Adobe Data Engineer Interview Guide: Process, Questions & Salary (2025)
Introduction
Preparing for an Adobe data engineer interview means showing you can design and scale pipelines that process billions of events, fast, reliably, and at scale. Beyond technical fluency in Python, SQL, and distributed systems, you’ll need to demonstrate how you collaborate with product, analytics, and ML teams to turn raw data into real business impact.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know: how Adobe structures its data engineer interviews, the types of technical and behavioral questions to expect, and the prep strategies that help candidates stand out. We’ll also cover coding and system design challenges, salary ranges, and negotiation tips. Whether you’re fresh out of school or bringing years of experience, this roadmap will help you prepare with clarity and confidence.
Role Overview & Culture
Working as a data engineer at Adobe means building the backbone that powers insights across products used by millions. Day to day, you’ll design and maintain large-scale data pipelines, ensure high data quality, and collaborate with product, analytics, and machine learning teams to transform raw data into actionable intelligence. Much of your work centers on Adobe’s Experience Platform (AEP) and Creative Cloud, where telemetry and user data fuel personalized experiences and predictive analytics at massive scale.
Adobe’s culture blends creativity with technical excellence. Engineers are encouraged to experiment, share ideas openly, and take ownership of end-to-end solutions. With a strong emphasis on continuous learning and innovation, you’ll find the autonomy to explore new tools and the support to make meaningful contributions from day one.
Why This Role at Adobe?
An Adobe data engineer role is about shaping how creative and marketing data becomes actionable at a global scale. Your work may enable real-time personalization in AEP, optimize performance across Creative Cloud applications, or streamline analytics for enterprise customers. Compensation is competitive, with U.S. data engineers typically earning $130K–$180K in total compensation, while senior engineers can exceed $200K with equity and performance bonuses.
What makes this role stand out is the growth trajectory. Many engineers at Adobe move into data science, ML engineering, or product-focused roles within two to three years, backed by mentorship and mobility programs. With petabyte-scale challenges, strong compensation, and clear pathways for advancement, this role offers both technical depth and long-term career impact.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Data Engineer Role at Adobe?
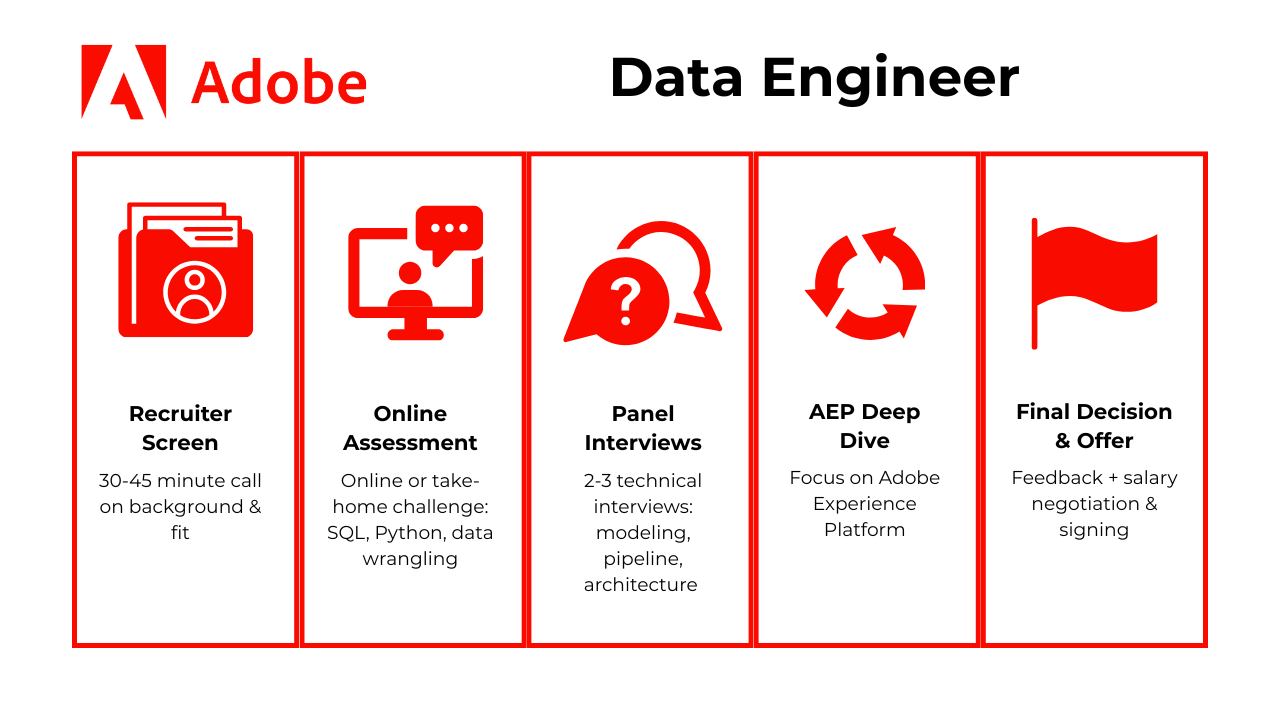
The Adobe data engineer interview process is designed to assess your technical depth, product intuition, and data infrastructure skills through several progressive rounds. While the exact steps may vary by team and location, most candidates follow this general sequence:
- Recruiter Screen
- Online Assessment (OA)
- Panel Interviews
- AEP Deep Dive
- Final Decision & Offer
Recruiter Screen
A recruiter will reach out for a 30–45-minute call to learn more about your background and overall fit for Adobe. They’ll ask about your resume highlights, past projects, and motivation for applying, while also giving you an overview of the interview process. This is your chance to make a strong first impression by tying your experience to Adobe’s data-driven culture and showing enthusiasm for the role.
Tip: Prepare a concise “elevator pitch” (2 minutes max) that covers your technical skills, impact from past projects, and why Adobe excites you.
Online Assessment (OA)
You may be given a timed online challenge or take-home assessment that focuses on SQL, Python, and data wrangling. Tasks often involve joining and aggregating large datasets, cleaning messy inputs, or writing efficient transformations. The objective isn’t just correctness. It’s how clean, readable, and optimized your solutions are, since these reflect day-to-day work as a data engineer.
Tip: Practice problems on platforms like Interview Query where you can test both coding accuracy and efficiency under time pressure.
Panel Interviews
This stage typically includes 2–3 back-to-back technical interviews with engineers and managers. You’ll be asked to solve live problems on data modeling, pipeline design, and distributed system architecture, while also walking through past projects in detail. Expect behavioral questions woven in to evaluate how you collaborate with product, analytics, and ML teams.
Tip: Use the STAR method when walking through past projects. Structure your answers so interviewers see both your technical depth and business impact.
AEP Deep Dive
For mid-level and senior candidates, one interview may focus on the Adobe Experience Platform (AEP). You’ll discuss real-time data ingestion, identity resolution, and customer journey orchestration at scale, often through a system design challenge. This round tests your ability to reason about data infrastructure trade-offs and align them with Adobe’s product needs.
Tip: Even if you haven’t worked directly with AEP, review streaming data concepts (Kafka, Spark, Flink) and think through how you’d design identity resolution or real-time pipelines.
Final Decision & Offer
After your interviews, the panel consolidates feedback and meets with the hiring manager or committee to make a final decision. Offers are typically extended within 3–7 business days, followed by background checks and onboarding details. This stage also gives you the opportunity to negotiate salary, equity, or signing bonuses.
Tip: Research Adobe’s compensation bands on Levels.fyi or Glassdoor, and be ready with specific numbers when negotiating. Candidates who prepare often secure stronger packages.
Behind the Scenes
Internal feedback loops at Adobe are fairly tight, with most candidates receiving updates within 3–5 days. Hiring decisions are made collaboratively by the panel and finalized by a hiring manager or small committee. For many teams, cultural alignment and communication are just as important as raw technical skill.
Differences by Level
Entry-level candidates (L1–L2) focus primarily on SQL, Python, and problem-solving, while senior candidates (L5 and above) are assessed for architectural thinking, mentorship, and leadership potential. Those applying for roles like senior data engineer or MTS 2 will likely face additional questions on stream processing, distributed systems, and team-scale decisions. The expectations increase not only in depth but in how you tie engineering efforts to business outcomes.
Now, let’s explore common asked questions in an Adobe data engineer interview.
What Questions Are Asked in an Adobe Data Engineer Interview?
Coding/Technical Questions
Below are sample Adobe Data Engineer interview questions that cover coding, SQL, and data pipeline challenges, including Adobe SQL interview questions and handling Adobe ETL workflows.
Select the top 3 departments with at least ten employees
This question focuses on SQL aggregations and filtering. You’ll need to group by department, count employees, and filter those with 10+ people using
HAVING, and then order by the employee count. Finally, useLIMITto get the top three results. This type of problem mirrors reporting or workforce distribution tasks commonly solved by data engineers.Tip: Always include edge cases, like departments with exactly 10 employees, and confirm whether “top” refers to count or another metric.
Calculate the first touch attribution channel per user
This is a classic example of Adobe SQL interview questions, as attribution models are central to Adobe’s analytics workflows. You’ll likely use a window function like
ROW_NUMBER()ordered by timestamp to find each user’s earliest channel. Alternatively, aMIN(timestamp)subquery joined back to the base table also works. Handle NULLs carefully and confirm how to treat ties.Tip: State explicitly how you’d validate results. For example, by checking if every user maps to exactly one channel in the output.
Select a random number from a stream with equal probability
This question evaluates your knowledge of reservoir sampling and efficient streaming algorithms. The key is to ensure every element has an equal chance of selection, even as the stream grows infinitely. Use O(1) memory to store just one candidate and update it with a
1/iprobability at the i-th element. This mirrors Adobe’s need for scalable solutions on continuous telemetry streams.Tip: Be ready to prove why the algorithm is uniform. Interviewers often test reasoning, not just code.
Format an array of words into lines of maximum width
This problem is a text formatting challenge often used to test algorithmic thinking. You’ll need to break words into lines no longer than a given width, distributing spaces evenly between words. Edge cases include words longer than the width or leftover spaces at the end. While less common in production, this type of question demonstrates your ability to reason through complex constraints.
Tip: When walking through your solution, explain your logic step by step rather than jumping straight to code. Clarity matters as much as correctness.
Find the integer removed from list X to form list Y
Here you’re given two lists where one is missing a single integer. Solutions include comparing sums (
sum(X) - sum(Y)), using a hash map to track counts, or sorting both lists and finding the mismatch. Aim for O(n) time with O(1) or O(n) space depending on your method. This question tests your debugging and data validation skills.Tip: Point out trade-offs: the summation method is fast but fails if integers can overflow; hashing is safer but uses more memory.
Write a function that flattens all the objects to a single key-value dictionary.
This task tests your ability to transform nested objects into a flat key–value map (e.g.,
user.address.city → "SF"), which is core to log normalization and ETL. Be explicit about how you’ll handle arrays (indexing vs. exploding to multiple rows), conflicting keys, and deeply nested paths. Aim for an iterative/stack approach to avoid recursion depth issues on large payloads and to keep memory predictable.Tip: Clarify array behavior up front and state time/space trade-offs; interviewers want to see a production-minded plan, not just code.
-
Generate ordered 2-word sequences from a sentence by tokenizing, normalizing case, and sliding a window across tokens. Discuss punctuation/emoji handling and locale (e.g., Unicode word boundaries) to show you can make the function robust. Note how the same pattern extends to n-grams for downstream text features and search suggestions.
Tip: Use a regex tokenizer and a simple
zip(tokens, tokens[1:])pattern; mention O(n) time and how you’d validate with edge cases (1-word or empty input).
Adobe Experience Platform (AEP) Questions
This section covers Adobe Experience Platform interview questions that test your ability to design large-scale personalization, targeting, and streaming analytics systems as an AEP data engineer.
Design a classifier to predict the optimal moment to show a commercial break
You’ll need to think about real-time feature extraction and labeling strategies. Frame the problem as a classification task with contextual features like user behavior or content tags. Consider latency and feedback loops. This is critical when designing user-interaction systems in the Adobe Experience Platform.
Tip: Explain how you would measure success. Business KPIs like watch time or engagement are just as important as model accuracy.
The Interview Query dashboard gives you an interactive space to practice similar problems. It lets you track progress across SQL, Python, and system design categories, bookmark questions for later review, and view step-by-step solutions when you’re stuck. For Adobe-focused prep, you can filter by data engineer or system design to surface questions directly relevant to big-data interview scenarios. Having this structure not only organizes your study plan but also ensures you’re practicing under interview-like conditions.
Describe the process of building a restaurant recommendation system
Focus on hybrid models combining collaborative filtering with contextual metadata. Explain how to handle cold-start problems, data sparsity, and evaluation metrics. Knowing this helps in building personalization features in Adobe AEP interview questions.
Tip: Mention how you’d evolve the recommender over time with user feedback loops and A/B testing to show a product-minded approach.
Design a recommendation algorithm for Netflix’s homepage
You’ll need to balance user preferences with diversity and freshness. Outline offline model training and online serving architectures. These recommendation engines mirror the use cases of Adobe Experience Cloud’s personalization tools.
Tip: Discuss trade-offs between latency and relevance. Adobe interviewers want to see you can reason about user experience at scale.
Create a recommendation engine for rental listings
Discuss spatial features, ranking algorithms, and user intent signals. Include considerations for latency and model updating. This ties directly into AEP’s customer intelligence and behavioral modeling.
Tip: Bring up fairness and bias mitigation. Housing, pricing, or geographic recommendations are sensitive areas where governance matters.
System/Big‑Data Design Questions
These Adobe big data interview questions focus on partitioning strategies, distributed systems, and ETL scalability using tools like Kafka and Spark.
Design a machine learning system to minimize wrong order predictions
Emphasize how to build robust pipelines for feature engineering and retraining using batch and stream data. Incorporate data validation, monitoring, and feedback loops. Discuss Kafka or Airflow to orchestrate real-time ingestion and processing. These are foundational in any adobe big data solution for minimizing customer dissatisfaction.
Tip: Highlight how you’d partition data streams (e.g., by customer ID or region) to reduce skew and increase throughput.
Design a YouTube video recommendation engine
Use a two-tower system to first generate candidates and then rerank with more features. Focus on embedding generation and distributed model inference using GPUs. Make sure to highlight the use of partitioning and scalable serving infrastructure. Adobe’s personalization systems require similarly scalable architectures.
Tip: Talk about monitoring drift in embeddings. Proactive checks show awareness of long-term system health.
Design a podcast search engine with transcript relevance ranking
Discuss transcript parsing, TF-IDF or BERT-based embedding comparisons, and sharded search infrastructure. Touch on how you’d partition transcripts for parallel indexing and retrieval. This demonstrates your understanding of large-scale NLP systems. Similar indexing and sharding concepts apply to Adobe ETL workflows when handling unstructured data.
Tip: Stress how you’d balance search quality with infrastructure costs. Partitioning and governance decisions are critical in big data environments.
Behavioral or Culture‑Fit Questions
This section covers behavioral questions relevant to Adobe Data Engineer interview questions, with an emphasis on cross-functional collaboration across Creative Cloud and Experience Cloud teams.
Tell me about a time you collaborated with both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Use the STAR method to outline how you navigated communication barriers and aligned diverse goals. Emphasize tools or strategies used to translate technical constraints into business outcomes. Adobe values engineers who can connect data solutions with product vision, especially across teams like Creative Cloud and Experience Cloud.
Example: On a project integrating usage logs with marketing dashboards, I held weekly syncs with analysts and UX designers, translating schema limitations into business-friendly visuals. The shared understanding helped reduce reporting errors by 25%.
Tip: Demonstrate empathy by explaining how you tailored your message to different audiences. Communication style is as important as technical detail.
Describe a time you had to debug a critical data issue in production.
Walk through your process for identifying, isolating, and resolving the issue. Mention how you communicated with impacted teams and documented the resolution. Adobe’s culture encourages accountability and proactive communication during incidents.
Example: A nightly ETL job failed, blocking A/B test data for a product team. I traced the error to a schema change, quickly patched the pipeline, and set up alerts. I then wrote a postmortem that standardized validation checks across our team.
Tip: Show not just how you fixed the issue, but how you prevented it from recurring. Adobe values proactive problem-solvers.
Give an example of a time when you had to advocate for data quality.
Focus on how you identified a gap, pushed for better validation or governance, and educated stakeholders. Adobe engineers are often expected to be data stewards as well as builders.
Example: I noticed inconsistent timestamp formats across ingest pipelines that broke downstream joins. I created validation scripts, presented the issue in sprint planning, and worked with QA to enforce a standard. This reduced query failures by 40%.
Tip: Stress the business impact of quality improvements. Framing data governance as enabling better decisions resonates strongly.
Tell me about a time when you disagreed with a product manager or analyst. How did you resolve it?
Highlight your ability to listen, reframe technical limitations as trade-offs, and find alignment through metrics or experiments. Adobe encourages thoughtful dissent, especially when paired with data-backed solutions.
Example: A PM wanted daily refreshes of a heavy attribution pipeline. I argued for weekly refreshes, then ran a pilot showing negligible accuracy gains but high infra costs. The compromise saved $50K annually while maintaining decision quality.
Tip: Show you can turn conflict into a learning opportunity. Adobe values engineers who push back constructively with data.
Describe a project where you had to learn a new technology quickly.
Explain what motivated the need (e.g., moving to Spark or Airflow), how you structured your learning, and what impact it had. This reflects Adobe’s culture of continuous learning and self-direction.
Example: When our team migrated ETL from Hive to Spark, I enrolled in a short course, built test pipelines on side data, and documented migration steps. Within two weeks, I led the team through the cutover with zero downtime.
Tip: Emphasize curiosity and initiative. Adobe looks for engineers who see new tools as opportunities to grow, not obstacles.
How to Prepare for an Adobe Data Engineer Interview
Drill LeetCode-style SQL and Python Problems
Go beyond basic queries. Adobe’s technical screens often push into advanced joins, subqueries, and window functions to test how you handle complex analytics logic. On the Python side, expect scenarios where you’ll need to parse large logs or telemetry data. Practice efficient data wrangling with Pandas and numerical analysis with NumPy, since you’ll often be asked to process, reshape, and validate data under time pressure.
Tip: Time yourself when solving practice problems. In the real interview, clarity and speed matter. Getting a working solution quickly, then optimizing if time allows, is the winning strategy. You can practice similar questions on Interview Query with solutions and timer to get you better prepared for the real interview.
Rehearse AEP Whiteboard Architecture
Go beyond basic queries—Adobe’s technical screens often push into advanced joins, subqueries, and window functions to test how you handle complex analytics logic. On the Python side, expect scenarios where you’ll need to parse large logs or telemetry data. Practice efficient data wrangling with Pandas and numerical analysis with NumPy, since you’ll often be asked to process, reshape, and validate data under time pressure.
Tip: Practice sketching out system diagrams (e.g., source → Kafka → Spark Streaming → data lake → serving layer) and explaining trade-offs aloud. Interviewers want to see that you can structure your thoughts clearly, not just draw boxes.
Master STAR Stories
Behavioral interviews at Adobe carry as much weight as technical ones. Prepare at least 4–5 STAR-format examples highlighting teamwork, handling ambiguity, debugging production failures, and working with cross-functional partners. Keep each story concise but detailed enough to show impact—Adobe emphasizes collaboration and user-first thinking, so align your examples with those values.
Tip: Tie each STAR story back to Adobe’s values (“Customer First,” “Genuine,” “Innovative,” “Exceptional”). This ensures your answers resonate with the company’s culture and not just the problem you solved.
Sharpen Data Engineering Fundamentals
Expect deep dives into data architecture tradeoffs. Be ready to explain when you’d use ETL vs. ELT, how you’d optimize batch vs. streaming pipelines, and why a data warehouse vs. data lakehouse might be appropriate depending on the use case. Adobe operates at a massive scale, so interviewers want to hear how you think about performance, cost, and reliability, not just that you know the buzzwords.
Tip: Know the difference between ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). ETL is better for complex transformations before loading into a warehouse, while ELT leverages modern warehouses (like Snowflake or BigQuery) to handle transformations after loading. Show that you understand not only the acronyms but also when each approach is optimal.
FAQs
What is the Average Salary for an Adobe Data Engineer?
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Adobe data engineer salary in the U.S. is highly competitive.
- Entry to Mid-Level: Total compensation typically ranges from $131K to $192K, with a 79.8% of base pay, 6.5% of bonus and 13.7% of stock.
- Mid-Level: Adobe data engineers with 4-6 years of experience see compensation around $160K-$239K per year, reflecting stronger impact and more ownership.
- Senior / Principal: Total compensation ranges from $178K- $267K, with a median of $216K.
How important is Adobe Experience Platform Knowledge?
For mid to senior roles, Adobe Experience Platform (AEP) knowledge is often a deciding factor. The AEP deep-dive round typically tests your understanding of large-scale data ingestion, identity stitching, real-time segmentation, and data governance—key components of Adobe’s customer data infrastructure. Expect AEP interview questions to focus on designing scalable pipelines, handling schema evolution, and integrating multiple data sources into unified profiles.
Are there mock interviews focused on Adobe SQL questions?
Yes! SQL is a core skill for every Adobe data engineer because much of the role involves transforming raw data into analytics-ready formats for the Experience Cloud and Creative Cloud products. Adobe’s pipelines generate billions of records, and engineers need to be fluent in advanced joins, subqueries, and window functions to extract insights and maintain data integrity at scale. You can explore our Adobe SQL interview questions to practice problems that reflect real scenarios, including joins, window functions, and optimization trade-offs.
How is an interview at Adobe like?
Adobe’s interview process usually includes a recruiter call, an online SQL/Python assessment, 2–3 technical panel interviews (covering ETL, data modeling, and pipeline design), and a behavioral round. Mid-level and senior candidates may also face an Adobe Experience Platform (AEP)–focused system design challenge.
How hard are Adobe interviews?
They are moderately challenging. Candidates often find the SQL and Python rounds straightforward if they practice window functions and data wrangling, but the system design and AEP rounds can be complex because they test scalability, governance, and cross-team communication.
Is it difficult to get a job at Adobe?
Yes. The competition is high. Fewer than 10% of applicants are typically shortlisted for interviews, and the acceptance rate after interviews is estimated at around 5–8%. Strong preparation in both technical and behavioral rounds is essential.
What is the career trajectory of an Adobe data engineer?
Most data engineers start as ICs (individual contributors) focused on pipelines and ETL. Within 2–3 years, many move into senior or staff data engineer roles with ownership of platform design. From there, engineers can transition into data architecture, machine learning engineering, or leadership paths like engineering manager.
Can you make $500,000 as a data engineer?
At Adobe, base salary and bonus alone usually don’t reach $500K. However, senior or staff-level data engineers with significant equity grants in high-cost regions (Bay Area, Seattle) could approach total compensation in the $250K–$300K range. Hitting $500K typically requires moving into director-level or principal architect roles, or combining equity refreshers with long tenure.
Conclusion
The Adobe Data Engineer interview process rewards preparation, system-level thinking, and clear communication. From tackling SQL challenges to designing AEP pipelines, your edge comes from practicing Adobe-specific scenarios and sharpening both technical and behavioral skills.
Ready to practice? Bookmark this guide. Practice Adobe Data Engineer interview questions.
For adjacent prep paths, check out our Adobe Software Engineer Interview Guide for curated questions, strategies, and walkthroughs.
Want the closest simulation to the real process? Book a 1-on-1 mock interview with an experienced coach to get targeted feedback on SQL, system design, and AEP case rounds before your actual interview.


