Visa Data Analyst Interview Questions & Guide (2025)
Introduction
Landing a Visa data analyst role means competing in one of the most rigorous interview processes in fintech. Analysts are tasked with turning raw stream of payments data into insights that drive billion-dollar business decisions. It’s more than just running SQL queries; It’s about proving you can design metrics, evaluate product performance, and communicate clearly with global stakeholders.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the Visa data analyst interview process, the types of questions you can expect, and proven preparation strategies. You’ll learn what day-to-day responsibilities look like, how Visa’s data-driven culture influences interviews, and which technical and behavioral areas to focus on. Whether you’re applying for an entry-level analyst role or preparing for a senior interview, this breakdown will help you practice effectively and stand out in a competitive hiring pool.
Role Overview & Culture
The Visa data analyst role revolves around finding patterns in complex payments data and translating them into strategic insights. On a daily basis, analysts write SQL to track card-spend trends, monitor performance dashboards, and design metrics that support product launches and risk initiatives. Collaboration is central. Analysts regularly partner with finance, product, and operations teams to ensure data drives decision-making across the company. Visa’s culture prizes precision and curiosity; under its “Network of Innovation” ethos, analysts are empowered to challenge assumptions, ask better questions, and influence cross-functional decisions with data. The role is as much about communication as it is about analysis.
Why This Role at Visa?
What makes this opportunity unique is the scale and visibility of the work. Visa data analysts don’t just analyze small datasets. They work with billions of transactions that reflect real consumer and business behavior across the globe. Compensation is competitive, with U.S. salaries typically ranging from $91K to $134K, and the role offers clear career mobility into senior analytics, product strategy, or data science within a few years. Analysts gain early exposure to leadership and are often pulled into high-stakes conversations around fraud prevention, cross-border payments, and new digital payment products. Preparing for Visa data analyst interview questions means sharpening not only your SQL and analytics skills, but also your ability to explain the “so what” behind the numbers. In the next section, we’ll walk through the interview process and what Visa looks for at each stage.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Data Analyst Role at Visa?
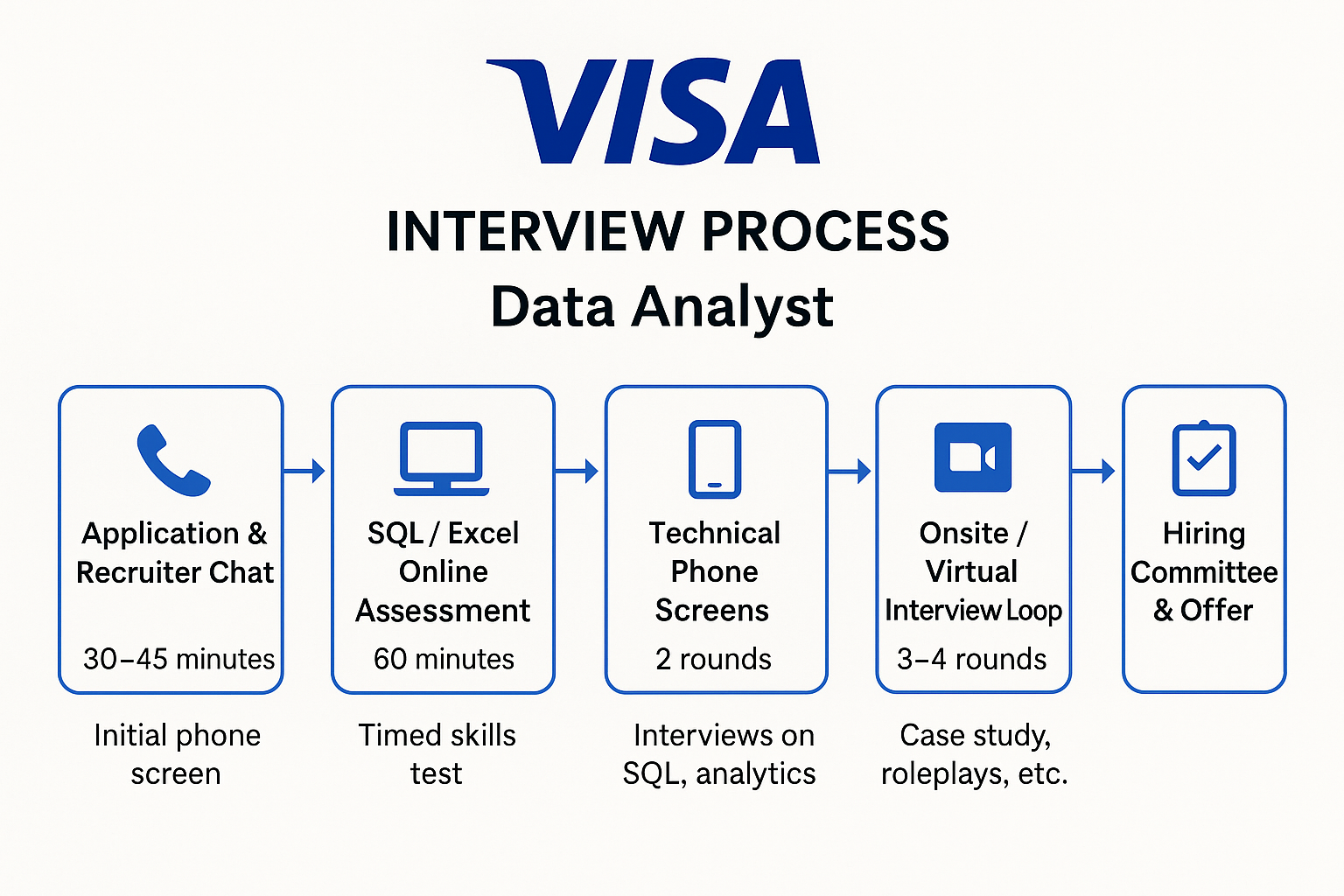
The Visa data analyst interview process is structured to evaluate your technical skills, business acumen, and ability to communicate insights clearly. Here’s a breakdown of the five main interview stages:
Application & Recruiter Chat
Once your resume is shortlisted, you’ll begin with a 30–45 minute phone call with a recruiter. This is a high-level screen to assess your experience, interest in the role, and familiarity with Visa’s mission and products. You’ll be asked about your background in SQL, analytics tools (e.g., Tableau, Python, Excel), and how you’ve used data to drive decisions. While not deeply technical, the recruiter may ask light questions about data cleaning or KPI tracking to ensure baseline competency.
Tip: Be ready with one clear example of how you used SQL or Excel to solve a real business problem. It shows both competence and communication.
SQL/Excel Online Assessment (60 minutes)
If the recruiter screen goes well, you’ll be sent a timed online assessment, typically lasting 60–90 minutes. This test evaluates your ability to write clean, optimized SQL queries across multiple tables, apply functions like JOIN, GROUP BY, WINDOW, and perform aggregations. It also includes Excel logic problems—think nested formulas, pivot tables, or VLOOKUP applications—often framed in a business context.
Tip: Always connect your SQL/Excel results back to a potential business insight, since Visa interviewers are testing for interpretation as well as syntax.
Two Technical Phone Screens
You’ll then progress to two technical interviews:
SQL Deep Dive: A 45–60 minute live-coding session (shared screen or interactive platform). You’ll be asked to solve real-world problems like segmenting users, identifying anomalies, or calculating KPIs with constraints. Follow-up questions may probe for edge cases or performance optimization.
Tip: Talk through your query-building logic out loud. Interviewers want to see how you structure problems, not just the final code.
Case + Applied Analytics: This round is part case study, part strategy. You might be given a scenario (e.g., “Visa launches a new rewards program—how would you measure impact?”) and expected to break down the metrics, propose data sources, and outline your analytical approach. Expect to discuss experimentation, causality, and data visualization strategy.
Tip: Anchor your case answer to Visa’s revenue levers (approval rates, transaction growth, fraud reduction) to show business alignment.
Onsite (or Virtual) Interview Loop
This is the most comprehensive round, usually including 3–4 back-to-back interviews:
Business Case Presentation: You may be asked to analyze a take-home dataset and present findings to a mixed technical/non-technical panel. Visa looks for clarity, structure, and storytelling.
Tip: Use a simple 5-slide flow (Problem → Drivers → Options → Recommendation → Impact) to keep your presentation crisp and strategic.
Stakeholder Simulation: Roleplay-style interview where you’re asked to interpret ambiguous requirements, balance competing priorities, or push back using data.
Tip: Show empathy for stakeholder concerns while keeping decisions grounded in data. Visa wants analysts who can influence without authority.
Behavioral Interview: Using STAR format, discuss past projects, conflict resolution, stakeholder engagement, and how you’ve translated analytics into business impact.
Tip: Prepare 3–4 STAR stories where you drove measurable impact (e.g., % increase in approval rates or reduced reporting time).
Advanced SQL or Coding Round: A final hands-on session testing your ability to manipulate messy data, use window functions, or derive actionable metrics from complex schemas.
Tip: Don’t just return the query. Explain how the metric you calculated could be used by Visa’s product or business teams.
Hiring Committee & Offer
Once all interviews are complete, your panelists submit feedback for a Hiring Committee review, which usually happens within 24 hours. The HC evaluates technical performance, cultural fit, and communication strength. If approved, a VP may give the final sign-off, and the recruiter will extend an offer—often including a base salary, bonus, equity (for select roles), and relocation support if applicable.
Behind the Scenes
Visa’s hiring process moves quickly, with feedback often shared in under 24 hours after your onsite. Final decisions typically go through a hiring committee review, where senior product leaders and a VP give the final sign-off.
Difference by Level
Visa adjusts the interview process by seniority. Associate and mid-level analysts are mainly tested on SQL, metrics, and stakeholder alignment to ensure they can deliver hands-on analysis and support product teams right away. Senior analysts, however, face an extra business-strategy round designed to evaluate whether they can think beyond queries and influence long-term priorities. This stage tests how candidates assess market opportunities, weigh trade-offs, and connect insights to Visa’s growth levers like cross-border payments, fraud reduction, and merchant adoption. To prepare, senior candidates should practice prioritization frameworks, market sizing, and align their recommendations with Visa’s recent launches and strategic goals.
Now that you know the structure, let’s break down the common Visa Data Analyst interview questions you’ll likely encounter.
What Questions Are Asked in a Visa Data Analyst Interview?
SQL/Technical Questions
Visa’s SQL and technical interview questions usually test your ability to work with large, transaction-level datasets under time pressure. Expect medium-to-advanced difficulty queries involving grouping, filtering, joins, and subqueries. You can practice these directly on the Interview Query dashboard, where each question includes step-by-step solutions and discussion threads to compare approaches.
1 . Summarize SQL queries to count total transactions by category
Use GROUP BY and COUNT(*) to break down transactions by category. This may also involve filtering based on date or transaction status. It’s important to clearly alias fields and avoid miscounting nulls or duplicates. This pattern is common in Visa data analyst interview questions when analyzing card activity across markets.
Tip: Watch for nulls or duplicates that can inflate counts.
2 . Identify users who placed fewer than 3 orders in total
Use GROUP BY clause to filter for low-engagement users. You may need to union this to a user dimension table to return user names or emails. Be careful with edge cases like duplicate order IDs. This type of analysis is essential when examining dormant user behavior at Visa.
Tip: Validate that order IDs aren’t duplicated.
3 . Create a subquery for the top 3 ads by popularity and join with their size data
Use a CTE or subquery to rank ads, then join on metadata like size or format. Pay close attention to join conditions and indexing, especially for large tables. Explain how you’d validate whether the join is causing a data explosion. Visa analysts often analyze large marketing datasets where join efficiency matters.
Tip: Check join conditions to avoid row explosion.
4 . Write a SQL query to calculate the approval-rate trend over time
Use GROUP BY on time intervals (e.g., weeks or months) and calculate the ratio of approved transactions. COUNT(CASE WHEN approved = TRUE THEN 1 END) is helpful here. Visualizing this trend can surface seasonality or policy impact. This query type is frequently encountered in visa data analyst interview questions focused on operational efficiency.
Tip: Use DATE_TRUNC for clean time-bucketing.
5 . Write a window-function query to calculate customer churn over the last 3 months
Use LAG() or ROW_NUMBER() to compare current and prior period activity. You’ll likely define churn as inactivity following a transaction window. This involves segmenting user behavior and checking continuity. Visa analysts rely on this logic to flag drop-off in card usage or app engagement.
Tip: Define churn consistently, e.g., “no transactions in 90 days.”
- Query to calculate approval-rate trend (use keyword once in first sentence).
- Window-function churn analysis.
Metrics & Case-Study Questions
Visa Data Analysts are often tasked with diagnosing unexpected KPI movements and proposing metrics for new features. These problems assess your ability to define success, set up dashboards, and detect causal patterns from complex systems.
6 . Determine if the optional location-sharing feature increased conversations
Use pre/post analysis or difference-in-differences if randomized rollout is not feasible. Control for seasonality and user-level heterogeneity. Be clear about assumptions and metrics of success. Visa often introduces features that affect consumer behavior across geographies.
Tip: Always define the counterfactual clearly—what would conversations have looked like without the feature?
7 . Determine if bucket assignments in an A/B test were randomly distributed
Run a chi-square test or t-test across key covariates like country, platform, and transaction value. This checks for implementation flaws that could bias your results. Explain how you’d escalate if randomness fails. It’s vital in global Visa A/B tests where population skew can affect decisions.
Tip: Present results visually with distributions or summary tables to make imbalances easy to spot.
8 . Analyze the performance of a new LinkedIn feature to improve recruiting leads
Break the funnel into profile views → job clicks → applications → hires. Define success and attribution windows. Recommend actionable insights, not just metrics. Visa analysts need to report clearly on B2B feature success across partners.
Tip: Don’t stop at describing conversion rates. Recommend where in the funnel Visa should invest resources to improve outcomes.
9 . Build a KPI set for a new Visa Direct feature launch
Begin with goals: is it engagement, conversion, retention, or revenue? Propose primary metrics (e.g., usage rate, transaction volume) and secondary ones (e.g., repeat usage, complaint rate). Explain how you’d instrument and track those KPIs over time. Visa cares deeply about ensuring feature adoption aligns with business impact.
Tip: Anchor every KPI back to Visa’s revenue levers, like payment volume growth or reduced chargeback costs.
10 . Diagnose a 5% drop in cross-border revenue
Start by segmenting the drop by region, customer type, and transaction type to isolate the impact. Check for external factors (e.g., FX rate changes, regulatory updates) and internal shifts like pricing, product outages, or partner deactivations. Propose a dashboard setup to monitor trends in real time. Visa relies heavily on analysts to flag early warning signs in global payment flows.
Tip: Walk interviewers through your investigative order of operations to show structured problem solving, e.g., start broad then zoom in.
- Build KPI set for new Visa Direct feature.
- Diagnose a 5 % drop in cross-border revenue.
Behavioral & Stakeholder Questions
Visa analysts must collaborate across engineering, product, and business—often without direct authority. These questions evaluate your ability to communicate insights and drive alignment with diverse stakeholders.
11 . Tell me about a time you influenced a product decision without formal authority
Use the STAR method to describe how you aligned with product managers or engineers through data insights. Focus on how you framed the problem in business terms and gained buy-in. Include visuals, prototypes, or data storytelling if relevant. Visa values analysts who serve as trusted advisors across teams. A strong STAR answer might show how you reframed a problem in business terms, built a dashboard to illustrate variance in approval rates, and persuaded product managers to prioritize fraud fixes, leading to measurable improvement.
12 . Describe a situation where your recommendation was challenged—how did you respond?
Show how you used data, active listening, and iterative testing to rebuild trust. Be honest about what you learned and how you communicated uncertainty. Include any follow-up validation you did. At Visa, product decisions often involve multiple rounds of stakeholder alignment. For instance, if your churn model was questioned, you could show how you validated it with a new cohort analysis and re-won stakeholder confidence.
13 . Tell me about a time when your analysis changed how a team prioritized work
Walk through the analysis, how you uncovered a blind spot, and how the team shifted course. Emphasize clarity of communication and business impact. This demonstrates leadership through insight—essential for an analyst in a matrixed organization like Visa. Here, you could describe uncovering revenue leakage due to merchant onboarding delays, presenting your findings to leadership, and helping reprioritize engineering resources to cut cycle times.
14 . Give an example of when you simplified a technical concept for a non-technical stakeholder
Break down the concept and describe your approach: analogies, visual aids, or business framing. Share the outcome and how it changed the decision or understanding. Visa data analysts must bridge the gap between data and strategy. A strong response might describe how you explained Visa’s complex authorization and settlement flow using a “relay race” analogy for the marketing team, which helped them understand its link to approval rates.
15 . Talk about a time you collaborated across departments to launch a new initiative
Highlight how you managed competing priorities, shared goals, and timelines. Describe how you communicated progress and integrated feedback. This tests your cross-functional influence—critical at Visa, where analysts work across regional and functional lines. A good story could be how you coordinated across product, compliance, and regional teams to launch tokenization ahead of schedule, building trust and credibility.
- STAR story: influencing product without formal authority.
How to Prepare for a Data Analyst Role at Visa
To succeed in the Visa data analyst interview, you’ll need more than SQL syntax. You’ll need business fluency, clean storytelling, and comfort under pressure. Visa’s process tests how well you connect data to decisions, particularly in high-stakes, real-time scenarios like fraud monitoring, spend analytics, and product launches. Whether you’re prepping for a stakeholder simulation or an Excel challenge, your goal should be clarity, accuracy, and strategic framing.
If you’re targeting a Data Analyst Visa opportunity, follow this focused prep plan to stand out.
Review Visa’s payments data schema & PCI rules
Get comfortable with how Visa structures transaction data—common fields like MCC (merchant category code), issuer/merchant IDs, and tokenized PANs often drive analysis. Knowing these lets you frame sharper case answers, for example segmenting approval rates by MCC when diagnosing a drop, or using tokenized card IDs to model retention without breaching PCI rules. In stakeholder interviews, you can also show awareness of compliance by suggesting aggregated reporting when raw identifiers aren’t accessible, signaling both technical fluency and business sensitivity.
Drill LeetCode-style SQL sets daily
Focus on joins, subqueries, window functions (RANK(), NTILE(), LAG()), and CTEs. Simulate questions that involve tracking user journeys, segmenting behavior, or summarizing trends across time.
Practice 15-min slide decks for case presentations
When preparing mock decks, think in terms of a structured data analysis report. Start with a clear problem statement (why this case matters), then outline your hypotheses and approach (frameworks like MECE or funnel analysis work well). Next, walk through data exploration and methodology (SQL queries, segmentation, or experiment design) before presenting findings supported by visuals. Close with business implications, trade-offs, and recommendations that align with Visa’s core metrics such as transaction volume, approval rate, or spend per card. Keeping the story crisp and business-tied shows interviewers that you can translate analysis into actionable product decisions.
Build STAR stories around data-driven wins
Have 4–5 strong examples where your analysis led to product changes, operational improvements, or measurable growth. Frame them using the Situation–Task–Action–Result format to keep responses crisp.
Do peer mock interviews; gather feedback on clarity
One of the best ways to prepare for the Visa data analyst interview is to simulate the pressure and structure of the actual process. Practicing alone helps you drill SQL queries and frameworks, but peer or guided mock interviews force you to think on your feet, explain your reasoning clearly, and respond to follow-up challenges, exactly what you’ll face in a live setting. The real value comes from feedback: peers can point out where your explanation was confusing, too technical, or lacked a clear business takeaway. Over time, you’ll develop sharper, more concise communication that resonates with both technical and non-technical interviewers.
You can practice with like-minded professionals and take guidance from career coaches with the help of the Interview Query mock interview. These sessions replicate Visa’s SQL, case, and behavioral rounds, helping you refine both your technical accuracy and storytelling under time constraints.
FAQs
What Is the Average Salary for a Visa Data Analyst?
Average Base Salary
Visa Data Analyst salaries in the U.S. typically fall in the $91K–$134K range for total pay (base salary plus bonuses)
Here’s a clearer breakdown:
- Overall U.S. total compensation: $91K–$134K, with an average base salary of about $104K and $7K in additional pay. (Glassdoor)
- Major hubs (e.g., Bay Area, Los Angeles): Total compensation often exceeds $112K, reflecting higher cost-of-living and market premiums. Indeed reports typical analyst packages in San Francisco around $118K–$166K
- Entry-level or lower-cost markets: Salaries tend to fall toward the lower end of the range, closer to $90K, especially where the cost of living is lower. (Glassdoor)
How Many Rounds Are There in the Visa Data Analyst Interview?
The Visa Data Analyst interview typically follows a five-step process: an initial recruiter chat, a SQL/Excel online assessment, two technical phone screens (one focused on SQL, the other on case studies), an on-site or virtual interview with multiple rounds, and finally, a hiring committee review. While the exact format can vary slightly by role level, the structure is designed to test both technical fluency and business judgment. Candidates should be ready to shift between writing efficient queries, diagnosing KPI movements, and communicating insights to diverse stakeholders.
Where Can I Find Visa Consulting & Analytics Interview Info?
See the full Visa Interview Questions & Process guide for additional insight!
Is a Visa company interview hard?
Yes, Visa interviews are considered moderately difficult compared to other fintech firms. The challenge lies in the breadth of skills tested: SQL and data analysis, product and metrics cases, and stakeholder management scenarios. Candidates who practice SQL queries, build STAR stories, and study Visa’s payments ecosystem typically find the interview very manageable.
Why do you want to work at Visa Inc.?
A strong answer ties your motivation to Visa’s global scale and impact. You might mention wanting to analyze data that powers billions of transactions, contribute to innovations like Visa Direct, or grow within a company known for its cross-functional mobility. Avoid generic answers about liking “fintech” and instead connect your goals to Visa’s mission of enabling secure, seamless payments worldwide.
How do I crack the Visa data analyst interview?
To succeed, combine technical prep with communication practice. Drill SQL and metrics problems, review Visa’s revenue model, and prepare STAR stories that highlight business impact. Mock interviews are especially helpful for refining how you explain your logic and handle follow-ups. You can check out Interview Query mock interviews for real-world practice.
What is the data analyst career trajectory at Visa?
Data analysts at Visa often start in regional or product-focused teams, supporting metrics and reporting. Within 2–3 years, strong performers can transition into senior analyst roles, product analytics, or Visa Consulting & Analytics (VCA). Long-term, analysts move into manager or product management tracks, leveraging Visa’s global scope and emphasis on cross-functional development.
What mistakes should I avoid during a data analyst interview?
The most common mistakes are writing inefficient or incorrect SQL, failing to connect metrics back to Visa’s business model, and giving generic behavioral answers. Avoid overcomplicating queries, skipping edge cases like nulls or duplicates, or framing STAR stories without measurable outcomes. Another pitfall is not asking clarifying questions in case studies. Visa expects structured problem-solvers, not guesswork.
Conclusion
Succeeding in the Visa data analyst interview means proving you can do more than write queries. You need to structure problems, tell clear stories with data, and influence decisions at scale. Early, focused prep makes a huge difference.
Start early by drilling with the Interview Query SQL practice set to build fluency in the exact kinds of queries Visa asks. Then expand your prep with the Visa Data Scientist and Visa Product Manager guides for cross-role insight.
Finally, put your skills to the test by booking a data analyst mock interview. You’ll get live feedback from experts on your SQL, case reasoning, and communication under pressure, which is the closest practice to the real Visa interview loop.
