OpenAI Data Engineer Interview Guide — Process, Questions, and Tips
Introduction
If you’re preparing for an OpenAI data engineer interview, you’re stepping into one of the most impactful and technically challenging roles in the industry. OpenAI’s recent growth—from a $3.7 billion revenue in 2024 to a projected $12.7 billion in 2025—has been powered by sophisticated data systems that fuel product innovation, user analytics, and financial operations. As a data engineer, you won’t just maintain pipelines. You will help scale AI products to over 500 million users, ensure clean and compliant training data, and drive insights for decision-makers across research and business. This guide will help you navigate the questions and expectations ahead as you aim to become part of OpenAI’s data department as an OpenAI data engineer.
Role Overview & Culture
As an OpenAI data engineer, you will be building the data backbone behind some of the world’s most widely used AI systems. Your day-to-day work will include writing ETL pipelines in Airflow and Spark, managing massive datasets in Snowflake or S3, and collaborating with researchers, product teams, and business stakeholders. The culture is fast-moving and mission-driven, with an emphasis on cross-functional impact, continuous learning, and building systems that scale. You will be trusted to shape data architecture, ensure high data integrity, and power everything from billing systems to model training. While the pace is intense, the work is meaningful and highly collaborative. This is not just a technical role—it is a strategic one that defines what it means to be an OpenAI data engineer.
Why This Role at OpenAI?
If you’re aiming to maximize both your technical impact and personal upside, the OpenAI data engineer role offers unmatched opportunities. You could earn up to $925,000 annually in total compensation at senior levels, with generous equity aligned to OpenAI’s $300 billion valuation. You’ll enjoy daily catered meals, premium healthcare, unlimited PTO, and flexible work arrangements. More importantly, you’ll work with world-class talent on systems that support 500 million weekly users and billions in revenue, sharpening your skills and industry value. OpenAI funds your professional growth through learning stipends and conference budgets. Whether your goal is financial freedom, deeper expertise, or long-term prestige, this role positions you for outsized rewards—both now and in whatever comes next.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Data Engineer Role at OpenAI?
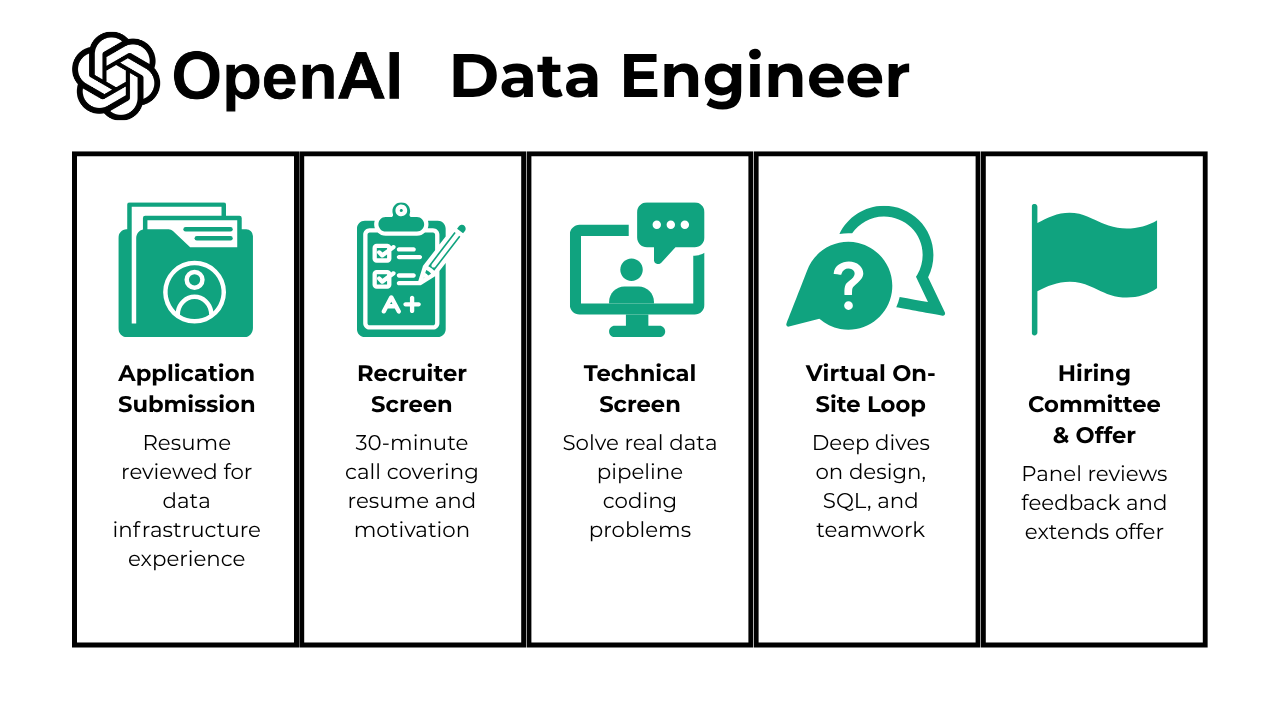
The OpenAI data engineer interview is structured to holistically assess your technical expertise, problem-solving, and cultural fit. The process typically spans 3–5 weeks from application to offer, with each stage designed to evaluate a specific set of skills. These stages include:
- Application Submission
- Recruiter Screen
- Technical Screen
- Virtual On-Site Loop
- Hiring Committee & Offer
Application Submission
You’ll start by submitting your resume and cover letter through OpenAI’s careers portal. The recruiting team reviews applications within one week, looking for strong data infrastructure experience, proficiency in languages like Python or Scala, and evidence of impact in previous roles. Tailor your resume to highlight experience with distributed systems, ETL pipelines, and technologies like Apache Spark or Kafka. Mentioning projects with measurable outcomes and alignment with OpenAI’s mission can help you stand out. If your application matches the requirements, you’ll be contacted for the next step within 7 days.
Recruiter Screen
This is a 30-minute informal phone call with a recruiter. Expect questions about your background, motivations for joining OpenAI, and how your skills align with the role. The recruiter will also walk you through the entire interview process and answer your questions about the company or position. Be ready to discuss your resume, career highlights, and what excites you about working in AI and data engineering. If there’s mutual interest, you’ll be notified within a few days and advanced to the technical stage.
Technical Screen
Typically lasting 60 minutes, this virtual interview focuses on practical data engineering skills. You’ll solve real-world problems—think building or debugging data pipelines, writing SQL queries with joins and aggregations, or architecting ETL workflows. The assessment may be live coding (often in Python or SQL) or a take-home project, emphasizing clarity, reliability, and scalability. Senior candidates may also face questions on distributed systems or architecture. You’ll hear back within a week regarding next steps, and feedback is specific to help you improve, even if you don’t advance.
Virtual On-Site Loop
If you clear the technical screen, you’ll enter the virtual onsite loop—usually 4–6 hours of interviews over 1–2 days. You’ll meet with 4–6 team members, including data engineers, product engineers, and managers. Expect a mix of technical deep-dives (data modeling, pipeline design, distributed storage), a system design challenge, and behavioral interviews focused on teamwork and adaptability. You may also present a take-home project or case study. Senior candidates face an extra architecture deep dive, while junior roles emphasize SQL fluency and hands-on tasks. You’ll receive feedback within a week of completing this stage.
Hiring Committee & Offer
After the onsite, every interviewer submits feedback within 24 hours. The hiring committee, which meets weekly, reviews all feedback and makes a collective decision. If you’re successful, you’ll get an offer within a week, often with a chance to discuss compensation and benefits. Senior candidates’ feedback weighs more on architectural vision and cross-team leadership, while junior feedback focuses on hands-on technical skills. If you’re not selected, you’ll still receive constructive feedback. Now that you know the stages, let’s drill into the exact questions you’ll face and how to prepare for each round
What Questions Are Asked in an OpenAI Data Engineer Interview?
The OpenAI data engineer interview process includes a range of technical and behavioral questions that assess how well you build pipelines, model data, collaborate across teams, and support mission-critical AI systems.
Coding / Technical Questions
These questions focus on your ability to write clean, scalable SQL and Python code, debug ETL pipelines, and make architectural trade-offs in real-world data scenarios:
To solve this, use the LEAST and GREATEST functions to ensure consistent ordering of source and destination locations. Then, group by these ordered pairs to eliminate duplicates and create the desired table with unique pairs.
2. Given a table of product subscriptions, write a query to check subscription overlap
To determine subscription overlap, compare each user’s subscription date range with others using a self-join. The overlap condition is defined as (StartA <= EndB) AND (EndA >= StartB). Group by user_id and use a conditional check to return 1 for overlap and 0 otherwise.
3. Write a function to sample from a truncated normal distribution
To simulate a truncated normal distribution, calculate the truncation point (lim) using the percentile threshold and the percentage point function (PPF) of the normal distribution. Then, generate random samples from the normal distribution and include only those values that are less than or equal to lim. Repeat this process until the desired sample size is achieved.
To solve this, calculate weekly revenue for each advertiser using a CTE, then identify advertisers with the highest weekly revenue using the RANK() function. Next, find the top three performing days for these advertisers using ROW_NUMBER(), and finally join the results with the advertisers table to display the advertiser name, transaction date, and amount.
5. Write a function to return the shape of an isosceles triangle as a binary array
To solve this, validate the inputs to ensure the base is odd and the height can form a triangle. Use arithmetic progression to calculate the increase in width at each level, and construct the triangle row by row using a 2D list filled with 0s and 1s. Return None if the inputs are invalid.
Data-Pipeline / System Design Questions
Expect to explain and design high-scale systems for real-time ingestion, data modeling, and analytics—often with constraints tied to cost, compliance, or performance:
6. Design a solution to store and query raw data from Kafka on a daily basis
To handle 600 million daily events with a two-year retention period, the solution involves using Kafka for data ingestion and Amazon Redshift for scalable storage and querying. Data pipelines like Spark Streaming or Amazon Kinesis Data Firehouse can transfer data from Kafka to Redshift, with optimizations like SORTKEY and DISTKEY for query performance. Cost efficiency can be achieved by running streaming jobs periodically and using an orchestrator like Airflow for automation and monitoring.
7. Design a data pipeline for hourly user analytics
To build this pipeline, you can use SQL queries to aggregate data from the data lake for hourly, daily, and weekly active users. A “local” solution involves running queries directly on the data lake for each dashboard refresh, while a “unified” solution aggregates and stores the data in a separate table or view for better scalability and latency. Tools like Airflow can be used to orchestrate hourly updates.
8. Migrating a social network’s data from a document database to a relational database
To approach this project, start by identifying the entities and relationships in the current document database. Normalize the data by creating separate tables for users, friends, posts, and interactions, ensuring proper foreign key relationships. This will improve data consistency and enable better analytics by leveraging SQL queries on the relational database.
9. How would you design a data warehouse for an e-commerce company looking to expand internationally?
To design the architecture, start by asking clarifying questions about transaction types, metadata handling, and event definitions (e.g., purchases, restocking, returns). Consider non-functional requirements like latency, frequency of updates, duplication, load capacity, and scalability. For the ETL pipeline, focus on recording events accurately and efficiently, while ensuring the reporting dashboard aggregates data effectively for vendors.
10. How would you build an ETL pipeline to get Stripe payment data into the database?
To build an ETL pipeline for Stripe payment data, start by extracting data using Stripe’s API, ensuring secure authentication. Transform the data by cleaning, validating, and structuring it into a format suitable for analytics. Finally, load the processed data into the internal data warehouse, using tools like Airflow for orchestration and scheduling.
Behavioral & Mission Alignment Questions
These prompts explore how you communicate insights, handle ambiguity, and uphold OpenAI’s values while contributing to large-scale AI infrastructure and research support:
11. What are some effective ways to make data more accessible to non-technical people?
OpenAI values cross-functional collaboration, so your answer should reflect how you communicate complex data to teams like product, policy, or ethics. Mention how you use visualizations, guided reports, or simple dashboards to bridge the technical gap. Also explain how you support these tools with well-written documentation or brief walk-throughs to help decision-makers act on data with confidence.
12. Tell me about a project in which you had to clean and organize a large dataset.
This question evaluates your practical experience with messy or incomplete data, which is common in model training and deployment pipelines. Focus on a real project where you encountered data quality issues and explain how you systematically cleaned, normalized, or restructured it. At OpenAI, the ability to work with large-scale and evolving datasets is essential, so describe how you would adapt your methods for bigger or more complex data systems.
13. How comfortable are you presenting your insights?
Data engineers at OpenAI often share results with researchers, engineers, and leadership. Talk about how you structure your findings so they are understandable and actionable, whether you are using slide decks, Jupyter notebooks, or live dashboards. Include specific situations where you successfully delivered insights in a clear and confident way to both technical and non-technical audiences.
14. How do you prioritize multiple deadlines?
Time management is important in a high-impact, fast-paced environment like OpenAI. Describe how you align your work with project timelines, research cycles, or data refresh needs. Explain your method for breaking down tasks, using planning tools, and communicating with teams to adjust priorities based on changing goals or constraints.
15. Describe a data project you worked on. What were some of the challenges you faced?
This question helps the interviewer understand how you work through ambiguity, scale, or resource constraints. Use the STAR method to describe the business or research need, your role, the actions you took, and the outcome. At OpenAI, it is especially valuable to highlight collaboration, iteration, and how you navigated complexity or unexpected results.
How to Prepare for a Data Engineer Role at OpenAI
Preparing for a data engineer role at OpenAI means blending technical mastery with strategic communication and mission alignment. Start by sharpening your SQL and Python skills—these are non-negotiable, and practicing on LeetCode’s database section or simulating real-time scenarios with AI Interviewer will give you the edge you need.
OpenAI’s interviews are practical, so focus on building and debugging data pipelines, not just rote algorithm drills. Dive into OpenAI’s latest papers and blog posts to understand their approach to data engineering and AI safety; referencing these insights in your answers shows you’re not just technically strong but also deeply invested in their mission.
For system design, run mock sessions with peers and zero in on streaming architectures—think Kafka and Spark—since real-time data is central to OpenAI’s scale.
Behavioral questions are inevitable, so prepare your STAR stories in advance, highlighting times you’ve owned complex projects or made tough calls to ensure data quality and safety.
Practicing full interview loops with friends or mentors helps you refine your clarity and pacing, and getting feedback will surface blind spots. Ultimately, the strongest candidates show not just technical skill but also a collaborative, safety-first mindset and a passion for OpenAI’s mission—qualities that consistently stand out in successful interviews.
Conclusion
Preparing for the OpenAI data engineer interview is a strategic move toward one of the most impactful and high-growth roles in tech today. With focused practice, a mission-aligned mindset, and a clear plan, you’ll be ready to stand out. Start by reviewing the full OpenAI Data Engineer Question Collection, then follow a proven Data Engineer Learning Path tailored to your level. For added motivation, read Chris Keating’s success story to see how they have landed the role. Whether you’re aiming for career impact, compensation, or future flexibility, your next step starts with smart, focused preparation.
