Stripe Machine Learning Engineer Interview Guide (2025) – Questions & Prep Tips
Introduction
The Stripe machine learning engineer role is one of the most sought-after technical paths at Stripe, offering the opportunity to build intelligent systems that directly impact global commerce. Whether you are working on fraud prevention, credit underwriting, or anomaly detection, the work you do as an MLE drives billions of dollars in secure transactions.
To get there, however, candidates must navigate the rigorous Stripe machine learning engineer interview process. This guide is your complete roadmap to preparing for the Stripe machine learning engineer interview. Inside, you’ll find a detailed breakdown of every stage of the process—from recruiter screen to final loop—along with sample technical, system design, and behavioral questions drawn from real candidate experiences. You’ll also get role-specific insights into what Stripe looks for, practical preparation strategies, and proven techniques to build confidence before your interview.
Whether you’re just starting your preparation or refining your final practice rounds, this guide will help you walk into your Stripe interviews with clarity, focus, and readiness to perform at your best.
Role overview & culture
Machine learning engineers at Stripe are expected to own models from end to end: scoping use cases, deploying real-time microservices, and continuously improving systems based on feedback and performance metrics. You will collaborate closely with product managers, data scientists, and infrastructure teams to ship production-grade ML features.
Stripe’s engineering culture is grounded in high standards and velocity. Core values like “Operate with rigor” and “Move with urgency” are not just slogans, they shape how teams prioritize experiments, design scalable ML systems, and evaluate long-term technical tradeoffs.
Why this role at Stripe?
Working as a machine learning engineer at Stripe means joining a company that treats AI and data as core product levers, not side experiments. Every decision you make, from designing model architectures to optimizing latency, directly shapes how millions of businesses move money safely online. You will work with cutting-edge infrastructure, massive real-time datasets, and tools like Ray and JAX to build scalable ML systems that power fraud detection, credit underwriting, and payments intelligence.
Beyond the technical challenge, the career trajectory at Stripe offers constant growth. Machine learning engineers often progress into staff, principal, or tech lead roles, driving entire product or infrastructure lines. Others transition into applied research, product management, or cross-functional leadership as they deepen their impact. Stripe’s culture of ownership and autonomy encourages you to explore new domains, mentor peers, and influence long-term technical direction.
This role combines technical depth, business impact, and leadership opportunity. For engineers passionate about applying machine learning to real-world financial systems, Stripe provides both the scale and the freedom to make a lasting contribution. To join the team, you will navigate the Stripe machine learning engineer interview process outlined below.
What is the interview process like for a machine learning engineer role at Stripe?
The Stripe machine learning engineer interview process is intentionally rigorous. It mirrors how Stripe builds products: with structure, clarity, and collaboration. Every stage assesses a different dimension of your readiness—from analytical depth and communication to technical craftsmanship and judgment. The process usually takes three to five weeks, depending on scheduling.
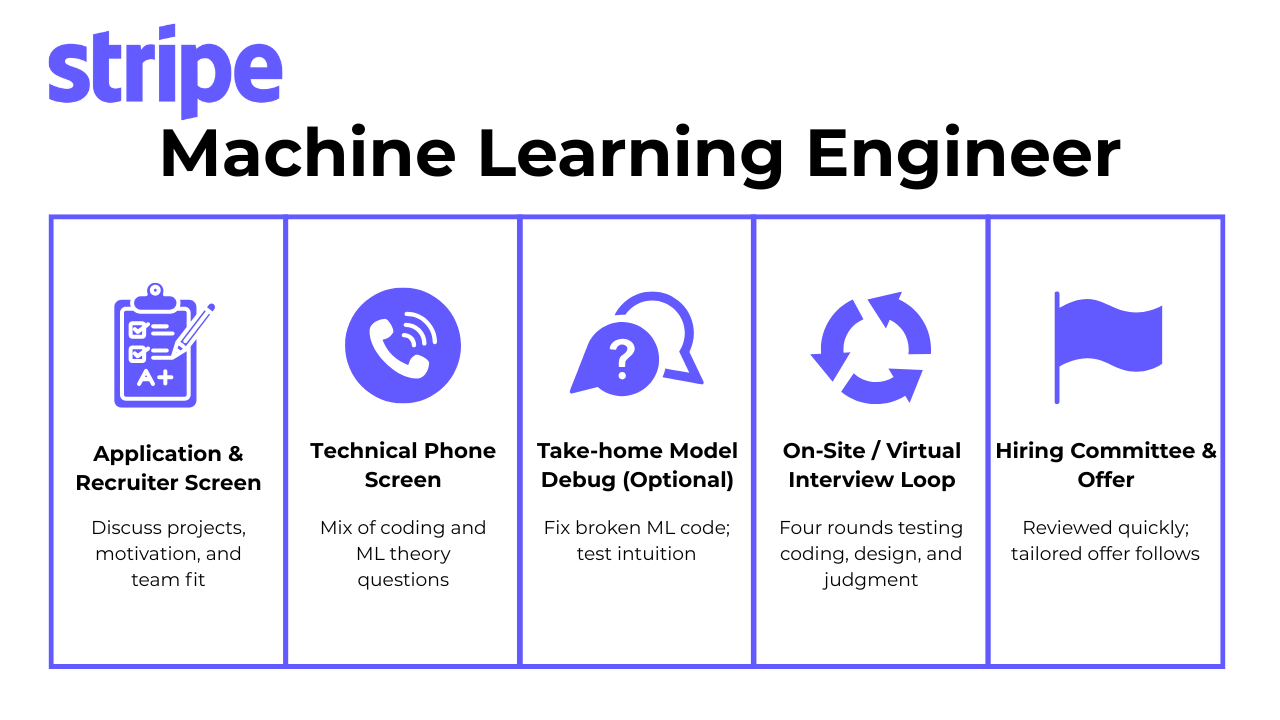
Application and recruiter screen
Your journey begins with a recruiter reviewing your resume and assessing how your experience aligns with Stripe’s engineering standards. They look for projects that show end-to-end ownership, such as building or deploying production ML systems that directly influenced business outcomes. During the 30 to 45-minute call, expect questions about your current work, long-term goals, and motivation for joining Stripe. Recruiters also want to hear how your values and career vision align with Stripe’s mission to grow the GDP of the internet.
Tip: Keep your answers outcome-oriented. Instead of saying, “I worked on a fraud model,” describe the measurable effect—“Our model reduced false positives by 20% and recovered $5 million in annual revenue.” This signals the kind of impact-driven thinking Stripe values.
Technical phone screen
This 45-minute session blends live coding with discussions around data structures, algorithms, and ML fundamentals. You might implement a Python function that manipulates transaction data or compute a metric efficiently under time constraints. Interviewers want to see how you reason, debug, and write code that is clean, readable, and safe for production use.
Tip: Talk through your reasoning as you code. Explain how you test your function, handle edge cases, and verify correctness. Stripe engineers care as much about your process as your final answer.
Take-home model debug (optional)
In this take-home round, you’ll tackle a short project that mirrors real Stripe engineering problems. You might debug a PyTorch model that has suddenly degraded in accuracy, analyze data drift in a payments dataset, or improve an imbalanced training pipeline. The goal is to see how you think in realistic conditions—reading existing code, identifying issues quickly, and documenting clean, verifiable fixes.
Example prompt:
A fraud detection model’s recall dropped sharply after a data refresh. Logs show no code changes, but the precision-recall curve has flattened. Diagnose the likely cause and outline a fix.
Quick approach:
- Inspect whether the training schema or feature definitions changed.
- Check for class imbalance or missing categorical mappings.
- Recompute distribution statistics and verify against historical data.
- Retrain on a smaller validated subset to confirm the root cause.
This exercise shows your ability to balance speed with correctness, a critical skill in a payments-scale environment.
Tip: Write your code and findings as if they were going straight into production. Include validation checks, notes on assumptions, and comments explaining your reasoning. Clean communication through code demonstrates maturity and reliability.
Struggling with take-home assignments? Get structured practice with Interview Query’s Take-Home Test Prep and learn how to ace real case studies. Practice take-home tests →
On-site or virtual final loop
The final loop consists of four structured interviews that test your technical strength, system design ability, product intuition, and culture fit. Each conversation is designed to simulate real collaboration inside Stripe.
Coding round
You’ll work through an algorithmic or debugging problem in Python, often touching ML-adjacent topics like data preprocessing or model evaluation. The interviewer is watching how you approach the problem, reason about trade-offs, and verify correctness.
Tip: Focus on clarity before optimization. Explain what you would test, how you’d monitor this code in production, and why your solution scales safely. Stripe values engineers who prioritize correctness and reliability over clever shortcuts.
ML system design round
This is one of the most critical rounds. You might be asked to design a real-time fraud detection service, a credit risk scoring pipeline, or an automated retraining system. Stripe wants to see that you can connect infrastructure decisions to measurable business impact.
Tip: Structure your response by walking through data flow, model lifecycle, and monitoring. Explicitly mention latency, retraining cadence, and data governance. When you justify design choices, tie them to Stripe’s goals of safety, speed, and reliability.
Want to practice real case studies with expert interviewers? Try Interview Query’s Mock Interviews for hands-on feedback and interview prep. Book a mock interview →
Product-sense and metrics round
Here, the focus shifts from systems to outcomes. You will be asked to reason about how ML drives value in Stripe’s products—how to measure success, interpret results, and decide when to ship. Scenarios often involve A/B testing, experiment design, or prioritizing model improvements that influence real revenue.
Tip: Start every answer with the user or business goal. Then identify measurable KPIs, trade-offs, and the metrics you’d track post-launch. Stripe favors candidates who think like product owners, not just model builders.
Values interview
This behavioral round evaluates how you collaborate, communicate, and learn. Interviewers look for humility, bias for action, and comfort with ambiguity. Expect situational questions about team conflicts, handling mistakes, or balancing speed with precision.
Tip: Frame each story using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). Highlight what you learned and how it improved your approach to teamwork or problem-solving. Stripe values engineers who combine rigor with reflection.
Hiring committee and offer
After the on-site rounds, all feedback is compiled into a detailed packet reviewed by Stripe’s hiring committee. The committee includes a bar raiser, an independent reviewer who ensures consistency and fairness in leveling decisions across teams. They look for consistent strength across rounds—technical depth, communication skill, and long-term potential.
Once approved, your recruiter will reach out within one to three business days with an offer. Stripe’s compensation philosophy emphasizes fairness and scope-based pay. Packages typically include a base salary, performance bonus, and equity refreshers that vest over time.
Tip: When negotiating, focus on scope and value rather than pure numbers. Explain how your experience aligns with the level of responsibility you expect to take on. It also helps to research market data for similar roles and ask thoughtful questions about promotion timelines and equity refresh cycles. Stripe appreciates candidates who negotiate with professionalism and transparency.
What Questions Are Asked in a Stripe Machine Learning Engineer Interview?
Stripe’s interview questions are designed to simulate real engineering environments. While technical correctness matters, your ability to communicate tradeoffs, optimize under constraints, and think like a product builder is just as important.
Coding/Technical Questions
In the Stripe machine learning interview, candidates often encounter coding tasks that blur the line between ML and systems thinking. Stripe MLEs are expected to write performant Python and be comfortable working close to data pipelines.
These problems test your grasp of algorithms, memory efficiency, and ML-adjacent tooling which are core to succeeding in Stripe ML roles.
-
Emphasize grouping by city, ordering by date, method choice (linear vs. time), boundary handling, and validation (no leakage across cities). Note pitfalls like irregular intervals and long gaps.
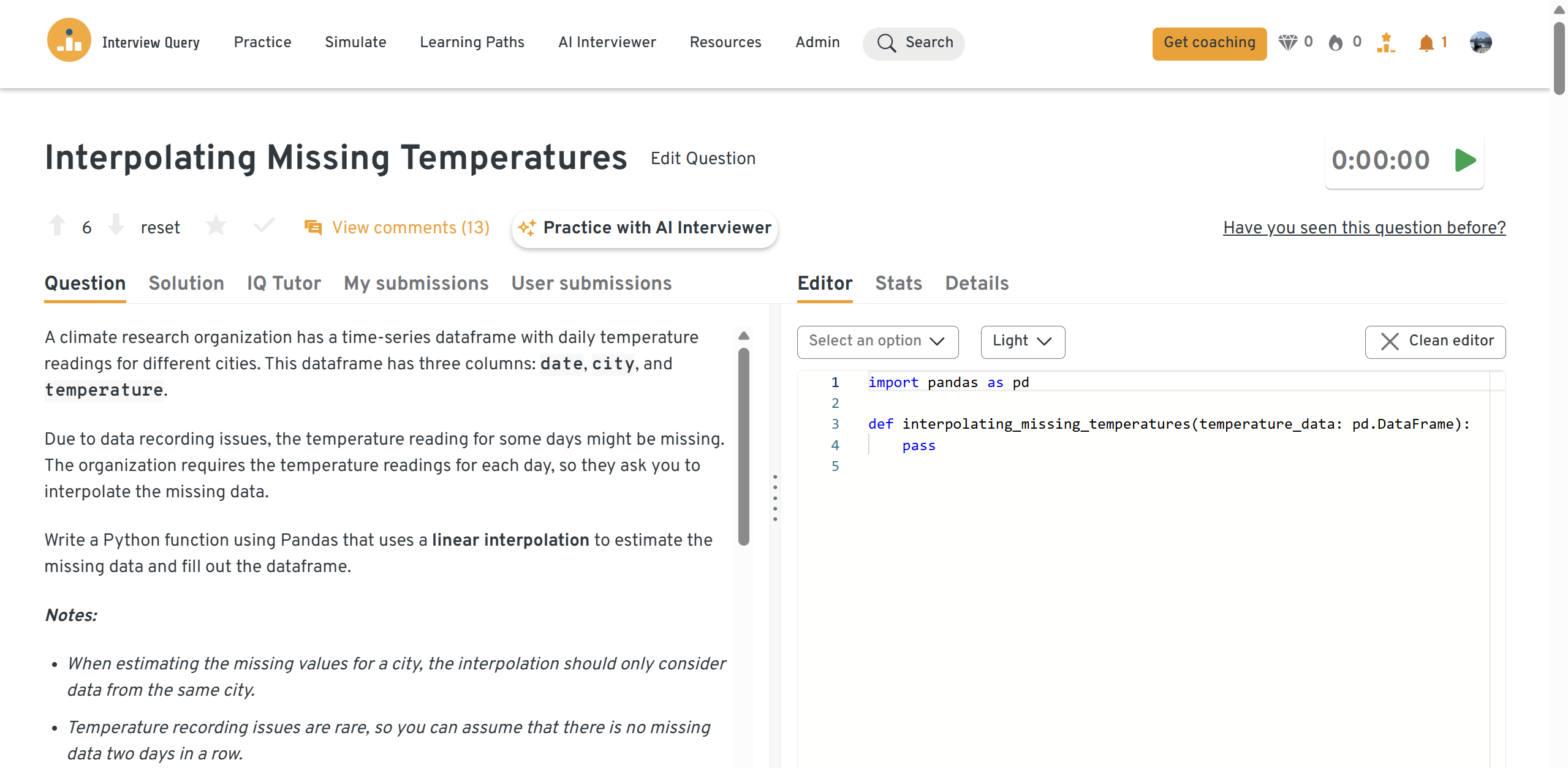
Tip: Explore the full solution inside Interview Query’s Dashboard
-
Describe grouping by department, computing the >100K share, filtering on headcount, ranking, and ties. Mention window functions vs. subqueries and how you’d productionize the metric definition.
-
Explain selecting the latest row per employee (by max effective_date or max id), handling duplicates, and ensuring uniqueness keys. Call out safeguards and backfill strategies for audit.
-
Talk date truncation, distinct user counts vs. active users, NULL handling, and ordering. Note index usage on timestamp columns and sanity checks with control totals.
-
Cover grouping by query, enforcing an “all ratings < 3” condition, dividing by total queries, and precise rounding. Mention edge cases (queries with one result, missing ratings) and performance on large logs.
Test your skills with real-world analytics challenges from top companies on Interview Query. Great for sharpening your problem-solving before interviews. Start solving challenges →
ML System / Product Design Questions
This portion of the Stripe Machine Learning Engineer interview evaluates how you design, deploy, and monitor ML systems at scale.
Strong candidates demonstrate architectural foresight and business-awareness and not just ML optimization.
-
Explain ingestion (webhooks vs. batch pulls), idempotency, schema design (payments, charges, refunds, disputes), late-arriving data, PII handling, and reconciliation. Cover CDC, partitioning, deduping, SLAs, lineage, and data quality checks that protect downstream metrics.
-
Walk through data splits, tree construction, stopping criteria, and voting then discuss complexity, memory, and how you’d validate correctness (unit tests, invariants) without scikit-learn. Call out pitfalls like class imbalance and deterministic permutations.
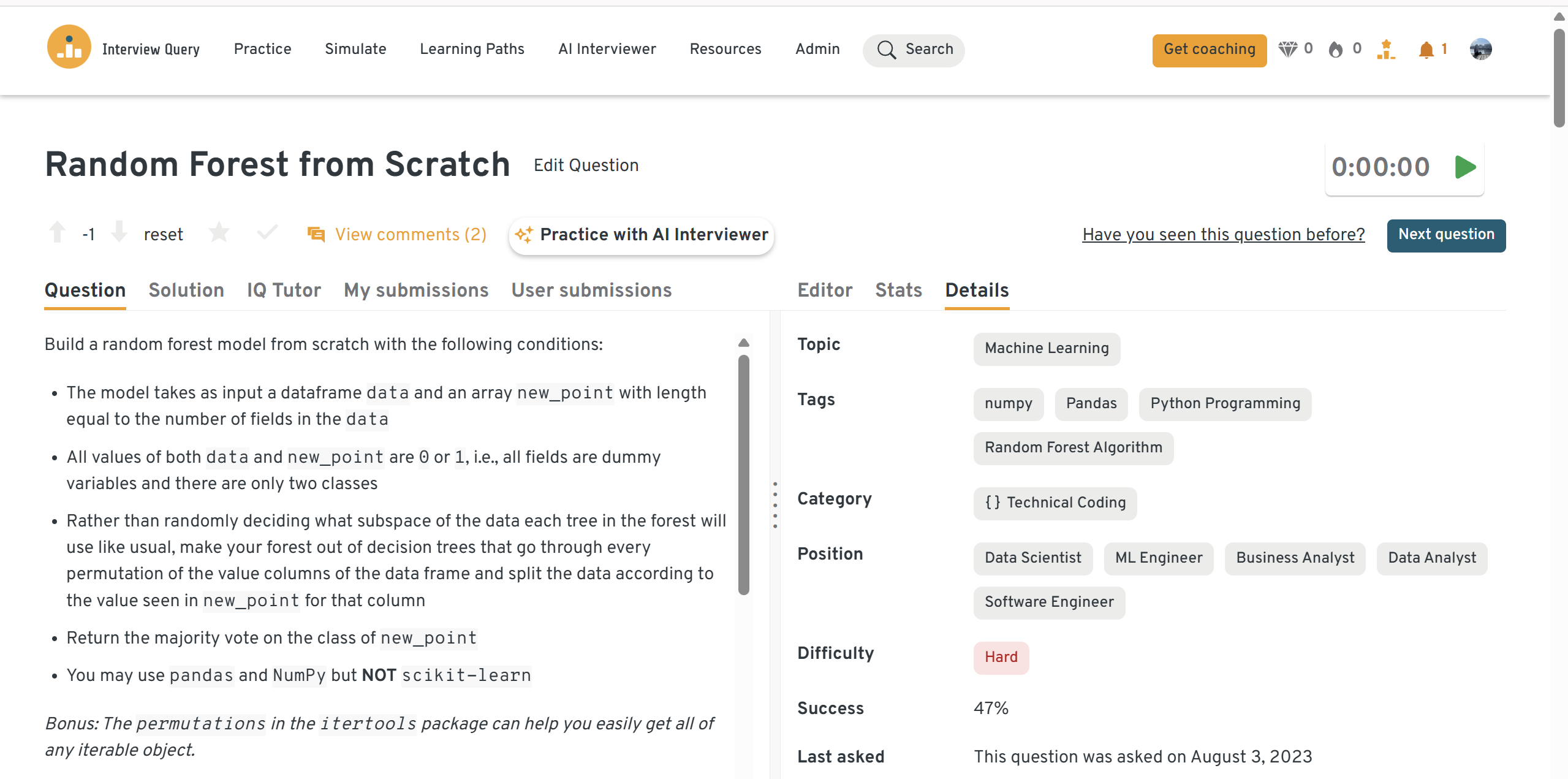
-
Cover feature engineering (calendar, weather, events), model choices (gradient boosted trees vs. sequence models), batch + streaming retraining, feature store, backfills, and deployment (batch forecasts + real-time adjustments). Include monitoring (drift, MAE/MAPE), SLAs, and rollback.
How would you design the YouTube video recommendation system, and what factors would you prioritize?
Discuss candidate generation vs. ranking, user/content embeddings, freshness/diversity, feedback loops, cold start, fairness/safety constraints, and evaluation (offline AUC/NDCG + online CTR/retention). Mention guardrails (caps, fatigue) and latency budgets.
-
Outline multimodal models (text, image, video), labeling strategy, hierarchical taxonomies, precision/recall trade-offs by severity, human-in-the-loop review, explainability, regional policies, and auditability (versioned models, policy configs, retention).
Behavioral/Culture Fit Questions
The behavioral rounds probe how you operate in Stripe’s fast-paced environment. Interviewers want to see whether you can own ambiguity, learn quickly, and collaborate with minimal oversight.
These questions gauge your adaptability, ownership, and technical humility as a Stripe Machine Learning Engineer.
Describe a data project you worked on. What were some of the challenges you faced?
Anchor the story to an ML-in-production effort (e.g., fraud scoring, dispute prediction, or authorization lift). Lay out the objective, success metrics, and constraints like PCI/PII handling, strict latency budgets, and data quality SLAs. Walk through issues such as label leakage, sampling bias, data drift, flaky upstream events, or backfill gaps, and how you diagnosed and fixed them with robust validation, feature stores, idempotent pipelines, and monitoring/alerts. Close with measurable impact (e.g., auth-rate lift, reduced chargebacks) and what you’d do differently.
Sample answer: I led the rollout of a fraud detection model that analyzed real-time card transactions. One challenge was severe data drift from a new merchant segment, which caused false positives. I built a drift monitor on top features and set automatic alerts when the PSI exceeded 0.2. We retrained the model with domain-specific sampling and restored precision to 95%. The experience reinforced the importance of continuous validation in live systems.
What are some effective ways to make data more accessible to non-technical people?
Frame accessibility as product thinking: define the core decisions your GTM, Ops, or Risk partners need to make, then design the smallest set of trustworthy artifacts to support those decisions. Mention curated dashboards with plain-language metric definitions, a semantic layer/metrics catalog, clear data contracts, runbooks, and scheduled narratives (“data newsletters”). For ML, highlight interpretable outputs (reason codes, calibrated scores, SHAP summaries), threshold playbooks, and guardrails so teams can self-serve without misusing signals.
Sample answer: At a previous fintech, Ops teams struggled to interpret our risk model’s confidence scores. I introduced SHAP summaries and generated human-readable reason codes for each decision, embedded directly in their dashboards. This transparency helped non-technical teams identify false positives faster, cutting review time by 30%. It showed me that explainability is not just a compliance requirement — it’s a usability feature.
-
Select strengths that map to Stripe MLE work: taking models to prod, measurement rigor, and reliability mindset. For weaknesses, choose a real growth edge that won’t undermine the role (e.g., over-indexing on perfect offline metrics, under-investing in internal UX early on). Show your mitigation plan: earlier stakeholder reviews, telemetry-first rollouts, writing ADRs/RFCs to align faster, or pairing with design/analytics. Keep it specific and outcomes-focused.
Sample answer: My manager would say I’m methodical and reliable when shipping ML systems — I care deeply about metrics integrity. My biggest area of growth is avoiding over-optimization of offline AUC before validating business impact. To address it, I now integrate live A/B feedback early and partner with product to define success beyond model metrics. It’s made my launches faster and more aligned with user outcomes.
-
Use a cross-functional example (e.g., Risk/Compliance/SRE disagreement on model rollout risk). Show how you translated model behavior into business risk, proposed a phased plan (shadow → canary → ramp), and set decision gates with clear metrics (precision at cost, false-positive budget, latency SLOs). Emphasize listening, shared vocabulary (glossary), written artifacts (one-pager, RFC), and how you sustained alignment via weekly check-ins and dashboards.
Sample answer: When rolling out a payment-authorization model, compliance was worried about bias in merchant scoring. We were speaking past each other — they used legal definitions while I referenced model fairness metrics. I wrote a short explainer aligning both perspectives and shared calibration plots for each segment. That document became the single source of truth and helped us move from debate to iteration. The model later passed external audit with no flags.
-
Tie your motivation to Stripe’s mission (“increase the GDP of the internet”), developer-first culture, and the leverage of ML on core money flows (auth rates, fraud, disputes, revenue recovery). Connect your experience with low-latency inference, data quality at scale, and model governance to Stripe’s bar for reliability and compliance. Outline what you’ll bring (building measurable, safe ML systems) and what you want to learn (global payments nuances, privacy-preserving ML).
Sample answer: Stripe’s mission resonates because I’ve spent my career improving trust and reliability in digital payments. At my current role, I built an anomaly detection model that reduced dispute rates by 18%, directly improving user trust. I want to bring that rigor to Stripe, where ML directly powers the global economy. I’m especially drawn to Stripe’s writing-driven, engineering-first culture — it’s how I already work best.
A production model caused a spike in false positives and blocked legitimate payments for several minutes. How did you respond, and what did you learn?
Walk through incident response: contain (rollback/disable new features, fall back to safe defaults), communicate (war room, status page for stakeholders), and diagnose (feature drift, broken upstream event, bad threshold). Explain post-incident actions: add canaries and shadow evals, stricter input validation, per-segment thresholds, real-time drift monitors, and a blameless postmortem with owners and deadlines.
Sample answer: We once had a regression in our fraud model that caused legitimate transactions to fail. I immediately triggered a rollback, communicated with support teams, and started tracing upstream features. The root cause was a schema mismatch from a partner API. We added validation checks and a shadow pipeline to catch this in the future. It reinforced the need for redundancy between model logic and integration monitoring.
Describe a time you had to persuade a partner team to implement a data or API change needed for model performance. How did you make the case?
Show how you quantified business impact (e.g., expected auth-rate gain or fraud savings), proposed a minimal integration path (backward-compatible schema, data contract), and reduced risk with a small pilot and clear success criteria. Highlight stakeholder mapping, addressing their costs (perf, security, maintenance), and securing alignment via an RFC, timelines, and shared dashboards, then share the outcome and lessons in cross-org collaboration.
Sample answer: Our model performance depended on merchant-level transaction metadata that the API didn’t expose. I quantified the benefit — a projected 4% lift in fraud catch rate — and wrote an RFC outlining the change with a low-risk pilot. The partner team agreed after seeing clear ROI and minimal maintenance impact. That collaboration led to a long-term data contract, improving both teams’ reliability and trust.
How to prepare for a machine learning engineer role at Stripe
Preparing for the Stripe machine learning engineer interview means more than brushing up on PyTorch. You will need to balance deep ML understanding with product intuition and clear communication. The steps below focus on the skills and habits that map directly to Stripe’s bar.
Master data-parallel training and serving
For candidates interested in Stripe ML infrastructure, mastering distributed training is essential. Practice debugging performance bottlenecks in PyTorch Distributed, and learn how to profile memory and GPU utilization in a live environment. Expect questions that explore the nuances of multi-GPU model serving.
Tip: Rehearse a 90-second explanation of how you would diagnose slow throughput in a multi-GPU job, including the exact profiling tools you would run and the order you would run them.
Need 1:1 guidance on your interview strategy? Interview Query’s Coaching Program pairs you with mentors to refine your prep and build confidence. Explore coaching options →
Drill ML system-design patterns
System design questions are central to the Stripe machine learning engineer interview. Be ready to architect solutions that consider latency, throughput, and failure modes. Think through tradeoffs around model freshness, cost of retraining, and stream versus batch updates in real Stripe-like use cases.
Tip: Structure your designs as “ingest → validate → store → feature compute → train → serve → monitor → retrain,” and keep one sentence ready for each box explaining failure handling.
Deep-dive on metrics and A/B
Many interviews touch on experimentation design. Learn to quantify false-positive costs in fraud detection or measure lift across segments in credit modeling. Go beyond standard A/B tests and be ready to discuss quasi-experimental approaches when clean randomization is not possible.
Tip: Prepare one worked example where you choose precision/recall and thresholds from a cost matrix, then explain how you would monitor post-launch drift and recalibrate.
Build story-driven STAR examples
Behavioral questions will probe how you take ownership, move with urgency, and collaborate across functions. Frame answers using STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Result) and align outcomes with Stripe’s principles. Highlight how your work as a Stripe machine learning engineer would drive real impact.
Tip: end every story with a “Result plus learning” sentence so you show reflection, not just delivery.
Mock interviews with peers
Simulate real pressure. Practice talking through ML system designs in under ten minutes. Get feedback on clarity, conciseness, and tradeoff navigation. A well-run mock interview can expose blind spots before Stripe does.
Tip: Record yourself and check for filler, missing assumptions, and whether your metric definitions are precise enough to implement effectively.
Want to practice real case studies with expert interviewers? Try Interview Query’s Mock Interviews for hands-on feedback and interview prep. Book a mock interview →
Know Stripe-specific domains and constraints
Stripe’s highest-leverage MLE work sits in fraud, credit risk, disputes, and payments authorization. That means strict latency budgets, financial correctness, and careful PII handling.
Tip: Study how fraud systems trade recall against false positives, and prepare to explain how you would cap user friction while keeping chargeback rates within targets.
Practice low-latency serving strategies
Stripe optimizes for p95 and p99 latencies. Be ready to discuss caching, pre-computation, approximate methods, and graceful degradation when upstream features are delayed.
Tip: Be able to state a concrete budget (for example, “5–20 ms model inference”), how you would meet it, and what you would turn off first if you breach it.
Model monitoring and safe rollout
Production readiness matters. You should be comfortable with canary and shadow deployments, rollback triggers, calibration checks, and feature drift detection.
Tip: Memorize three alerts you would always ship with a fraud model: calibration shift, segment-level precision drop, and upstream feature staleness.
Data quality and contracts
Stripe values reliable data. Expect to discuss schema evolution, idempotency, late-arriving events, and validation at the edges.
Tip: Describe the exact checks you would add at ingest (row counts, uniqueness, null thresholds) and which ones would block the pipeline versus page on call.
Evaluation and thresholding by segment
Global metrics can hide risk. Stripe teams often tune thresholds per region, merchant tier, or device class.
Tip: Bring one example where segment-specific thresholds increased revenue or reduced friction compared to a single global cutoff.
Production Python hygiene
Readable, testable code is part of the bar. Think typing, unit tests, config management, structured logging, and dependency pinning.
Tip: Outline the tests you would write for any coding problem (happy path, edge cases, resilience to malformed inputs) before you start typing.
Design docs and RFCs
Stripe is a writing culture. Short, clear documents help drive alignment and speed.
Tip: Practice a one-page template with sections for context, decision, alternatives considered, risks, and rollout plan; aim to write it in fifteen minutes after a mock prompt.
Security and privacy basics
Handling PII and financial data requires care. Be ready to discuss encryption at rest and in transit, access control, and data minimization.
Tip: Have a ready-made statement on how you would redact, hash, or tokenize sensitive features while preserving model utility.
Notebook-to-production handoff
Your work should move from exploration to a service. That means feature reproducibility, dependency control, and parity between offline and online code.
Tip: Explain how you would extract reusable feature code into a library or feature store and validate that online features match offline training features.
Salary Summary
What is the average salary for a machine learning engineer at Stripe?
As of 2025, Stripe Machine Learning Engineers in the United States earn exceptionally high compensation, reflecting the company’s focus on AI-driven infrastructure. The median total compensation across levels is about US$405,000 annually or US$33,800 per month. (Levels.fyi)
At the L2 level, total pay averages US$29,000 per month, composed of around US$16,400 in base salary, US$11,700 in stock, and a US$1,000 bonus.
At the L3 level, mid-level engineers typically earn about US$34,300 per month, including US$20,800 in base pay, US$11,200 in stock, and roughly US$2,300 in annualized bonus value.
By the L4 (Staff Engineer) level, monthly compensation climbs to approximately US$64,300, with US$23,900 in base salary, US$35,800 in stock, and US$4,500 in bonus.
At higher senior levels (L5–L7), total packages often exceed US$700,000 per year, primarily driven by large stock grants and long-term equity incentives.
Tip: Stripe rewards engineers who deliver impactful, scalable model deployments across payments, fraud prevention, and infrastructure optimization. Long-term value creation is key—the largest gains come from equity growth and technical leadership rather than short-term bonuses.
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
How long does the Stripe machine learning engineer interview process take?
Most candidates complete the interview loop within 3 to 5 weeks. Stripe moves quickly once you are in process, but scheduling flexibility can help you align rounds in a single week. Many successful applicants batch the technical screen and on-site loop to maintain momentum.
Do I need research-level publications?
No. Stripe prioritizes impact over academic prestige. While research experience is a bonus, the bar is practical application: robust experimentation, sharp model-debugging instincts, and good engineering hygiene. Case studies are valued more than conference citations.
Where can I practise Stripe-style ML design questions?
You can find targeted Stripe-style ML design problems on Interview Query’s ML question bank and simulate real sessions through mock interviews. These help sharpen your thought process and prepare you for system design under pressure.
Take the Next Step Toward Your Stripe MLE Offer
Cracking the Stripe machine learning engineer interview is not just about writing code, it is about demonstrating clarity, ownership, and deep technical intuition across every round. Success comes from combining rigorous fundamentals, systems fluency, and a mindset aligned with Stripe’s operating principles.
Whether you are just starting or actively prepping, leverage these resources to gain an edge:
Success story: See how Jerry Khong used Interview Query Premium to transition into an MLE role, turning prep into offer.


