Interviewers care more about how you design, deploy, and maintain models in production than about memorizing algorithms. Expect questions that emphasize trade-offs, system behavior, and real-world constraints.
How important is real-time systems experience for Uber MLE roles?
Real-time experience is a strong advantage but not a strict requirement. Candidates without direct real-time exposure can still succeed if they demonstrate strong system thinking and an understanding of latency, monitoring, and failure handling in production environments.
What programming languages should I be comfortable with for Uber interviews?
Python is the primary language tested in Uber machine learning engineer interviews. You should be comfortable writing clean, efficient code and explaining your logic clearly. SQL is also commonly used for data analysis and metric validation.
How deep do Uber’s machine learning system design interviews go?
Uber system design interviews go beyond high-level diagrams. Interviewers expect you to reason through data flow, model serving, monitoring, and failure scenarios. Depth of thought and clarity of trade-offs matter more than naming specific tools.
Does Uber expect prior rideshare or marketplace experience?
Marketplace experience is helpful but not required. Uber values transferable skills from other domains such as e-commerce, logistics, ads, or fintech. What matters most is your ability to reason about two-sided systems and feedback loops.
How are behavioral interviews evaluated at Uber?
Behavioral interviews focus on ownership, collaboration, and decision-making under ambiguity. Interviewers look for engineers who take responsibility for outcomes, learn from failures, and communicate clearly with cross-functional partners.
Can candidates be down-leveled or up-leveled during the process?
Yes, leveling decisions are based on interview performance and scope demonstrated across rounds. Strong system ownership and clear impact can lead to higher leveling, while gaps in production readiness may result in a lower level offer.
Become an Uber Machine Learning Engineer with Interview Query
Preparing for the Uber machine learning engineer interview means building strong applied machine learning skills, sound system design judgment, and the ability to operate models reliably in real-time, high-impact environments. By understanding Uber’s interview structure, practicing production-focused modeling scenarios, and refining how you communicate trade-offs across data, infrastructure, and product constraints, you can approach each stage with confidence. For targeted practice, explore the full Interview Query’s question bank, try the AI Interviewer, or work with a mentor through Interview Query’s Coaching Program to sharpen your reasoning and clearly articulate your impact, so you are fully prepared to stand out in Uber’s machine learning engineer hiring process.


