PayPal Business Analyst Interview Guide: Process, Questions & Prep Tips (2026)
Introduction
The International Institute of Business Analysis or IIBA’s 2025 global report reveals that for 76% of firms, the impact of business analysis on their strategy is growing. Beyond their salaries increasing by 5%, business analysts are highly sought-after across industries like financial technology, where PayPal currently dominates with 400M+ consumer accounts and millions of merchants.
At PayPal, business analysts leverage the current business analytics trends taking over finance, from “agentic analytics” to streamline data pipelines to big data and cloud frameworks that optimize payment experiences for merchants and consumers alike.
In this guide, you’ll learn exactly what to expect in the PayPal business analyst interview. We’ll break down the specific analytics, product, and systems questions PayPal asks, explain how case studies and payment-flow scenarios work, and share practical preparation tactics grounded in real hiring patterns. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to stand out in the PayPal analytics interview process and demonstrate the impact-driven thinking that hiring managers look for.
What Does a Business Analyst at PayPal Do?
A PayPal business analyst plays a central role in improving how money moves across PayPal’s consumer, merchant, Braintree, and Venmo ecosystems. The role blends analytics, systems thinking, and product strategy to optimize payment outcomes, reduce friction, and support teams focused on fraud mitigation and merchant risk.
Core responsibilities include:
- Requirements gathering and system analysis to understand how checkout, risk, and dispute flows work across PayPal’s infrastructure.
- KPI design and dashboard creation, turning ambiguous business questions into clear metrics and measurable success criteria.
- Data analysis using SQL to evaluate experiments, identify root causes of payment failures, and assess the impact of product changes.
- Experiment evaluation, helping teams understand A/B results and quantify improvements to conversion or authorization rates.
Example day-to-day tasks:
- Analyzing conversion metrics for a new checkout feature.
- Mapping end-to-end flows for disputes, chargebacks, or API-based transactions.
- Partnering with engineering to define functional requirements for new or enhanced APIs.
- Supporting merchant-facing B2B products by evaluating onboarding funnels, cohort performance, and risk-model changes.
Explore Interview Query’s Learning Paths to cultivate the essential skills for a PayPal business analyst through structured courses for SQL, product metrics, and more.
PayPal Business Analyst Interview Process
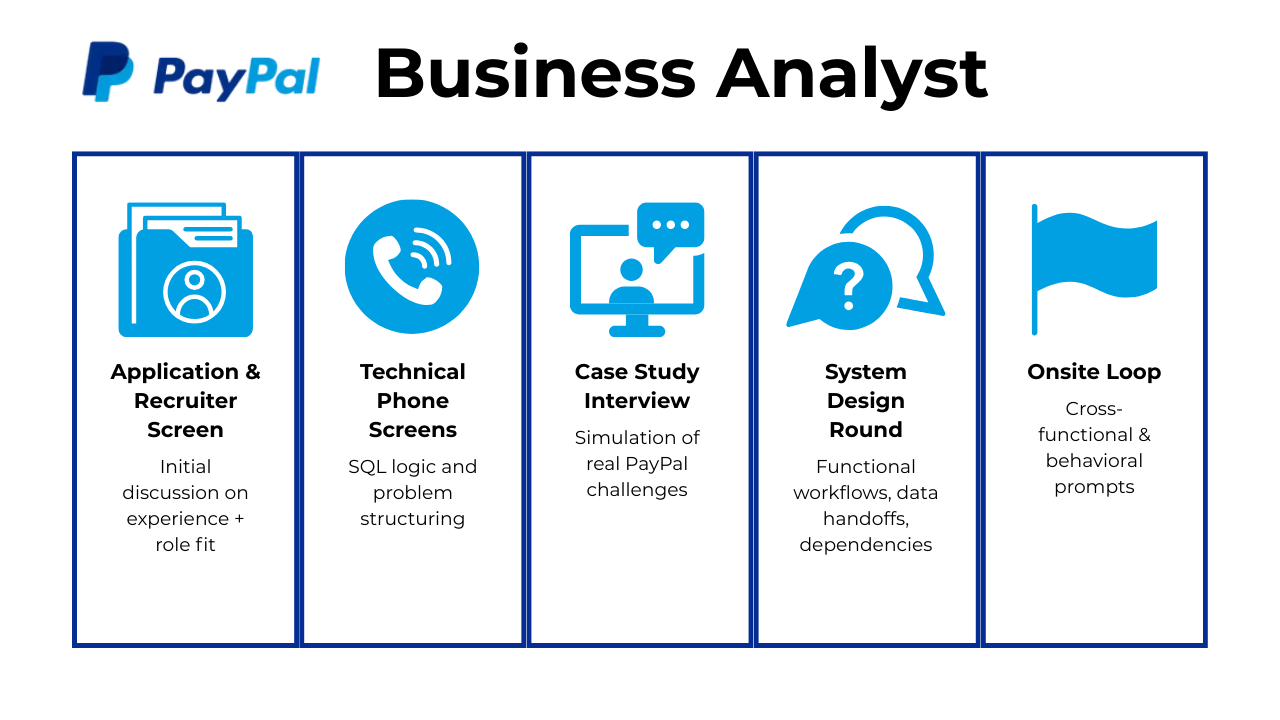
Landing a PayPal business analyst role requires navigating a multi-step interview process designed to evaluate both analytical rigor and business judgment. Candidates are assessed across data analysis, product intuition, systems understanding, and cross-functional collaboration. Below, we break down each stage, what to expect, and actionable strategies to excel.
Application & Recruiter Screen
The recruiter screen confirms whether your experience matches PayPal’s expectations for a business analyst.
What recruiters look for:
- Familiarity with and exposure to payments, B2B merchant flows, Venmo, and Braintree.
- Experience writing or reviewing SQL.
- Comfort gathering requirements and defining KPIs.
- Strong cross-functional communication skills.
Expect questions like:
- “How have you translated business needs into technical requirements?”
- “Which metrics matter most for evaluating merchant performance?”
Tip: Prepare a concise “business problem → solution → impact” story for each experience, emphasizing measurable outcomes relevant to PayPal’s payments operations.
Technical & Analytics Phone Screen
The technical phone screen evaluates your analytical execution and problem-structuring ability. You’ll work through SQL logic, metric definitions, funnel breakdowns, fraud or chargeback patterns, and lightweight modeling or estimation tasks.
Typical problem areas:
- Computing approval and conversion rates.
- Segmenting payment failures and identifying root causes.
- Recommending KPIs for flows like checkout or merchant onboarding.
- Cleaning messy datasets and explaining assumptions.
Tip: Practice explaining your SQL logic and metric choices clearly, as interviewers evaluate both correctness and your ability to communicate insights to non-technical stakeholders.
Case Study Interview
The case study simulates real PayPal challenges, pushing you to dissect complex payment or merchant problems and recommend data-backed solutions.
Common themes include:
- Checkout latency or conversion drops.
- Dispute and chargeback journeys.
- KPI deep dives for merchant growth or retention.
- Payment failure diagnostics and root-cause exploration.
A typical prompt might involve declining merchant volume, requiring you to analyze trends, surface hypotheses, and propose product or operational interventions that respect risk and compliance constraints.
You may observe similarities with what other tech companies highlight in their business cases, such as Amazon-style data-driven justification, Google’s analytical depth, and Netflix-style experimentation.
Tip: Structure your case answers using a framework: problem definition, analysis plan, insights, and recommendations. This helps convey systematic thinking under time pressure.
System / Design Interview
In this BA-focused systems design round, you’re evaluated on how well you understand functional workflows, data handoffs, and system dependencies without diving into engineering-level coding.
You may be asked to map or define:
- Payment authorization and settlement flows.
- Risk rule paths and decisioning logic.
- Edge cases within dispute or refund workflows.
- Acceptance criteria and functional requirements for new features.
The goal is to demonstrate that you can capture requirements, visualize dependencies, and anticipate downstream constraints to ultimately enable effective solutions in cross-functional teams.
Tip: Use diagrams and stepwise explanations to clearly communicate system flows. Explore system design questions here on Interview Query to practice highlighting potential failure points or trade-offs.
Onsite Loop: Cross-Functional + Behavioral
The onsite loop examines how you navigate ambiguity, resolve conflicts, and influence diverse stakeholders. Interviewers present scenarios that mirror PayPal’s cross-functional, data-driven environment.
Areas typically covered:
- Managing competing priorities across product, risk, and engineering.
- Aligning metrics when teams have different success criteria.
- Clarifying incomplete requirements.
- Communicating complex analytical insights to non-technical partners.
Behavioral prompts may include:
- “Tell me about a time you balanced conflicting priorities.”
- “How do you determine which KPI is most important when starting a project?”
Your ability to show ownership, clarity, and structured thinking is essential here.
Tip: Prepare STAR-format stories that highlight collaboration, analytical impact, and leadership in ambiguous business contexts.
Hiring Decision & Offer
After the interviews, the panel calibrates feedback, determines your leveling, and finalizes compensation. Offers typically reflect role level, market benchmarks, and candidate experience.
What influences the offer:
- Analytical depth across all technical stages.
- Ability to reason about payment flows and merchant behavior.
- Strength of behavioral evidence around collaboration and leadership.
- Alignment with PayPal’s data-driven, customer-focused culture.
Strong, consistent performance across these dimensions significantly increases the likelihood of a competitive offer.
Tip: Consider scheduling a mock interview on Interview Query to rehearse structured answers, case problem-solving, and technical explanations before final evaluations.
PayPal Business Analyst Interview Questions
PayPal’s business analyst interviews blend SQL problem-solving, product reasoning, experimentation, and systems thinking. Expect questions that explore how you break down complex payment flows, quantify changes to risk or checkout performance, and communicate trade-offs clearly. The questions below represent common themes reported by candidates across PayPal data analyst interview questions, business analyst loops, and technical screens.
Read More: Business Analyst Interview Questions: A Comprehensive Guide
SQL & analytics interview questions
PayPal uses SQL heavily across fraud analytics, merchant reporting, checkout optimization, and risk scoring. Interviewers want to see how you reason through joins, identify the right metrics, and handle edge cases in massive transaction datasets. Expect questions that test your ability to calculate conversion funnels, classify failed payments, compare merchant cohorts, or analyze chargeback trends. Clarity matters; PayPal values analysts who can explain why a query solves the business need, not just write syntactically correct SQL.
Compute total spend per product by PayPal merchants who registered in 2022.
This question checks your ability to join tables, filter by date, and aggregate transaction values. You would first narrow the user base to merchants who registered in 2022, join them to the purchase records, and then sum total spend grouped by product. Ensuring the date filter uses the correct year extraction is the key step.
Tip: Highlight your awareness of PayPal’s merchant lifecycle data by explaining how registration cohorts often tie into product adoption and spend behavior.
Retrieve the latest PayPal transaction of each day, ordered chronologically.
Interviewers use this to assess comfort with window functions and identifying “last event” patterns. The common approach is to apply a
ROW_NUMBERor MAX-over-window on the timestamp partitioned by date, then select the top-ranked transaction for each day. Finally, sort the resulting set by the transaction timestamp to restore chronological order.Tip: When discussing your solution, relate it to how PayPal teams monitor real-time transaction queues; showing that you understand why “latest event” logic matters operationally can set you apart.
Practice this question on the Interview Query dashboard, which is a great place to drill SQL skills with instant feedback. Tools like the IQ Tutor and built-in code editor let you test solutions, fix errors quickly, and learn the exact techniques interviewers expect for analytical questions like this one.
Calculate the three-day rolling average of PayPal user deposit amounts by day.
This tests your grasp of window frames and time-series aggregation. Group deposits by day, then use a window function with a date-based range or row-based frame to compute the rolling three-day average. Properly handling days without transactions and ensuring values are filtered to deposits only (positive amounts) keeps the results accurate.
Tip: Mention how rolling averages feed directly into PayPal’s risk and liquidity monitoring dashboards, demonstrating that you know how time-series metrics support real decision-making.
Using a chargebacks table, calculate the chargeback rate by merchant segment and identify segments with statistically significant spikes.
Analytical skills around ratio calculations and anomaly detection are the focus here. Start by grouping chargeback counts and total transactions by merchant segment to compute each segment’s chargeback rate. From there, compare current-period rates to historical baselines—using z-scores, confidence intervals, or standard deviation thresholds—to surface segments showing meaningful spikes.
Tip: If you can, reference how PayPal segments merchants (e.g., by size, industry, or risk tier) and frame your analysis around how spikes might impact loss forecasting or dispute operations.
Given a payments table with status codes, how would you classify and count payment failures by root cause (issuer decline, network error, fraud block, etc.)?
This evaluates your ability to categorize raw status codes into business-meaningful buckets. Map each failure code to a defined root-cause category using a
CASEstatement or reference table and then aggregate counts of failures by category. Adding filters for time periods or merchant cohorts can help reveal deeper patterns if needed.Tip: Tie your classification logic to PayPal’s ecosystem by noting that issuer declines, network failures, and fraud blocks have different remediation paths. Strengthen your understanding of business implications by answering more PayPal-specific SQL problems from our question bank.
A/B testing & experimentation interview questions
PayPal regularly experiments on areas like checkout flows, fraud-model thresholds, authentication steps, and merchant onboarding, so it’s common to see interview questions focused on how you’d design thoughtful, measurable tests. Expect to talk through how you’d set up clear hypotheses, define crisp success metrics and guardrails, and account for factors like fraud risk or compliance constraints. Ultimately, interviewers want to see structured reasoning, i.e. how you protect experiment validity, watch for hidden biases, and make sense of noisy real-world payments data.
-
This question gauges your ability to structure multi-cell experiments and balance budget allocation against statistical rigor. A solid approach is to randomize users or markets into channel-specific exposure groups, normalize spend across cohorts, and compare acquisition efficiency using metrics like cost per new active merchant. Including a holdout group helps quantify incremental lift relative to baseline spending.
Tip: Reference how PayPal regularly evaluates channel-level ROI, showing that you understand how acquisition nuances across markets can signal strong business context awareness.
Outline how you would test and evaluate the impact of a PayPal merchant subscription price increase.
The goal here is to assess whether you understand pricing experiments, revenue trade-offs, and user behavior impacts. You would split eligible merchants into control and treatment groups, expose only the treatment group to higher pricing, and measure changes in conversion, churn, and net revenue. Evaluating both short-term revenue lift and longer-run retention risks provides a fuller view of whether the price change is viable.
Tip: It helps to mention that PayPal’s pricing changes often require coordination with finance and compliance. Outlining how you’d communicate experiment risks and expected outcomes can demonstrate cross-functional readiness.
-
This assesses fundamental knowledge of hypothesis testing and experiment evaluation. After running the A/B test, you’d compare CTR between variants using a proportion test and calculate confidence intervals or p-values to determine significance. It’s also helpful to validate sufficient sample size and check for novelty effects before drawing conclusions.
Tip: Highlight that PayPal values quick yet responsible decision-making, so noting how you’d validate data quality and check device- or region-level behavior can show you think beyond a single aggregate metric.
For deeper practice with A/B testing scenarios like this, the Interview Query dashboard offers guided support through the IQ Tutor and access to user comment threads that break down alternative solution paths. Exploring how others reason through statistical tests can help you refine your approach and build confidence for PayPal’s experimentation questions.
PayPal wants to test a new risk-scoring model. What primary metrics and guardrail metrics would you track, and why?
Primary metrics could include fraud loss reduction, approval rate improvements, or precision/recall shifts for high-risk users. Guardrails should monitor false positives, customer complaints, and downstream operational load to ensure the model doesn’t introduce friction or unexpected harm.
Tip: Bring up how PayPal balances fraud reduction with user experience. Interviewers also appreciate when candidates acknowledge that risk models affect multiple internal teams.
If merchant onboarding time drops by 20% in variant B, what additional analyses would you run before recommending rollout?
After observing the reduction, you’d examine activation quality, downstream conversion, support contacts, and fraud-related outcomes to ensure speed hasn’t introduced risk or degraded merchant value. Cohort analysis, funnel checks, and stress-testing for specific merchant segments provide extra confidence before scaling the change.
Tip: Mention that PayPal cares deeply about onboarding quality for different merchant tiers, so layering in segmentation analyses or vertical-specific checks can show you understand the platform’s diverse user base.
System/technical interview questions
Unlike engineering system design, PayPal’s BA system questions center on functional flows, edge cases, and how you break down complex payment operations. Expect prompts about chargebacks, multi-layer risk checks, or designing flows to monitor failures. You must show clear systems thinking, not low-level architecture. Interviewers want to see how you think about data movement, user experience, and operational safeguards across PayPal’s global payments stack.
-
A strong approach outlines how transaction events flow through a streaming system (such as Kafka or Kinesis) into an aggregation service that updates leaderboard metrics in near real time. It also helps to describe a schema that supports fast writes and rank queries, often leveraging columnar stores or in-memory caches like Redis. Mentioning monitoring, latency considerations, and data quality checks rounds out a complete solution.
Tip: Show that you understand the tradeoff between update frequency and system cost at PayPal scale.
Walk me through the end-to-end chargeback lifecycle and identify where PayPal can intervene to reduce losses.
This tests understanding of payments operations, dispute workflows, and loss-mitigation levers. A solid answer walks from initial dispute creation through evidence gathering, representment, network review, and final resolution while pointing out the data signals available at each step. Interventions typically include early fraud detection, automated evidence compilation, seller-education nudges, and post-dispute analytics to refine risk models.
Tip: Demonstrate familiarity with PayPal’s seller tools and dispute APIs by mentioning how improved metadata capture or automated evidence suggestions could meaningfully reduce seller friction.
Design a high-level flow for multi-layer risk decisioning that includes rules-based checks, machine-learning scoring, and manual review flags.
Detail how lightweight rules trigger instant declines or escalations, then introduce a model-scoring step that produces probabilistic risk scores. The final layer routes high-risk or ambiguous cases to manual review with appropriate metadata and audit trails. Emphasizing latency budgets and explainability demonstrates deeper understanding.
Tip: Tie your answer to how PayPal balances global compliance requirements with real-time risk decisions, and note that BA candidates often collaborate closely with model governance teams to refine thresholds.
Explain how you would design a system to retry failed payments without causing duplicate charges or fraud vulnerabilities.
Here the interviewer is looking for knowledge of idempotency, retry logic, and safe transaction orchestration. The solution usually involves generating idempotency keys, enforcing state checks before retrying, and leveraging queues or scheduled jobs to space out attempts. Show awareness of fraud and operational risks by calling out safeguards that detect inconsistent gateway responses and monitor for anomalous retry patterns.
Tip: Mention that PayPal heavily emphasizes customer trust, so articulating how you’d monitor abnormal retry clusters or user experience friction can set you apart from generic payments answers.
Map the data sources and decision points needed to evaluate a merchant’s risk profile during onboarding.
Mention core inputs such as KYC documents, business registration data, historical processing behavior (if applicable), third-party identity checks, and device/IP metadata. Decision points typically include identity verification, industry classification, predicted transaction patterns, fraud-risk scoring, and sanctions or negative-file checks. Highlighting feedback loops to refine risk tiers adds polish.
Tip: Explain how onboarding logic must adapt to regional regulations, and call out that aligning risk flags with downstream teams (e.g., underwriting or portfolio management) is a BA differentiator.
Need more system questions to try? Visit Interview Query’s question bank for exclusive access to technical interview questions designed for business analyst roles.
Product & behavioral questions
PayPal often focuses on how you handle ambiguity, work through cross-functional tension, and respond to user-facing issues such as payment errors or refund delays. Many behavioral prompts draw from real situations, e.g. risk escalations, regulatory limitations, merchant concerns, or competing demands from product, engineering, and compliance. What interviewers really want to see is how you think, communicate, and create clarity when the stakes are high.
-
This question evaluates your self-awareness, analytical maturity, and ability to understand trade-offs in a complex payments ecosystem. PayPal BAs constantly balance accuracy, speed, and ambiguity; demonstrating how you recognize your analytical tendencies and apply them to real decisions is crucial.
Sample Answer:
“I’m particularly strong at identifying edge-case patterns in payment flows, which helped me catch an unexpected spike in soft declines during a checkout experiment. A weakness I’ve worked on is overinvesting time in deep dives; to counter that, I now define ‘decision-ready’ thresholds before I start the analysis.”
Behavioral prep matters just as much as technical depth, and the Interview Query dashboard makes it easy to practice both. Beyond SQL and analytics, the IQ Tutor can walk you through sample behavioral prompts, offer structured frameworks, and simulate how to tighten your stories for clarity and impact.
-
This question tests your product thinking, metric design, and understanding of PayPal’s demand drivers, especially across checkout flows, merchant funnels, and B2B adoption. Strong candidates connect the metric framework directly to actionable decisions.
Sample Answer:
“I’d start by defining core demand metrics like qualified leads, activation rate, onboarding completion, and early transaction volume, then supplement them with supporting signals such as merchant integration steps or API error rates. Tracking these over time makes it clear whether drop-offs stem from awareness, onboarding friction, or product value. That breakdown helps the team decide whether to prioritize funnel optimizations, messaging updates, or technical fixes.”
Tell me about a time you resolved conflicting requirements between engineering, compliance, and product in a regulated environment.
PayPal values analysts who can translate constraints, negotiate trade-offs, and align cross-functional teams. Your answer should demonstrate how you navigated complexity without slowing execution.
Sample Answer:
“In a past role, engineering wanted the simplest build, compliance required an additional verification step, and product pushed for a frictionless user flow. I hosted a working session to map the risk scenarios and created two workflow variants that satisfied regulatory thresholds while preserving the primary UX. Once teams saw the trade-offs visually, alignment came quickly and we shipped the feature on schedule.”
Describe a time you had to make a recommendation with incomplete data. How did you handle the risk of being wrong?
PayPal’s systems generate massive data volume, but analysts still face partial, delayed, or noisy datasets, especially in fraud, reliability, and merchant performance. This question highlights your ability to act decisively while acknowledging uncertainty.
Sample Answer:
“When we lacked full funnel data during an outage investigation, I triangulated trends from payments logs, user reports, and historical baselines to propose a temporary rule adjustment. I was transparent about assumptions and provided a rollback trigger in case the signal was misleading.”
How would you manage a situation where a key stakeholder pushes for a feature that conflicts with risk or regulatory constraints?
This question probes your ability to protect the business, communicate risk clearly, and propose viable alternatives.
Sample Answer:
“I’d start by explaining the specific regulatory and financial risks in concrete terms, such as potential dispute exposure or KYC violations, so the impact feels tangible rather than theoretical. Then I’d propose compliant alternatives or phased approaches that preserve the stakeholder’s core goals. This keeps the conversation collaborative while still ensuring we stay within acceptable risk boundaries.”
Watch Next: Business Analyst Interview Questions ANSWERED
If you prefer learning through visuals, this quick breakdown offers a helpful overview of how candidates can prepare for BA interviews and what themes tend to show up repeatedly. It’s a great complement to the question set above.
In the video, Interview Query co-founder Jay Feng highlights how essential structured thinking and clear communication are in the interview process for business analysts, especially when discussing data-driven decisions. It also reinforces the importance of showing measurable impact whether analyzing SQL results, proposing experiments, or improving a payment flow.
Want to practice these scenarios using real company case questions? Try Interview Query’s Question Bank to drill SQL, analytics, system flows, and product reasoning with PayPal-style challenges.
PayPal Domain Knowledge Business Analysts Must Know
To succeed in a PayPal business analyst interview, you need a working understanding of how PayPal earns revenue, manages risk, and serves merchants at scale. Interviewers expect you to reason about payments from both a product and systems perspective.
Revenue Model Fundamentals
PayPal’s core revenue streams shape how analysts connect metrics (conversion, approval rates, disputes) to financial impact.
- Transaction fees: Percentage + fixed-fee pricing across PayPal, Braintree, and Venmo.
- Merchant services: Tools like subscription billing, vaulting, checkout integrations, and dispute handling.
- BNPL (PayPal Pay Later): Revenue from merchant fees and financing.
- Other streams: Currency conversion fees and small-business lending.
Risk & Fraud Architecture Basics
PayPal relies on layered controls to balance fraud loss and user experience.
- Risk scoring: Models that flag suspicious activity based on behavior or account patterns.
- Rule engines: Deterministic checks for high-risk patterns or compliance flags.
- Post-transaction monitoring: Chargebacks, disputes, and buyer/seller protection.
- Core trade-off: Stopping fraud vs. keeping approval rates high.
Merchant Handling, Payouts, and Settlement
Analysts must grasp how money moves across the merchant lifecycle.
- Onboarding: Business verification, account setup, early monitoring.
- Payouts: Moving money to merchant bank accounts.
- Settlement cycles: How long it takes for funds to clear and reconcile.
Competitor Benchmarks
PayPal expects high-level awareness of other major payments players, such as:
- Stripe Connect: Marketplaces and strong developer tools.
- Square Payments: Integrated hardware and small-business focus.
- Apple Pay: Device-based checkout with bank-controlled approvals.
Understanding these differences signals strong market awareness and product intuition.
While you don’t need to be a payments expert, you should understand the fundamentals well enough to explain issues, choose the right metrics, and think through trade-offs. Explore Interview Query Coaching to get targeted guidance and insider tips from coaches with expertise in business analytics and fintech.
How to Prepare for a PayPal Business Analyst Interview
Preparing for a PayPal business analyst interview requires more than generic analytics practice; you need targeted knowledge of PayPal’s systems, metrics, and merchant ecosystem. The interview is designed to test whether you can think like a PayPal analyst on day one. Below is a preparation plan aligned directly with the skills PayPal screens for.
| Preparation Area | What to Focus On | Resources / Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Flows & Disputes | - Authorization → capture → settlement - Common failure reasons - Dispute/chargeback lifecycle |
- PayPal Help Center - YouTube explainers on payment lifecycle |
| Risk & Fraud Fundamentals | - Risk rules and models - Fraud vs. approval-rate trade-offs - Early-life merchant monitoring. |
PayPal Seller Protection pages |
| System Diagrams (Disputes / Chargebacks) | - Customer → merchant → PayPal flow - Bank chargeback timeline - Edge cases |
Draw.io, Figma, or Lucidchart for diagram practice. |
| PayPal Earnings Reports | - Payment volume trends - Merchant services growth - BNPL performance - Cost initiatives |
PayPal Investor Relations quarterly earnings PDFs |
| API Familiarity | Basic concepts: payment intent, payout objects, authorization objects, webhook events | Public Braintree & PayPal developer docs |
| Timed Mock Interviews | - SQL timing - Case reasoning under pressure - Structured communication |
Interview Query AI Interviewer |
PayPal Business Analyst Salary
Salaries for PayPal business analysts vary by level, experience, and location, reflecting the high demand for analytical expertise across its global payments ecosystem.
According to Levels.fyi, median yearly compensation is approximately $165K, but here is a more detailed breakdown by base salary, stock, and bonus components across role levels.
| Role | Total Compensation | Base Salary | Stock | Bonus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Business Analyst I-II | $104K - $124K | $86K - $106K | $11K - $13K | $5K - $7K |
| Senior Business Analyst | $116K | $101K | $8.5K | $7K |
| Staff Business Analyst 1-2 | $206K - $232K | $155K - $170K | $37K - $45K | $15K - $17K |
| Senior Staff / Principal BA | $256K+ | $185K | $55K | $16K |
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Location Variations
- Regional differences mainly reflect cost of living, competitive market pay, and local demand for fintech analytics talent.
- High-cost markets: San Jose, Austin, New York City typically offer higher base salaries and stock grants.
- Other markets: Smaller packages in cities such as Dallas, Atlanta, or Phoenix, though bonuses often help close the gap.
Visit our industry-wide salary guides to explore up-to-date compensation insights and career planning resources.
Key Takeaways
- Use compensation benchmarks from sources like Levels.fyi and recent PayPal BA ranges to justify your ask. Bringing concrete numbers makes the conversation more objective and less personal.
- Career growth emphasizes not just technical skills, but also domain expertise, systems knowledge, and strategic impact—with pathways into managerial or specialized BSA roles.
- Emphasize domain strengths such as payments, risk modeling, or experimentation, since these are high-impact areas at PayPal and can support a higher band or stronger equity offer.
For candidates seeking growth and competitive compensation, Interview Query’s Coaches with PayPal background and experience can also provide personalized guidance on understanding leveling and career development.
FAQs
Why choose a business analyst role at PayPal?
A business analyst role at PayPal offers the chance to influence millions of transactions across a global payments ecosystem. By partnering with product, engineering, and compliance teams, this cross-functional role gives analysts broad visibility and the ability to shape high-impact decisions. It’s also a strong long-term career move, with clear pathways into product, data science, or systems leadership within a company that values analytical rigor and customer-centric innovation.
How do you answer “Describe your business” for PayPal?
A strong answer highlights PayPal as a global payments platform enabling secure digital transactions for consumers and merchants. Mention its multi-product ecosystem (PayPal, Braintree, Venmo, PayPal Credit) and its role in authorization, fraud prevention, checkout optimization, and dispute handling. Keep the framing high-level, mission-oriented, and data-driven.
What KPIs matter most in PayPal’s merchant analytics?
Key metrics include checkout conversion, payment authorization rates, fraud/chargeback rates, dispute win rates, average revenue per merchant, onboarding completion time, and payment failure classification. Many teams also track latency, decline reason codes, and risk-model precision/recall.
How technical is the PayPal business systems analyst interview?
BSA interviews emphasize understanding of system flows, requirements gathering, APIs, integration points, and functional edge cases. While not as code-heavy as engineering roles, expect to describe payment lifecycles, risk decisioning layers, and dependency mapping across backend services.
Do PayPal BAs need SQL or Python?
SQL is essential for nearly all analytics and product-facing BA roles. You’ll query transaction tables, conversion funnels, and cohort datasets regularly. Python is not required for most business analyst roles, but it can help in teams that build dashboards, conduct statistical analysis, or support machine learning evaluations.
How is PayPal’s interview different from Stripe, Square, or Adyen?
PayPal interviews place a heavier emphasis on risk, compliance, and global regulatory considerations. Compared to newer payment companies, PayPal’s scale introduces more complex dispute flows, issuer interactions, and cross-border challenges. Expect deeper evaluation of fraud logic, risk thresholds, and merchant-impact trade-offs.
Does PayPal ask system design questions for business analysts?
Yes—typically functional, not engineering-focused. You may map flows like the chargeback process, merchant onboarding, or multi-step payment authentication. Interviewers expect clarity around user touchpoints, system dependencies, risk checks, and data inputs.
How are risk and compliance integrated into BA workflows?
Risk and compliance are core partners. BAs work with them to evaluate rule changes, mitigate emerging fraud patterns, measure false positives/negatives, and ensure product updates meet regional regulatory standards.
What’s expected in a PayPal case study interview?
Case studies simulate real PayPal problems: diagnosing conversion drops, analyzing decline reason codes, improving onboarding speed, or identifying fraud-pattern anomalies. You must break down the problem into metrics, propose hypotheses, outline data you’d pull, and communicate trade-offs clearly.
What’s the career progression like for PayPal business analysts?
Career progression for PayPal business analysts is well-defined, moving from BA to Senior, Staff, and ultimately BSA/Analytics Lead or managerial roles as analysts develop deeper product, payments, and systems expertise. For those who excel, the path opens into leadership roles where they guide global initiatives, mentor teams, and help shape PayPal’s product and data strategy.
Does PayPal hire remotely for analytics roles?
Yes—PayPal supports hybrid and remote work depending on team needs. Analytics and product teams frequently include fully remote members across the U.S.
How quickly does PayPal move after the onsite?
Most candidates hear back within one to two weeks. PayPal’s process typically involves panel calibration and final leveling before extending an offer.
Are PayPal business analysts expected to know payment regulations?
Not in-depth, but familiarity with PSD2, AML, KYC, and card network rules helps when discussing risk trade-offs and cross-border flows.
Do PayPal interviews include troubleshooting or debugging scenarios?
Yes, especially around payment failures, latency spikes, or API errors. Interviewers assess your ability to prioritize hypotheses and communicate a structured investigation plan.
Ace Your PayPal Business Analyst Interview with Interview Query
Succeeding in the PayPal business analyst interview requires both analytical precision and deep appreciation for how global payments work. PayPal’s mission, which is to democratize financial services and enable secure, seamless commerce, depends on analysts who can improve risk decisions, streamline merchant experiences, and optimize every step of the transaction lifecycle.
As you prepare, focus on mastering the metrics, system flows, and experimentation patterns that drive PayPal’s products. For a complete set of real-world practice problems, explore Interview Query’s resources:
- Question Bank to sharpen your SQL, product sense, and experimentation skills,
- Learning Paths to brush up on foundational and advanced BA topics, and;
- Mock Interviews to boost your confidence and performance throughout the full loop.
With structured preparation and clear communication, you’ll be ready to stand out in the PayPal business analyst interview process.


