Apple Data Analyst Interview Guide: Questions & Salary
Introduction
Apple runs one of the largest consumer data ecosystems in the world. Its products reach more than 2 billion active devices globally, and its services segment alone generates over $100 billion in annual revenue, spanning the App Store, Apple Music, iCloud, Apple TV+, and more. Every support interaction, product session, diagnostic signal, and transaction generates data that helps Apple improve user experience, streamline operations, and strengthen product quality. Data analysts sit at the center of this ecosystem by transforming raw information into clear insights that guide decisions across engineering, support, retail, and product teams.
If you are preparing for the Apple data analyst interview, this guide explains the role, what Apple evaluates, and how the interview process works. Many candidates strengthen foundational skills through the data science interview learning path, since Apple’s data analyst interviews often include SQL, analytics, dashboards, and structured problem solving.
If you want to see real Apple data analyst interview questions and solutions, explore the Apple data analyst question bank.
What does an Apple data analyst do
Apple data analysts support technical and business teams by structuring data, improving reporting pipelines, and providing insights that drive product performance and operational efficiency. They work across complex datasets, build dashboards, and partner closely with engineering, AppleCare, operations, finance, and product teams to translate raw data into actionable recommendations.
Core responsibilities include
- Collecting, cleaning, and analyzing large datasets to identify trends and anomalies
- Building dashboards, automated reports, and recurring business reviews
- Designing metrics that track backlog health, operational throughput, and team performance
- Managing databases, pipelines, and data models to ensure accuracy and consistency
- Partnering with engineering and product teams to define data requirements
- Presenting insights to technical and non-technical stakeholders
Candidates preparing for this role often practice their analytical reasoning and SQL skills through SQL interview questions, since SQL is a major part of Apple’s process.
Why this role at Apple
The Apple data analyst role is a strong fit for candidates who enjoy combining analytical rigor with product and operational intuition. Analysts influence decisions that affect millions of users and thousands of internal workflows, from customer support experiences to retail operations to product health metrics.
Reasons candidates choose this role
- Opportunity to work with large-scale, high-impact datasets spanning hardware, software, and services
- Direct influence on product decisions, backlog management, operational efficiency, and customer experience
- A culture that values clarity, simplicity, and thoughtful measurement
- Cross functional exposure across engineering, AppleCare, operations, and product teams
- Clear pathways for growth into analytics engineering, operations analytics, data science, and product analytics roles
Candidates exploring related roles often compare this process with the broader Apple interview guide, which outlines interview expectations across analytics, data science, and engineering disciplines.
Apple Data Analyst Interview Process
Apple’s data analyst interview process emphasizes analytical rigor, SQL mastery, data interpretation, and structured communication. While the specifics vary across teams like AppleCare, Retail Operations, Services Analytics, Finance, People Analytics, and Product Analytics, most follow a multi stage structure that evaluates your ability to work with large datasets, design meaningful metrics, build dashboards, and translate complex signals into actionable insights.
Candidates often supplement their preparation with the SQL interview learning path and the data analytics learning path, especially because Apple’s loops frequently mix SQL, metric design, stakeholder problem solving, and business reasoning.
| Stage | What it focuses on |
|---|---|
| Application and resume review | SQL fluency, dashboard experience, impact on business or operational metrics |
| Recruiter screen | Background alignment, communication clarity, motivation for Apple |
| Technical phone screens | SQL, data cleaning, KPI design, analytical reasoning |
| Take home or analytics assessment (team dependent) | Data cleaning, metric building, dashboarding, insight synthesis |
| Onsite or virtual loop | 4–6 interviews covering SQL, metrics, data interpretation, business case analysis, communication, and behavioral skills |
| Hiring manager + team conversations | Deep dive into past work, cross functional collaboration style, and role fit |
| Final decision | Team sync, signal calibration, and offer determination |
Application and resume review
Apple’s initial screen identifies candidates with strong SQL foundations and demonstrated business impact. Reviewers look for experience building dashboards, designing metrics, and supporting cross functional teams through clear analytical insights.
What Apple looks for
- Proficiency in SQL and experience working with relational datasets
- Ability to build dashboards or recurring reporting pipelines
- Examples of end to end problem solving
- Evidence of improving operational, support, or product metrics
- Communication that makes complex findings accessible
You can compare your experience with examples in the Apple data analyst question bank.
Tip: Lead resume bullets with measurable outcomes. For example, “Reduced ticket backlog by 12 percent by redesigning performance metrics.”
Recruiter screen
The recruiter call evaluates your communication clarity, analytical background, and understanding of what Apple analysts do. This stage also sets expectations for technical depth and team alignment.
What you will discuss
- Overview of your SQL, analytics, and dashboarding experience
- Projects where your insights influenced decisions or improved throughput
- Potential alignment with teams like AppleCare or Retail Ops
- Your interest in Apple and the analyst role’s problem space
- Interview format and scheduling
If you want to compare expected skill breadth, you can preview topics in the data analyst learning path.
Tip: Prepare a short, polished summary of your analytics background that connects naturally to Apple’s scale.
Technical phone screens
The technical phone screen tests whether you can write correct SQL, reason through messy data, and design clear metrics. Apple values accuracy and clarity rather than cleverness.
Focus areas
| Area | What to expect |
|---|---|
| SQL | Joins, aggregates, window functions, time series filtering, query debugging |
| Data cleaning | Identifying inconsistencies, null handling, validating output grain |
| Metric design | Building KPIs, backlog metrics, throughput metrics, guardrail metrics |
| Analytical reasoning | How you break down ambiguous business questions |
You can practice this style in Interview Query’s scenario based SQL problems.
Tip: Always restate assumptions and explain your reasoning as you write the query. Apple actively listens for thought process.
Take home or analytics assessment (team dependent)
Some teams give a short assessment to evaluate your ability to handle realistic Apple style analytics tasks. These assessments mirror internal workflows such as backlog reviews, operational diagnostics, or early product analyses.
Possible formats
| Format | Examples |
|---|---|
| Data cleaning | Identifying anomalies, correcting schema issues, validating metrics |
| KPI and reporting design | Building backlog or performance metrics, defining guardrails |
| Dashboarding | Drafting a simple dashboard or describing your approach |
| Insight summary | Writing a concise narrative of findings and recommended actions |
Clarity matters more than visual complexity. You can practice similar tasks through the takehomes library.
Tip: Use a simple structure: context, method, findings, recommendation. Apple values direct, decision oriented writing.
Onsite or virtual loop
The onsite loop consists of 4 to 6 interviews that evaluate SQL depth, metric design ability, cross functional communication, and business intuition. Interviews are structured yet conversational.
Typical interview components
| Category | What it covers |
|---|---|
| SQL and data manipulation | Writing and debugging queries, checking edge cases, validating logic |
| Metrics and dashboarding | Designing KPIs, improving reporting workflows, explaining dashboard decisions |
| Data interpretation | Explaining patterns, diagnosing anomalies, interpreting charts and tables |
| Business case analysis | Backlog trends, retention funnels, operational throughput, product performance |
| Behavioral and cross functional | Communication, prioritization, ambiguity management, stakeholder alignment |
Analytical structure is critical. Apple wants to see how you frame a problem, identify data needs, evaluate drivers, and translate findings into actions.
For more practice in structured reasoning, many candidates review parts of the data science interview learning path.
Tip: Use a consistent, top down problem solving flow. For example: clarify goals → identify drivers → outline approach → test hypotheses → recommend next steps.
Hiring manager conversation
This conversation goes deeper into your past work, analytical rigor, and collaboration style. Managers look for your ability to scope problems independently and communicate clearly across technical and non-technical partners.
Hiring managers evaluate
- How you break down ambiguous analytical requests
- Your approach to metric design and dashboard structure
- Depth of your SQL logic and analytical reasoning
- How you collaborate with engineering, support, product, or operations
- Your long term growth trajectory inside Apple’s analytics organization
Tip: Choose a flagship project and be ready to explain every technical and strategic decision in detail.
Final decision
After all interviews, Apple aligns interviewer feedback and evaluates your overall signal. Both technical performance and communication maturity heavily influence the final decision. Hiring timelines can range from a few days to several weeks.
Tip: Follow up professionally with your recruiter. They can often provide clarity on the next steps and timeline expectations.
Apple Data Analyst Interview Questions and Answers
Apple data analyst interview questions emphasize SQL precision, analytical reasoning, and the ability to transform ambiguous data into clear, actionable insights. You can expect a mix of SQL and data manipulation tasks, metric design questions, dashboarding scenarios, and product or operations focused case prompts. Practicing realistic problems in the data analyst question bank and the SQL interview learning path helps build the structure Apple expects.
SQL and data manipulation interview questions
SQL interviews test whether you can clean, join, and restructure real-world datasets accurately. Reviewing scenario based SQL questions in the SQL interview learning path helps reinforce the fundamentals Apple expects.
Calculate cumulative sales since the last restocking.
Explain how you would join product, sales, and restocking tables, then use window functions to partition by product and reset cumulative totals at each restocking event. Interviewers evaluate whether you can communicate table grain, handle edge cases, and avoid miscounting.
Tip: Always define the output grain before writing any query to show structured thinking.
Build a table to track exam scores for each student.
Describe how you would reshape the dataset so each student appears once with four exam scores. This tests pivoting, handling missing records, and ensuring completeness. Apple looks for stable logic when transforming uneven or sparse data.
Tip: Call out how you validate missing or duplicate records before building the final output.
Identify shipments delivered within membership periods.
Show how to join shipment timestamps to membership intervals using conditional logic. Apple tests whether candidates can work with temporal joins and explain nuanced assumptions clearly.
Tip: Mention how you would test for off-by-one errors or mismatched date formats.
Get the number of upsold customers.
Clarify an upsell definition, then use window functions or ordered filtering to detect later purchases beyond the first transaction. Apple evaluates your ability to convert business rules into precise analytical logic.
Tip: Distinguish between same-day purchases and true upsells to avoid overcounting.
Count daily active users per platform.
Group by date and platform, aggregate distinct users, and ensure correct filtering to the specified year. This tests time series reasoning and the ability to explain output consistency.
Tip: State how you check for timezone misalignment or missing dates.
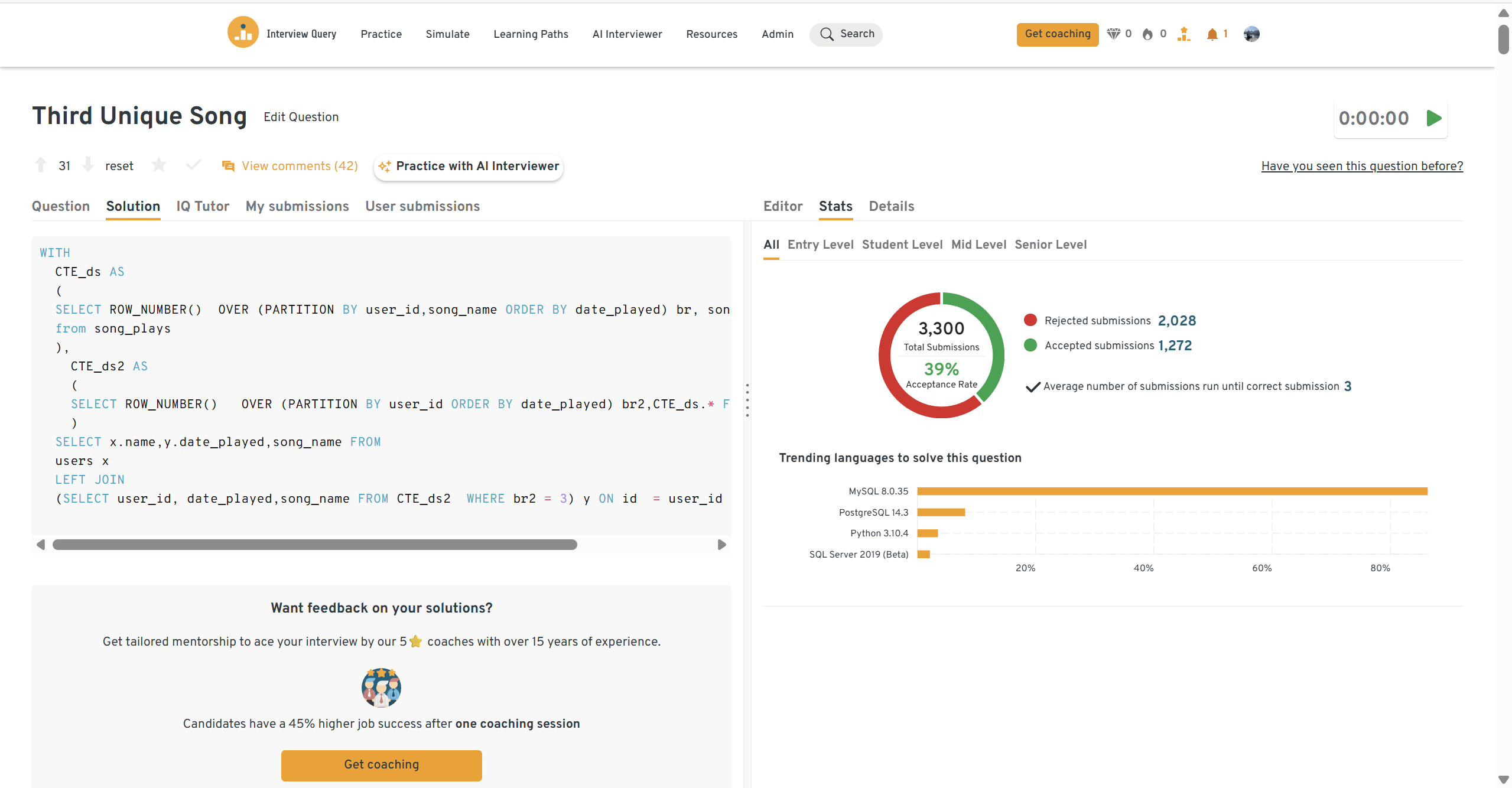
Find the earliest date a user played their third unique song.
Use window functions to rank unique songs per user, then filter to the third occurrence. Apple evaluates how cleanly you deduplicate, rank, and extract sequential events.
Tip: Mention how you would handle users with fewer than three unique events.
You can practice this exact problem on the Interview Query dashboard, shown below. The platform lets you write and test SQL queries, view accepted solutions, and compare your performance with thousands of other learners. Features like AI coaching, submission stats, and language breakdowns help you identify areas to improve and prepare more effectively for data interviews at scale.
Metrics, analytics, and dashboarding interview questions
Analytics interviews evaluate your ability to define KPIs, interpret anomalies, and design dashboards for operations, AppleCare, or product teams. Reviewing reasoning based questions in the data analyst interview learning path helps reinforce the structured thinking Apple expects.
A backlog metric increases unexpectedly. How would you diagnose the cause?
Start by validating the metric, then segment by geography, workflow stage, or device type. Investigate whether the increase stems from volume spikes, slower processing times, staffing changes, or data pipeline shifts. Apple evaluates structured triage and clarity in your investigative steps.
Tip: State your segmentation strategy up front before listing possible causes.
How would you design a dashboard to monitor AppleCare support performance?
Define key KPI groups such as volume, efficiency, quality, and customer experience. Explain which filters matter (issue type, region, device family) and how you prevent dashboard overload. Apple looks for thoughtful prioritization and user-centric design.
Tip: Mention which metrics refresh daily versus weekly to show operational awareness.
How would you measure the impact of a new App Store placement?
Identify exposure metrics, engagement metrics, conversion rates, and revenue outcomes. Add guardrail metrics like bounce rate or page load performance. Apple evaluates whether you can balance product KPIs with user experience considerations.
Tip: Summarize the experiment structure even if no formal A/B test is mentioned.
A weekly data quality check reveals a sudden drop in events. What steps do you take?
Validate upstream pipelines, compare known backup tables, check for schema or ingestion changes, and inspect timestamp irregularities. Apple wants candidates who can debug calmly and systematically.
Tip: Always discuss how you would quantify the scope and severity of the issue.
How would you determine customer service quality from chat interactions?
A strong answer begins by identifying measurable proxies for service quality. These could include resolution rate, time to first response, sentiment extracted from messages, escalation frequency, or follow up actions. Next, outline how you would classify conversations using NLP signals such as sentiment polarity, keyword frequency, or message length. Finally, segment results by business type, product category, or customer type to surface meaningful insights.
Tip: Mention both quantitative measures and qualitative reviews, showing that you understand how Apple calibrates customer experience.
Product and business case interview questions
Business case interviews assess how you frame ambiguous problems, identify what data matters, and recommend actions that improve workflows. Practicing similar open-ended cases in the data science learning path can help build structure.
AppleCare sees an increase in delayed ticket resolutions. How would you investigate?
Validate the definition of “delayed,” segment by issue type, examine throughput, and check for recent policy or tooling changes. Apple evaluates whether you combine operational context with data-driven reasoning.
Tip: State the decision each part of your analysis would inform.
Apple is considering launching a new support workflow. What analysis would you run before recommending launch?
Outline KPIs such as handle time, completion rate, backlog impact, and customer satisfaction. Estimate workload changes and identify cost savings or risks. Apple wants to see balanced, decision-ready thinking.
The App Store review process experiences inconsistent processing times. How do you analyze this?
Map the workflow, examine stage-level durations, identify bottlenecks, and quantify their impact. Apple evaluates comfort with multi-step operational tracing.
Apple Retail wants to improve in-store pickup accuracy. How would you approach the problem?
Identify mismatch drivers, analyze device-level trends, quantify operational cost, and propose a pilot test. Apple values clarity, structure, and practical actionability.
Behavioral and cross functional interview questions
Behavioral interviews at Apple evaluate collaboration, communication clarity, ownership, and your ability to work with engineering, product, AppleCare, and operations teams. Interviewers want to see structured storytelling, self-awareness, and how you navigate ambiguity or conflict. Reviewing patterns in the behavioral question set can help you refine your delivery.
Describe a data project you worked on. What challenges did you face?
Apple looks for end-to-end ownership and maturity in identifying both technical and stakeholder challenges. Interviewers want to see how you debug data inconsistencies, clarify requirements, and manage expectations across teams.
Tip: Mention one technical challenge and one stakeholder challenge to show full-spectrum problem solving.
Sample Answer: I built a churn reporting pipeline for a global support org. Midway through the project, I discovered inconsistent keys across regional systems, which caused join failures and missing segments in dashboards. I partnered with engineering to map identifier lineage and created a reconciliation layer to stabilize ingestion. Stakeholders also needed faster updates, so I produced an interim aggregated report while fixes were deployed. The final output reduced missing data by more than 40 percent and improved weekly planning accuracy.
What are effective ways to make data more accessible to non technical people?
This question tests your communication clarity and your ability to tailor insights to different audiences. Apple values analysts who reduce complexity without losing analytical rigor.
Tip: Tie your approach to better, faster decision making rather than just nicer visuals.
Sample Answer: I begin by asking which decisions the audience needs to support. Then I design dashboards with only the core KPIs, add plain language definitions, and standardize layout and color. For deeper logic, I create a short one page guide explaining metric construction. I also record brief walkthrough videos so teams can learn asynchronously. This reduces dependency on analysts and improves adoption.
What would your manager say are your strengths and weaknesses?
Apple wants self-awareness and a thoughtful improvement plan. Strong answers include specific examples rather than generic traits.
Tip: Choose strengths that the role values and weaknesses that are real but non-critical.
Sample Answer: My manager would say my strengths are structured problem solving and reliability during ambiguous analytics work. A weakness I am improving is spending too long validating edge cases before sharing updates. To address this, I now time box early exploration and review assumptions sooner with stakeholders, which accelerates iteration.
Talk about a time you had trouble communicating with stakeholders. How did you overcome it?
This evaluates adaptability and your ability to adjust communication style to stakeholder preferences.
Tip: Focus on what you changed in your own approach.
Sample Answer: I worked with a PM who preferred concise recommendations, while my reports were highly detailed. After recognizing the mismatch, I switched to one page summaries with optional deep dive sections. This improved alignment and reduced review cycles. The PM later adopted this format across the team.
Why do you want to work with us?
Apple expects candidates to connect their motivation to the scale, mission, and analytical impact of the role.
Tip: Reference both Apple’s products and the analyst function’s influence on decision quality.
Sample Answer: I want to work at Apple because analytics directly influence how millions of customers experience products. I enjoy turning complex operational and product data into clear, decision-ready insights. The analyst role sits at the intersection of product, engineering, and operations, which matches the environment where I do my best work.
Tell me about a time you disagreed with a stakeholder and how you resolved it.
Apple looks for calm decision making, evidence based reasoning, and respect for alignment.
Tip: Show that you sought clarity and used data to drive resolution.
Sample Answer: A regional lead believed backlog growth was due to staffing shortages. My analysis suggested the driver was a workflow change that increased rework time. I presented segmented evidence, proposed running a pilot to compare both hypotheses, and included the engineering partner responsible for the change. The pilot validated the workflow issue and we aligned on updating the tool rather than adding headcount.
Describe a time you had to prioritize conflicting analytical requests. How did you decide what to deliver first?
This evaluates judgment, communication, and prioritization skills.
Tip: Demonstrate a simple, repeatable framework rather than intuition alone.
Sample Answer: When supporting two teams with competing urgent requests, I created an impact and urgency matrix and reviewed it with both stakeholders. The higher impact request moved forward first, and I provided an interim dataset to the second team so they were not blocked. This transparent approach reduced friction and established a clear prioritization process for future requests.
This breakdown by Interview Query founder Jay Feng covers the five most common data analyst interview questions and how to answer them with clarity, structure, and insight. It’s an efficient way to tighten your fundamentals before tackling Apple–style analytics interviews.
How to Prepare for an Apple Data Analyst Interview
Preparing for an Apple data analyst interview means demonstrating structured analytical reasoning, SQL proficiency, clear communication, and the ability to build decision ready insights from ambiguous datasets. The role often sits between engineering, operations, product, AppleCare, and retail teams, so the strongest candidates show both technical competence and cross functional alignment.
You can reinforce your technical foundations through Interview Query’s SQL interview learning path, strengthen your case reasoning through the data analyst learning path, and review broader concepts in the data science interview learning path for product or experimentation focused roles.
Strengthen your SQL fundamentals with real scenario practice
SQL is the most consistently tested skill across Apple analyst roles. Expect multi table joins, window functions, event sequencing, deduplication logic, and debugging queries with unexpected outputs. Apple values accuracy, clarity, and step by step reasoning more than clever syntax.
To align your preparation, practice scenario based problems in the SQL interview learning path and the SQL scenario library.
Tip: Verbalize the grain of your output before writing the query. This mirrors the structured thinking Apple evaluates.
Build confidence in metrics, KPIs, and operational dashboards
Many Apple analyst teams rely on analysts to define KPIs, design dashboards, and measure workflows such as support performance, App Store quality, or device level behavior. Your preparation should focus on creating simple but meaningful frameworks for metrics.
You can practice similar reasoning styles through the data analyst learning path and operational case studies in the Interview Query question bank.
Tip: When defining any metric, mention one limitation or blind spot. Apple values balanced thinking.
Learn to communicate insights with structured, concise storytelling
Apple places strong emphasis on clarity. Analysts must summarize complex datasets for non technical teams, interpret anomalous trends, and convert findings into actionable recommendations. Your answers should highlight your ability to simplify without losing rigor.
You can practice this style through take home style problems in the takehomes library and by reviewing explanations in the data analyst question bank.
Tip: Start with the business question, then the insight, then the supporting detail. Apple expects this top down communication style.
Prepare examples of resolving ambiguity and collaborating cross functionally
Apple analysts frequently partner with engineering, product managers, operations, and retail teams. Interviewers evaluate whether you handle ambiguous requirements, ask clarifying questions, and keep stakeholders aligned when priorities shift.
Review common patterns in the behavioral question bank and practice delivering structured STAR stories that highlight ownership and communication maturity.
Tip: Choose examples that show both technical depth and stakeholder alignment to mirror Apple’s expectations.
Strengthen your ability to analyze and debug data quality issues
Apple’s internal datasets integrate signals across devices, retail, AppleCare, and services. Data issues such as missing events, schema changes, or mismatched keys are common. Interviewers expect a calm, systematic debugging framework.
You can reinforce this thinking through SQL debugging problems in the SQL learning path and case style reasoning in the data science learning path.
Tip: Always verify upstream changes before assuming the metric is wrong. Apple looks for analytical discipline.
Prepare one or two end to end projects you can explain in detail
The onsite loop typically includes deep dives into past work. Apple expects analysts to explain the goal, data sources, modeling logic or SQL approach, validation steps, results, and impact. You should be ready to discuss trade offs, alternatives, and what you would improve with more time.
Interview Query’s mock interviews and challenges can help you rehearse delivering polished walkthroughs.
Tip: Choose projects where you owned the problem definition, analysis, and communication rather than tasks where you only executed instructions.
Practice ambiguous business cases and operational reasoning
Apple frequently asks open ended questions involving backlogs, customer satisfaction, App Store review workflows, device quality signals, or support processes. These assess your ability to structure unscoped problems and propose measurable next steps.
You can build this skill by practicing reasoning questions in the data analyst interview learning path and the data science learning path for roles with experimentation or product components.
Tip: Use a consistent structure: validate the metric, segment the data, identify potential drivers, and propose actions.
Apple Data Analyst Salary
Apple data analyst salary and compensation varies depending on level, team, and location, but most U.S. roles fall between $86K and $192K per year for early to mid career levels. Based on Levels.fyi data, Apple’s median total annual compensation for data analysts is approximately $168K, with base salary making up the largest portion and stock grants increasing significantly at higher ICT levels.
These numbers reflect Apple’s investment in analysts who support AppleCare, Retail, Apple Services, Device Analytics, Supply Chain, and operational intelligence teams across the company.
| Level | Total Compensation | Base Salary | Stock | Bonus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICT2 (Junior Data Analyst) | $86.4K | $80.4K | $3.5K | $1.7K |
| ICT3 (Data Analyst) | $168K | $144K | $25.2K | $3K |
| ICT4 (Senior Data Analyst) | $192K | $168K | $25.2K | $8.3K |
Although compensation varies by team, Apple data analyst roles typically fall slightly below data scientist roles in both stock and bonus components. However, analysts in operations, supply chain, and services analytics often progress into higher ICT levels with competitive increases in base and stock.
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Apple data analyst salary and compensation varies depending on level, team, and location, but most U.S. roles fall between $86K and $192K per year for early to mid career levels. Based on Levels.fyi data, Apple’s median total annual compensation for data analysts is approximately $168K, with base salary making up the largest portion and stock grants increasing significantly at higher ICT levels.
These numbers reflect Apple’s investment in analysts who support AppleCare, Retail, Apple Services, Device Analytics, Supply Chain, and operational intelligence teams across the company.
| Level | Total Compensation | Base Salary | Stock | Bonus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICT2 (Junior Data Analyst) | $86.4K | $80.4K | $3.5K | $1.7K |
| ICT3 (Data Analyst) | $168K | $144K | $25.2K | $3K |
| ICT4 (Senior Data Analyst) | $192K | $168K | $25.2K | $8.3K |
Although compensation varies by team, Apple data analyst roles typically fall slightly below data scientist roles in both stock and bonus components. However, analysts in operations, supply chain, and services analytics often progress into higher ICT levels with competitive increases in base and stock.
FAQs
How technical is the Apple data analyst interview?
Apple’s interviews lean more technical than most FAANG analyst roles. You can expect SQL challenges, analytics case studies, product reasoning questions, and scenario-based data cleaning problems. Many teams also evaluate Python or scripting comfort. Reviewing the SQL problems in the SQL interview learning path helps match the level of rigor Apple expects.
Does every Apple analyst role require SQL?
Almost always yes. SQL is a core skill for analysts across AppleCare, Operations, Apple Services, and Retail Analytics. Even roles that emphasize dashboards or reporting still require the ability to manipulate data, optimize joins, and write analytic queries.
Is Python required for Apple data analyst roles?
Python is not mandatory for all roles, but it is highly preferred. Teams that build automation pipelines, experimentation frameworks, or device analytics systems often evaluate Python skills in interviews. For preparation, some candidates review the coding section in the data science interview learning path.
How many interview rounds should I expect?
Most candidates complete five to seven stages that include recruiter screens, technical interviews, product and analytics case discussions, and behavioral conversations tied to collaboration and communication. You can find a more detailed breakdown above in the interview process section.
Does Apple use take home assignments?
Some teams do. The assessment typically involves a realistic data cleaning or exploratory analysis task, not a heavy modeling assignment. The focus is on clarity of insights and reproducibility rather than complex code.
How should I prepare for ambiguous analytics questions?
Structure is key. Apple interviewers value candidates who can turn unclear questions into measurable frameworks. Practicing scenario-based problems in the analytics case interview guide can strengthen this skill.
How important are visualizations during interviews?
Very important. Apple values analysts who communicate insights clearly through dashboards, charts, or summaries. Interviewers often ask how you would present findings to an executive or cross-functional audience.
Do Apple analysts need product sense?
Yes. Even though the role is not product management, analysts frequently support decisions that shape user experience, operational strategy, or customer satisfaction. Interviewers may ask how you would evaluate the impact of a feature, metric, or workflow change.
Build the Level of Analytical Thinking Apple Actually Hires For
Apple does not look for analysts who simply answer questions. Apple hires analysts who reshape the questions entirely—who take ambiguous data, uncover what truly matters, and turn insights into decisions that impact millions of users worldwide. That is why their interview loop demands precision in SQL, clarity in communication, and a structured approach to analytics that mirrors how teams across AppleCare, Retail, Services, and Operations work every day.
If you want to practice the same style of reasoning Apple evaluates, the best next step is to follow a structured preparation plan. Start with the SQL interview learning path to lock in query fundamentals. Then move into real case breakdowns through the analytics learning path so you can practice turning messy prompts into measurable frameworks. Finally, sharpen your communication and interview presence with mock interviews designed to simulate Apple’s high-signal conversations.
Mastering Apple’s interview is ultimately about mastering how to think like an Apple analyst: structured, curious, and impact-driven. With the right preparation, you can walk into your loop ready to do exactly that.

