Top SQL Interview Questions for Data Engineers: The Ultimate Guide
Overview: Why SQL Matters for Data Engineers
Every system, from traditional databases to modern cloud warehouses, speaks some flavor of SQL. Whether you’re designing schemas, transforming tables, or optimizing queries, SQL is the common thread that ties together data pipelines, analytics, and business decisions.
For data engineers, SQL isn’t optional, it’s the backbone of ETL, data modeling, and debugging. You’ll use it to extract, clean, and load data across platforms like Snowflake, Redshift, and BigQuery, and to make sure every query scales cleanly. That’s why SQL is one of the most tested skills in data engineering interviews. Recruiters and hiring managers want to see more than just syntax knowledge; they’re assessing how you think about data, design efficient queries, and handle real-world scenarios involving messy, large-scale datasets.
In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to master SQL for data engineering interviews, from fundamental concepts and theory questions to hands-on coding exercises, real-world ETL and analytics problems, and advanced topics like cloud SQL and big data. By the end, you’ll know exactly what to expect, how to reason through problems, and how to showcase your SQL expertise with confidence in any interview.
Types of SQL Interview Questions for Data Engineers
SQL interviews aren’t one-size-fits-all. They’re designed to test not only how well you write queries, but how you think, communicate, and design solutions for real data problems. Understanding the types of SQL interview questions helps you prepare strategically and avoid surprises on interview day.
Technical & Theory-Based Questions
These questions test your conceptual understanding of SQL. Expect definitions, comparisons, and explanations of how SQL structures data and ensures consistency.
Technical questions usually appear in early rounds or as warm-ups to assess your foundation before diving into hands-on coding.
Coding & Query Writing Questions
Here, you’ll need to write SQL queries to solve specific problems. These tasks simulate the daily work of a data engineer, such as extracting, cleaning, and transforming data.
Coding questions often test logic, accuracy, and optimization. You’ll be expected to explain your reasoning as you go, not just produce the final query.
Scenario-Based Questions
Scenario-based SQL questions mirror real-world data challenges, such as debugging ETL steps, designing queries for reporting, or optimizing joins in large datasets.
These questions test not just SQL syntax but your ability to reason about data pipelines, performance trade-offs, and workflow design.
Database Design & Architecture Questions
Expect interviewers to ask about schema design, data modeling, and query optimization. These go hand-in-hand with SQL since a poorly designed database can make even simple queries inefficient.
These questions evaluate how you think about scalability and maintainability, which are the two pillars of strong data engineering.
Behavioral & Communication Questions
Even though SQL interviews are technical, soft skills matter. Teams want engineers who can communicate clearly, collaborate with analysts, and explain decisions to non-technical stakeholders.
Strong answers show teamwork, curiosity, and accountability, not just technical expertise.
Tip: As you prepare, match your study plan to these categories. For instance, practice coding challenges on platforms like Interview Query or LeetCode, review theory from database textbooks or docs, and think through real projects where you applied SQL for problem-solving. Structuring your prep this way ensures balanced readiness across all interview types.
SQL Interview Questions by Experience Level
Not all data engineering interviews test SQL at the same depth. What you’re asked depends heavily on your experience level, whether you’re just breaking into the field or leading large-scale data systems. Recruiters and hiring managers tailor their questions to evaluate the right mix of fundamentals, problem-solving, and design thinking for your role.
This section breaks down what to expect at each stage, from writing clean, simple queries to optimizing distributed databases and architecting data models.
Read more: SQL Scenario Based Interview Questions
Entry-Level Data Engineer SQL Questions
At the entry level, interviews focus on core SQL fluency. You’ll be tested on how well you understand the basics such as selecting, filtering, joining, aggregating data, and whether you can think logically about datasets.
Expect straightforward coding tasks and foundational theory questions that assess:
- Your ability to write correct and readable SQL
- Understanding of joins, groupings, and subqueries
- Comfort with data cleaning and transformation logic
- Awareness of constraints, indexes, and normalization basics
These questions typically simulate hands-on data wrangling, such as identifying duplicates, calculating aggregates, or writing multi-table joins. Clear, consistent logic matters more than advanced syntax here.
Write a query that returns all neighborhoods that have 0 users.
This question tests
LEFT JOINsandNULLhandling. It’s specifically about detecting neighborhoods with no matching user records. To solve this,LEFT JOINneighborhoods to users onneighborhood_idand filter rows where the user side isNULL. In practice, this pattern is used to find coverage gaps, under-served areas, or data integrity issues.Tip: Explain why
LEFT JOINis better thanNOT INhere since it’s faster and handlesNULLvalues more reliably in most SQL engines.Select the 2nd highest salary in the engineering department
This question tests basic ranking and de-duplication. It’s specifically about excluding the maximum and retrieving the next highest value within a department filter. To solve this, filter to engineering and use a ranking function (e.g.,
ROW_NUMBER/DENSE_RANK) orORDER BYwithLIMIT/OFFSETto fetch the second highest salary. In real analytics, this helps with compensation benchmarking and percentile-based reporting.Tip: Mention when to prefer
DENSE_RANKoverROW_NUMBER, since the former correctly handles ties in salary values.Count transactions filtered by several criterias.
This question tests filtering with
WHEREand basicCOUNTaggregation. It’s specifically about applying multiple conditions (e.g., date range, payment method, status) before counting. To solve this, add all constraints inWHEREand useCOUNT(*)(orCOUNT DISTINCT transaction_id) to get the final total. In practice, filtered counts underpin KPI dashboards like daily orders, successful payments, or refund rates.Tip: Clarify when you’d use
COUNT(DISTINCT), it prevents double-counting in datasets with potential duplication.Write a query to find the overall acceptance rate of friend requests.
This question tests conditional aggregation. It’s specifically about computing offer acceptance rates. To solve this, use SUM(CASE WHEN accepted=1 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)/COUNT(*) grouped by recruiter/team. In real-world analytics, this supports HR funnel metrics.
Tip: Always cast numerator or denominator to a float to avoid integer division, which is a subtle bug many candidates overlook.
Write a query to get the average order value by gender.
This question tests aggregation. It’s specifically about computing spend per order and averaging across customers. To solve this, group by order_id, compute SUM(price*quantity), then AVG across orders. In practice, this is a foundational retail metric.
Tip: Show awareness of data quality, and mention that you’d handle missing or unknown genders to ensure cleaner analytics.
What share of Apple-platform actions ranked in the top-5 during November 2020?
You must filter on platform, restrict to November 2020, aggregate counts, then rank with
DENSE_RANK. Handling ties properly and producing an ordered output shows mastery of grouping plus ranking logic in real engagement analyses.Tip: Clarify how you handle ties, many interviewers appreciate when you explicitly note that
DENSE_RANKkeeps consistent ranks for equal counts.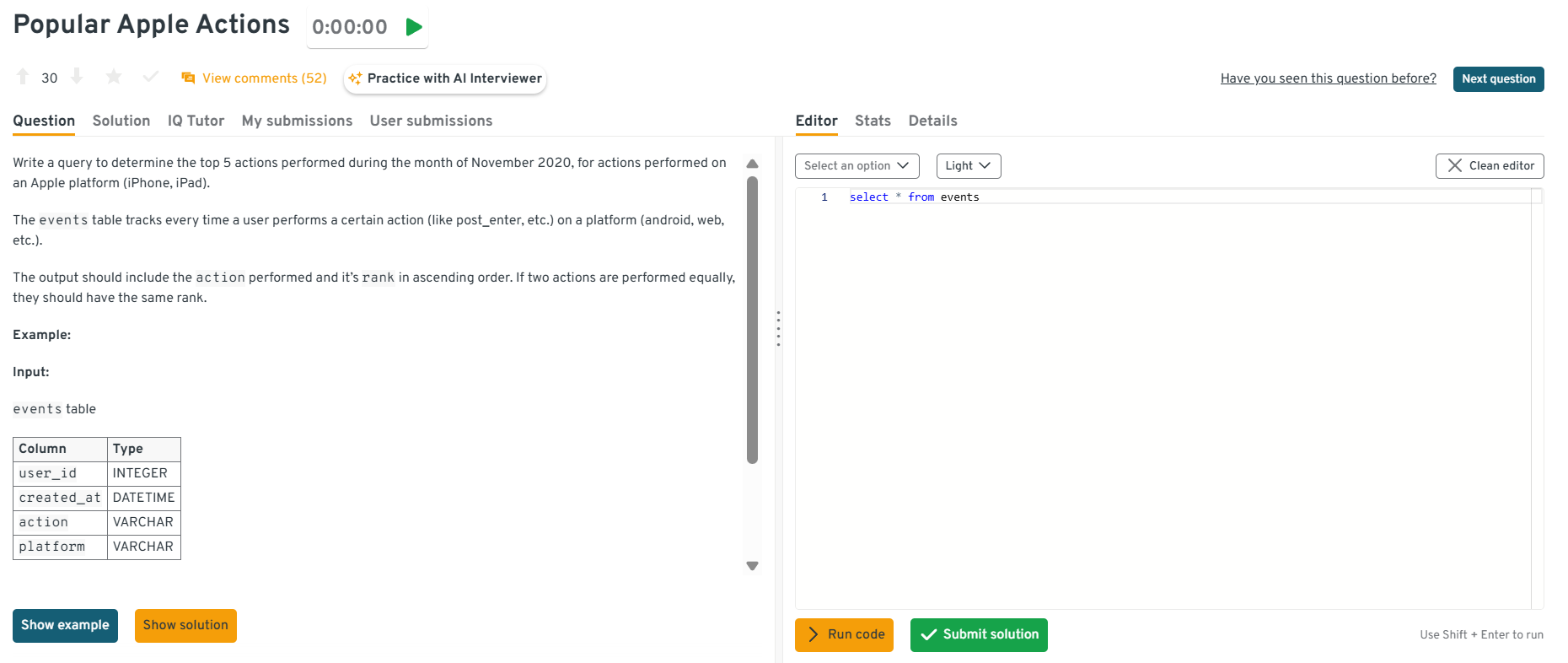
You can explore the Interview Query dashboard that lets you practice real-world SQL and Data Engineering interview questions in a live environment. You can write, run codes, and submit answers while getting instant feedback, perfect for mastering Data Engineering problems across domains.
-
The query filters on the timestamp window, groups by both
ssidanddevice_id, counts packets, then appliesMAX()(orROW_NUMBER()withDESCordering) per SSID. Explaining that you choose an index on(ssid, created_at)to speed the time filter demonstrates practical sense, yet the core logic remains a straightforward aggregation.Tip: Always mention index usage when working with time-based filters, it signals understanding of performance and scalability.
-
A clean answer uses
COUNT(DISTINCT employee_id)in the denominator, guarding against duplicates, then orders by the computed ratio and limits to five. The exercise spotlights practical data-quality thinking (deduping) without venturing into advanced optimization.Tip: Reinforce that
DISTINCTprotects data integrity, it’s a small addition that prevents skewed analytics during audits or dashboard builds.
Mid-Level Data Engineer SQL Questions
Mid-level interviews move beyond syntax to test efficiency, scalability, and data modeling judgment. You’re expected to demonstrate not just how to query data, but why your approach works best in production.
You’ll encounter scenario-based and performance-oriented questions involving:
- Query optimization and indexing strategies
- Window functions, common table expressions (CTEs), and analytical queries
- Debugging ETL or reporting pipelines
- Designing schemas for analytics or operational systems
Interviewers are looking for engineers who understand trade-offs, for instance, when to denormalize for performance, or how to rewrite queries for better execution plans.
Write a query to select the top 3 departments by average salary
This question tests ranking and aggregation. It’s specifically about computing average salary per department and selecting the top three. To solve this, group by department, compute
AVG(salary), then applyORDER BYandLIMIT. In real analytics, this reflects benchmarking and compensation analysis across groups.Tip: Mention using
ROUND(AVG(salary), 2)for cleaner output and note that adding an index ondepartment_idimproves aggregation speed in larger datasets.Get the current salary for each employee.
This question tests anomaly detection with SQL. It’s specifically about identifying mismatched or inconsistent salary records due to ETL errors. To solve this, use joins or window functions to check duplicates, missing entries, or unexpected distributions. In business, this ensures data quality in payroll and finance systems.
Tip: Emphasize validation, and mention using a subquery or
EXCEPTto detect employees with duplicate “current” records to show end-to-end data quality control.-
This question tests joins and comparisons. It’s specifically about identifying projects where actual spend exceeds budget. To solve this, join projects to expenditures and filter where spend > budget. In real-world analytics, this supports cost control and project management.
Tip: Show awareness of NULL handling and use
COALESCE(actual, 0)to prevent incorrect labeling when spend data is missing. -
This question tests ranking and conditional filters. It’s specifically about ranking search results based on relevance or clicks. To solve this, partition by
query_id, order byrank_score, and applyRANK(). In practice, this underlies search quality measurement.Tip: Explain that aggregate filters like
HAVING MAX(rating) < 3are more efficient than row-by-row subqueries, it shows your optimization mindset.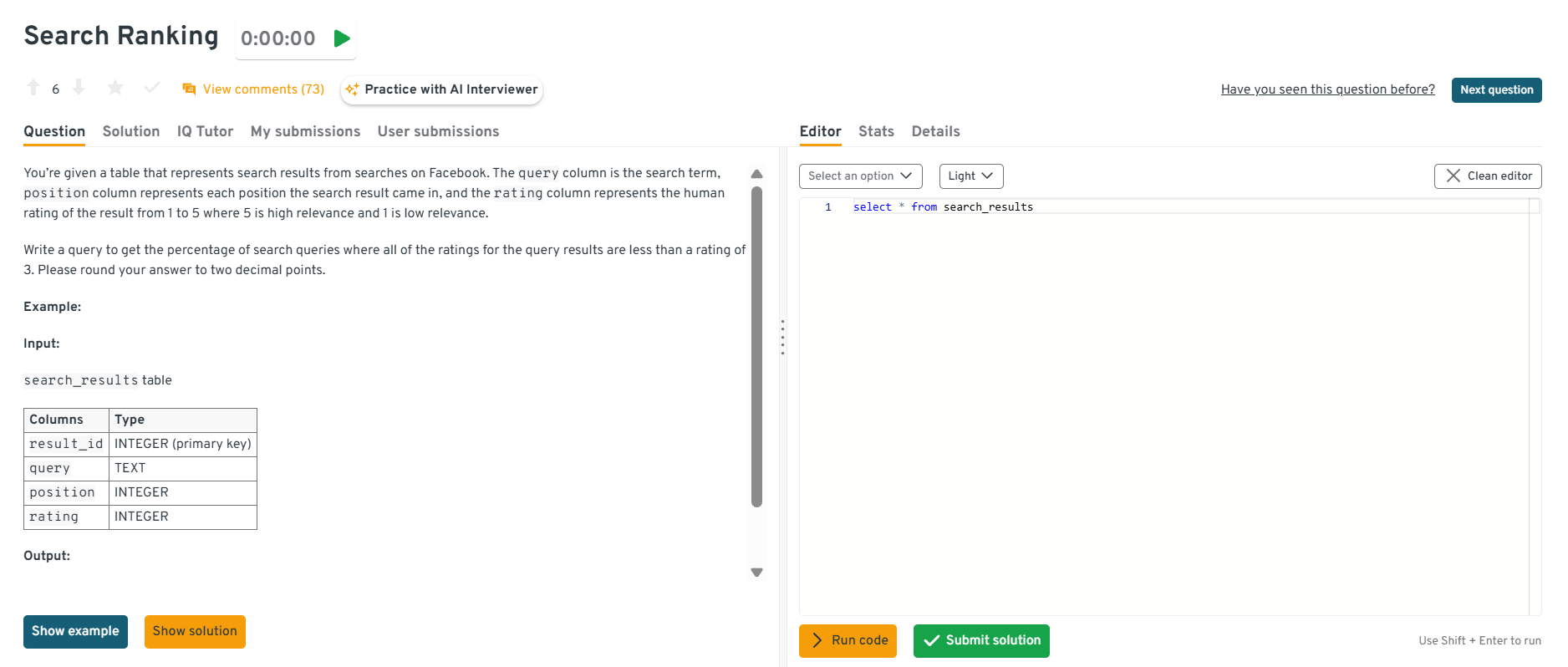
You can explore the Interview Query dashboard that lets you practice real-world SQL and Data Engineering interview questions in a live environment. You can write, run codes, and submit answers while getting instant feedback, perfect for mastering Data Engineering problems across domains.
Get the top five most expensive projects by budget to employee count ratio.
This question tests joins and aggregation logic. It’s about computing efficiency metrics by dividing total budget by employee count per project. To solve this, join
projectswithemployee_assignments, useCOUNT(DISTINCT employee_id)for the denominator, and order by the ratio. This evaluates data modeling and ratio computation fluency.Tip: Mention handling division by zero using
NULLIF(employee_count, 0), since small details like this show production-ready thinking.Find the month_over_month change in revenue for the year 2019.
This question tests time-based windowing. To solve this, group revenue by month using
DATE_TRUNC('month', order_date)and useLAG(SUM(revenue)) OVER (ORDER BY month)to compute the difference, then divide by the previous month’s revenue for a percent change.Tip: Clarify that you’d filter out the first month since it has no prior comparison, since such clean handling of edge cases always impresses interviewers.
Write a query to get the number of friends of a user that like a specific page
This question tests joins across relationship and action tables. It’s specifically about intersecting a user’s friend list with a page-likes table. To solve this, join the friendships table to
page_likesonfriend_idand filter by the page, thenCOUNT(*)(orCOUNT DISTINCT friend_id). In practice, this supports social graph analytics and targeted growth/virality tracking.Tip: Mention using
COUNT(DISTINCT friend_id)instead ofCOUNT(*)to prevent overcounting when multiple actions exist per friend.Who are the top three highest-earning employees in each department?
Using
employeesanddepartments, build a ranked list of the three largest salaries per department, outputting employee name, department name, and salary. The question probes your ability to applyRANK()orDENSE_RANK()within partitions and handle departments with fewer than three staff.Tip: Highlight how
RANK()can skip positions with ties whileDENSE_RANK()doesn’t, being explicit about tie behavior shows advanced SQL maturity.Create a January-2020 histogram of comments per user, with one-comment bins.
From an
eventstable, count how many comments each user left in January 2020, then bucket those counts (0, 1, 2, …) and tally users per bucket. This query requires a subquery or CTE for per-user counts followed by aGROUP BYon that count. It represents engagement analysis in product metrics.Tip: Explain how you’d generate missing bins using a helper table or series (e.g.,
generate_series()in PostgreSQL), this shows real-world completeness thinking.Find the score closest to a benchmark in SAT results
This question tests ordering and numerical filtering. Compute
ABS(score - benchmark)as a distance metric, then order by it and limit to the smallest difference. It evaluates your ability to combine math functions with SQL logic.Tip: If multiple results tie, mention handling it via
LIMIT 1or additionalORDER BYcriteria (e.g.,student_id ASC) to show deterministic query design.
Senior Data Engineer SQL Questions
Senior-level interviews are less about memorizing syntax and more about strategic thinking. The focus shifts to how you architect, optimize, and scale data systems using SQL at enterprise or big data levels.
Expect deep-dive discussions around:
- Query planning, performance tuning, and partitioning
- Sharding, replication, and handling distributed databases
- Data governance, consistency, and fault tolerance
- Integration of SQL with cloud warehouses and orchestration tools (e.g., dbt, Airflow)
- Designing complex transformations for multi-source ETL workflows
These questions assess whether you can think like a data systems architect, explaining trade-offs, diagnosing bottlenecks, and proposing scalable SQL-driven solutions.
Compute click-through rates (CTR) across queries
This question tests your ability to design performant queries for search analytics using selective filters, proper join order, and targeted indexes. It’s asked to evaluate whether you can compute click-through rates across query segments while minimizing full scans and avoiding skewed groupings. To solve this, pre-aggregate impressions/clicks by normalized query buckets, ensure a composite index on
(query_norm, event_time)with covering columns for counts, then join safely to deduped clicks; validate withEXPLAINto confirm index usage. In production, this matters because search CTR dashboards must be low-latency and cost-efficient to support experimentation and relevance tuning at scale.Tip: Explain how caching or materialized views can further reduce compute costs, this shows practical architectural awareness beyond pure SQL logic.
Compute cumulative users added daily with monthly resets
This question tests advanced window framing and partition strategy on large time-series datasets. It evaluates your ability to compute per-month cumulative counts efficiently. To solve this, use
SUM(1) OVER (PARTITION BY DATE_TRUNC('month', created_at) ORDER BY created_at ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW)and cluster bycreated_atfor better performance. In BI, this powers growth trend reporting with minimal recomputation.Tip: Mention verifying partition boundaries with sample outputs to show that you understand how frame definitions impact accuracy and performance.
Compute average response time to system messages
This question tests self-joins and
LAG()with precise ordering keys and indexes. It’s asked to ensure you can pair system→user events efficiently without whole-table windows. To solve, partition bythread_id, order by timestamp,LAG()to find the previous system msg, compute deltas, and ensure(thread_id, ts)indexing to avoid sorts. In operations analytics, this drives SLA and responsiveness dashboards.Tip: Always mention how you’d handle missing or delayed responses (null lag values), it reflects robust production-ready SQL logic.
Calculate daily minutes in flight per plane
This question tests timestamp arithmetic and grouping. It’s specifically about converting departure/arrival timestamps into minute-level duration per plane and day. To solve this, compute
EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM arrival - departure)/60, group by plane_id and flight_date, and round down fractional minutes; handle overnight flights carefully. In aviation analytics, this supports aircraft utilization dashboards.Tip: Point out how time zone normalization ensures consistent reporting, which is a detail senior engineers are expected to catch.
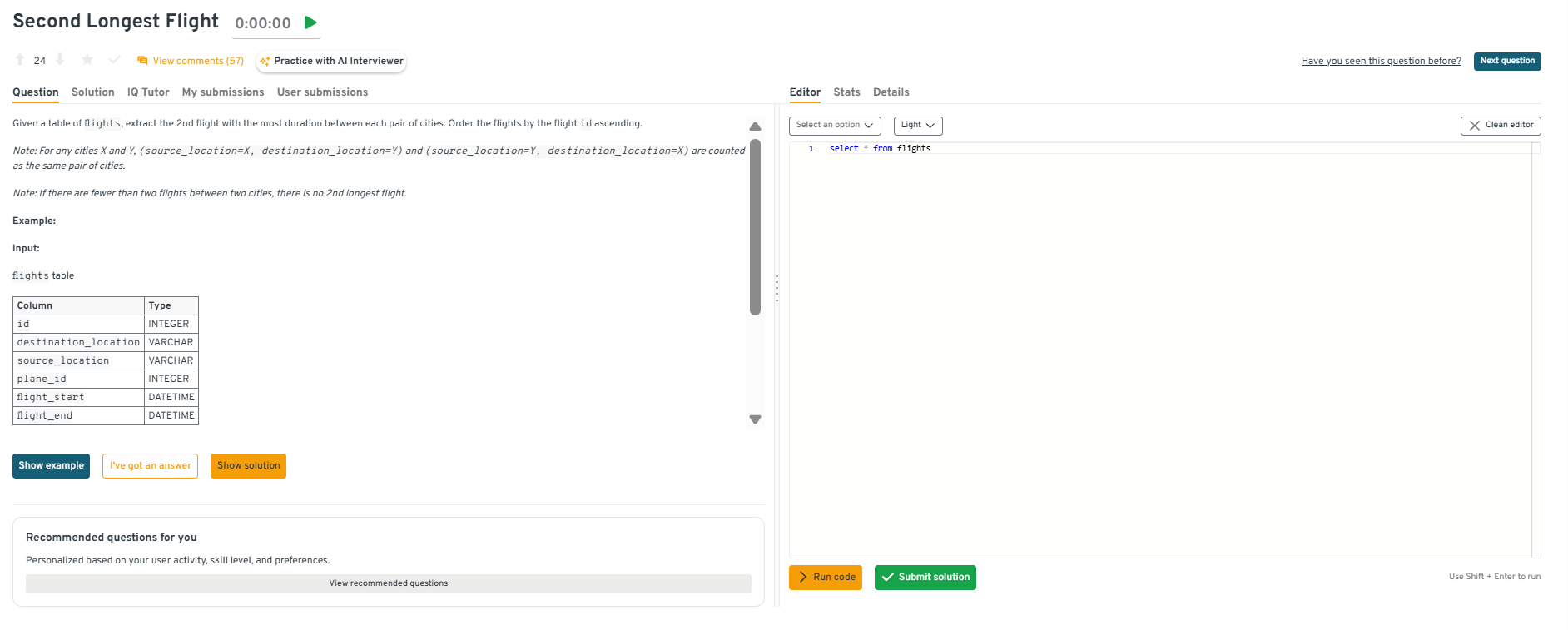
Return the second-longest flight for each city pair
This question tests ranking within groups. It’s specifically about normalizing city pairs (A-B = B-A), computing durations, and finding the 2nd-longest. To solve this, store sorted city names as
city_a,city_b, compute duration_minutes, then applyROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY city_a, city_b ORDER BY duration_minutes DESC)and filter where rank=2. Airlines use this to plan backup aircraft allocations for long-haul routes.Tip: Mention how precomputing city pair mappings or using hash keys can simplify joins and improve performance at scale.
You can explore the Interview Query dashboard that lets you practice real-world SQL and Data Engineering interview questions in a live environment. You can write, run codes, and submit answers while getting instant feedback, perfect for mastering Data Engineering problems across domains.
Calculate rolling balances for bank accounts
This question tests window functions for running totals. It’s about maintaining a cumulative balance over time per account. Use
SUM(amount) OVER (PARTITION BY account_id ORDER BY transaction_date)and ensure ordered storage by account and date. In finance analytics, this supports fraud detection and audit trails.Tip: Mention isolating negative balances or overdrafts via conditional windows (
CASE WHEN balance < 0 THEN …) to highlight real-world insight beyond mechanics,Write a query to detect overlapping subscription periods
This question tests interval logic and self-joins. It’s about identifying customers with overlapping subscriptions. Join
subscriptionstable to itself where onestart_datefalls between another’sstart_dateandend_date. Businesses use this for churn and double-billing prevention.Tip: Emphasize indexing both
start_dateandend_datefor interval queries, this detail shows senior-level understanding of query performance on temporal data.Count successful vs failed notification deliveries
This question tests conditional aggregation for monitoring KPIs. Use
SUM(CASE WHEN status = 'success' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)and group by message type or platform. It’s common in operational analytics for reliability tracking.Tip: Mention that adding an
UNION ALLvalidation layer comparing app logs with delivery DBs ensures end-to-end data integrity, since senior engineers think across systems, not tables.Write a query to assign first-touch attribution in campaigns
This question tests window functions and event sequencing for marketing analytics. Partition by
user_id, order byevent_time, and selectROW_NUMBER() = 1to assign conversions to the first campaign touchpoint. It models marketing influence over user behavior.Tip: Highlight how you’d handle multi-channel overlap (e.g., paid vs. organic), showing business context awareness elevates technical answers.
Count second-order likes (liker’s likers)
This question tests recursive joins or multi-level self-joins. It’s about extending direct user relationships (friends) to second-degree connections. To solve this, self-join the
likestable whereliker_idfrom the first join maps touser_idin the second. This simulates “friends of friends” analysis in social graph data.Tip: Mention applying limits or depth constraints to recursion to avoid exponential joins, which is a hallmark of scalable social network querying.
Database Design & Modeling Questions
Data engineers don’t just write SQL queries, they design the systems those queries run on. That’s why database design and modeling are frequent interview themes, especially for mid- to senior-level candidates. A well-designed schema makes queries faster, transformations cleaner, and pipelines more reliable.
Expect interviewers to assess how you think about data organization, relationships, scalability, and performance. These questions often blend theory with real-world judgment: not just what normalization is, but when you’d break it for speed or scalability.
Read more: Top 32 Data Modeling Interview Questions
Here are some of the most common database design and modeling topics you’ll encounter in interviews:
| Topic | What It Tests | Key Concepts / Discussion Points |
|---|---|---|
| Database Schema Design | Your ability to structure data efficiently and logically. | - Identifying entities and their relationships (1-to-1, 1-to-many, many-to-many) - Choosing primary and foreign keys - Balancing normalization vs. denormalization - Designing for data integrity and scalability |
| Normalization and Denormalization | How well you understand data redundancy and consistency. | - Explain normalization up to 3NF with examples - When to choose denormalization (e.g., in data warehouses) - Impact of normalization on ETL performance |
| ER Diagrams and Relationships | Your ability to model complex data interactions clearly. | - Cardinality (1:1, 1:N, N:M) - Referential integrity constraints - Mapping logical vs. physical models |
| Partitioning and Sharding | Your understanding of scalability strategies in distributed systems. | - Difference between partitioning and sharding - How to partition a - Trade-offs in maintaining consistency across shards |
| Data Modeling for Real-World Pipelines | Whether you can connect design principles to production pipelines. | - Designing a star schema (fact and dimension tables) - Modeling event logs for real-time dashboards - Handling schema evolution and versioning in production |
Tip: In interviews, always explain why you made certain design decisions. For example, say:
“I chose a denormalized structure for faster read performance since the reporting workload is read-heavy.”
Clear, trade-off-driven reasoning demonstrates senior-level understanding more than perfect syntax.
Example Questions and Answers
How would you design a database schema for an online bookstore system?
Here, interviewers test your ability to map real-world entities into structured, relational tables. Start by identifying core entities like
Books,Authors,Customers, andOrders, and then define relationships such as one-to-many betweenAuthorsandBooksor betweenCustomersandOrders. Choose appropriate primary and foreign keys to maintain integrity, and ensure columns like ISBN or email have uniqueness constraints. This question checks whether you can design for scalability and clarity while maintaining normalization. Consider indexing high-traffic fields likebook_idorcustomer_idfor performance.Tip: Always describe how your schema supports both current and future features, like adding a
Reviewstable later without major redesign.Explain how you’d normalize a customer-orders table up to the third normal form (3NF).
This question tests your understanding of normalization and data redundancy elimination. Start by ensuring 1NF (atomic columns, no repeating groups), then 2NF (removing partial dependencies by separating orders from customer data), and finally 3NF (removing transitive dependencies like city or state into a separate location table). The result should be separate
Customers,Orders, andLocationstables linked by keys. This matters because normalization ensures data integrity and makes updates efficient, though in analytical systems you might selectively denormalize for performance.Tip: Mention that normalization helps transactional systems stay consistent, while denormalization can improve analytical query performance.
How would you represent a many-to-many relationship between students and courses in an ER diagram?
This tests your understanding of ER modeling and referential integrity. The best approach is to introduce a junction table like
Enrollmentscontaining foreign keysstudent_idandcourse_idthat link the two main entities. This design avoids data duplication while enabling efficient joins to fetch course enrollments or student lists. It reflects your ability to translate conceptual relationships into physical models that scale across queries. Edge cases like handling dropped courses or null grades can also be modeled with nullable columns or soft deletes.Tip: Always mention the cardinality in your answer, it shows you understand both data structure and relationship constraints.
How would you partition a large
transactionstable to improve query performance?Interviewers test your scalability thinking here. You can partition the
transactionstable by date (e.g., month or year) using range partitioning to ensure faster queries for time-bound analytics. For example, filtering on a specific date range would scan fewer partitions, improving performance. Alternatively, for geographically distributed systems, you could shard data by region to balance load across nodes. This question reveals how you optimize for read/write efficiency without overcomplicating data management.Tip: Explain how partitioning reduces scan time and storage overhead, and mention monitoring partition growth to prevent uneven data distribution.
How would you model sales data for a reporting pipeline using a star schema?
This tests your understanding of data modeling for analytics. Design a central
FactSalestable with foreign keys linking toDimCustomer,DimProduct,DimStore, andDimTime. The fact table stores numeric metrics like sales amount and quantity, while dimension tables store descriptive attributes. This setup simplifies aggregations and makes reporting queries efficient. It demonstrates that you can design for both scalability and analytical clarity, which are two key traits in production-grade data pipelines.Tip: Emphasize that star schemas are optimized for OLAP systems where read-heavy workloads benefit from pre-joined, denormalized data structures.
SQL ETL and Data Pipeline Interview Questions
For data engineers, SQL is the lifeblood of ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), the process that powers every data pipeline. Whether it’s cleaning raw logs, joining multiple sources, or aggregating data into warehouse tables, SQL is what turns messy inputs into structured, actionable insights.
Interviewers use ETL and pipeline questions to test how well you understand the end-to-end data flow from extraction to transformation and loading, and how efficiently you can translate business logic into SQL operations. These questions often blend technical skills with architectural thinking, requiring you to design or optimize real-world workflows.
Read more: Top 47 ETL Interview Questions & Answers
Here are the key areas that most ETL-related SQL interview questions focus on:
| Topic | What It Tests | Key Concepts / Discussion Points |
|---|---|---|
| ETL Fundamentals | Your understanding of ETL stages and workflows. | - Difference between ETL and ELT - Role of staging tables - Handling incremental and batch loads |
| Data Transformation | How you manipulate data using SQL for cleaning and aggregation. | - Common transformations (joins, aggregations, pivot/unpivot) - Handling missing or inconsistent data - SQL-based business logic transformations |
| Error Handling & Data Quality | How you ensure reliability and accuracy in pipelines. | - Null checks, constraints, deduplication - Logging and exception tracking - Validation queries |
| Performance Optimization | Your ability to tune ETL queries for speed and scale. | - Indexing and partitioning in transformations - Query execution plans - Reducing I/O and shuffle operations |
| Workflow & Scheduling | How you manage and orchestrate ETL jobs. | - SQL job dependencies - Use of stored procedures or scripts - Incremental updates and scheduling tools (Airflow, Cron) |
Tip: Strong answers to ETL and pipeline questions blend SQL logic with workflow thinking. Always show how your transformations fit into a bigger data ecosystem like extraction sources, downstream consumers, and monitoring all matter as much as the query itself.
Example Questions and Answers
What’s the difference between ETL and ELT, and when would you use each?
This question tests your understanding of pipeline design patterns. In ETL, data is transformed before loading into the warehouse, while in ELT, data is loaded first and transformed inside the warehouse (like BigQuery or Snowflake). Use ETL when transformations are heavy or data quality must be verified before storage; use ELT when you can leverage the compute power of modern cloud warehouses. Knowing this distinction shows architectural awareness of how SQL fits into large-scale workflows.
Tip: Mention that ELT has become more common with modern MPP databases that can handle transformations directly using SQL.
How would you handle incremental loads in a sales transactions table using SQL?
Here, interviewers test your ability to manage large data volumes efficiently. Track new or changed records using a
last_updatedtimestamp or surrogate key. You can use queries likeWHERE last_updated > (SELECT MAX(last_updated) FROM target_table)to load only new rows. This approach minimizes load time and avoids full refreshes, which are resource-heavy. Incremental logic is vital in daily or hourly pipelines where performance directly impacts downstream analytics.Tip: Always highlight how you handle late-arriving data or timestamp mismatches to show attention to real-world reliability.
How would you detect and remove duplicate records in a large dataset during ETL?
This question tests data validation and cleaning logic. Use window functions with
ROW_NUMBER()to rank duplicates based on unique identifiers or timestamps, then filter where rank > 1. For example,DELETE FROM table WHERE id IN (SELECT id FROM (SELECT id, ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY customer_id, order_date ORDER BY updated_at DESC) AS r FROM table) WHERE r > 1). This shows your ability to apply SQL transformations for maintaining data quality.Tip: Emphasize that deduplication is context-dependent, and sometimes you may keep the latest record, or sometimes the first valid entry.
How do you optimize SQL queries in an ETL pipeline that’s running slowly?
Interviewers are checking your understanding of performance tuning. Begin by identifying the bottleneck, whether it’s a join, aggregation, or subquery. Use
EXPLAINplans to analyze execution paths, ensure proper indexing on join keys, and replace correlated subqueries with CTEs when possible. For large-scale systems, consider partition pruning or caching lookup tables in memory. Optimizing SQL at the transformation layer is crucial because it scales directly with data volume and cost.Tip: Mention that you also monitor query performance metrics (e.g., scan time or shuffle size) to continuously improve ETL efficiency.
How would you design an automated ETL job to refresh daily reports?
This tests your understanding of workflow orchestration and scheduling. Start by creating parameterized SQL scripts for extraction and transformation, then automate execution with a scheduler like Airflow or Cron. Include validation checks after each stage, and load data into reporting tables or materialized views for quick access. This demonstrates an understanding of reliability and reproducibility, which are key traits in production pipelines.
Tip: Mention adding alerting or logging for failed jobs so you can troubleshoot issues proactively.
SQL Analytics and Reporting Problems
Data engineers don’t just move data, they make it meaningful. SQL analytics and reporting questions evaluate how effectively you can transform raw datasets into actionable metrics, trends, and insights. These problems mirror real-world scenarios like tracking user engagement, analyzing sales trends, or monitoring system performance.
The key challenge isn’t only producing the right answer, it’s writing queries that are accurate, efficient, and production-ready. Interviewers want to see how you think through aggregations, ranking logic, and time-based analytics, not just your SQL syntax.
Read more: SQL Interview Questions for Data Analysts
Here are some common categories of analytics and reporting questions.
| Category | What It Tests | Key Concepts / Discussion Points |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregation & Grouping | Ability to summarize large datasets effectively. | - Using SUM, COUNT, AVG with GROUP BY - Applying conditional aggregates ( - Handling multi-level aggregations |
| Window Functions | Skill in analyzing sequential or partitioned data. | - Ranking (RANK(), ROW_NUMBER()) - Calculating running totals and differences ( - Partitioning and ordering datasets |
| Query Optimization | How you design efficient queries for analytics. | - Simplifying nested queries - Using indexes or materialized views - Reducing full-table scans |
| Date & Time Analysis | Handling time-series and retention metrics. | - Extracting and filtering by dates - Calculating trends, growth rates, and cohorts - Working with rolling or cumulative metrics |
| Metrics & KPI Design | Translating business requirements into SQL metrics. | - Building derived KPIs - Aggregating at multiple dimensions - Supporting dashboards and automated reports |
Tip: Analytics questions reward clarity. Always explain why your query structure matches the business goal, connecting SQL logic to measurable insights shows that you think like both an engineer and an analyst.
Example Questions and Answers
-
Here, interviewers test your grasp of grouping and filtering in analytics queries. Filter the dataset using a
WHEREclause for the specific date, then group bycarrierandcountry, counting confirmation responses withCOUNT()or conditional aggregation. This tests both SQL fundamentals and business reasoning, ensuring you can deliver clear insights for communication analytics. Edge cases may include missing response records or time zone mismatches.Tip: Mention using a
CASE WHEN status = 'confirmed' THEN 1 ENDexpression insideCOUNT()to handle mixed statuses cleanly. -
This question evaluates your ability to use window functions for behavioral metrics. You can calculate consecutive visit streaks by comparing event dates with
LAG()and resetting counts when a break occurs, then aggregate by user to find the longest streak. This problem tests analytical thinking, partition logic, and efficient event ordering, all key in product analytics pipelines.Tip: Emphasize handling edge cases where users skip days or have multiple events on the same day since both can break streak logic if not managed properly.
-
Interviewers test your understanding of cumulative metrics with partitioned windows. Use a combination of
SUM(sales_amount) OVER (PARTITION BY product_id ORDER BY sale_date)and a reset condition after each restock. This showcases your ability to tie window logic to business processes, ensuring metrics remain consistent between inventory cycles.Tip: Clarify how you’d define “last restocking”, for instance, using a
restock_flagor joining with arestock_eventstable to isolate cumulative segments. Calculate how many users logged in an identical number of times on January 1st, 2022.
This question tests grouping and nested aggregation logic. First, count logins per user on that date, then group those results by login count to see how many users share the same frequency. It evaluates your ability to use subqueries effectively and interpret frequency distributions in behavioral data.
Tip: Mention validating your query with small samples or edge cases (e.g., users with zero logins) to ensure data completeness and accuracy.
Optimize a query that calculates total monthly revenue by joining three large tables (orders, customers, products).
This question tests your ability to identify and fix inefficiencies in complex queries. Begin by examining join conditions and filtering logic, like move filters to early stages, ensure proper indexes exist on
customer_idandproduct_id, and consider pre-aggregating data using CTEs or temporary tables. Check query plans to detect full scans or cartesian joins, and use partitioning or clustering if supported by your system. This shows you can scale analytics without sacrificing accuracy or runtime.Tip: Mention analyzing the
EXPLAINplan or cost metrics to prove awareness of query execution internals, which is a big plus in senior interviews.Design a SQL query to compute the conversion rate KPI for users who viewed a product and made a purchase within 7 days.
Here, interviewers test your ability to translate business requirements into measurable metrics. Start by joining view and purchase events by
user_id, filter purchases within 7 days using aDATEDIFF()condition, and calculate conversion as(purchasing_users / total_viewers) * 100. This question reveals your skill in bridging analytics logic with SQL expressions and understanding time-based KPIs.Tip: Explain that you’d verify window boundaries carefully, for instance, handling cases where users have multiple views before purchase, to ensure an accurate metric.
Watch next: Amazon SQL Mock Interview Question: Conversation Distribution
In this mock SQL interview, Jitesh, a data engineering coach at Interview Query with a decade of experience in data engineering and analytics, explains how to determine the daily distribution of conversations initiated by users in a chat application for 2020. He guides viewers through interpreting user interaction patterns, structuring the SQL query, and preventing double-counting in the data, which are skills that you can apply in your own interview prep.
Advanced SQL: Big Data, Cloud, and Dialect Differences
SQL isn’t limited to relational databases anymore. It now drives massive data lakes, cloud warehouses, and distributed systems that power real-time analytics and business insights. Each of these environments has its own SQL dialect, optimization model, and execution architecture, all of which data engineers are expected to understand.
In advanced interviews, you’ll face questions that test your architectural awareness, such as how you handle distributed joins, optimize queries for cost and performance, or adapt to cloud-native features. The goal is to assess not just what you know about SQL, but how you scale and apply it in modern data ecosystems.
| Category | What It Tests | Key Concepts / Discussion Points |
|---|---|---|
| Big Data SQL | Your understanding of distributed query execution and data partitioning. | - Hive, SparkSQL, Presto fundamentals - Schema-on-read vs. schema-on-write - Optimizing joins and shuffles |
| Cloud SQL Systems | Your familiarity with cloud-native databases and cost-performance trade-offs. | - BigQuery, Snowflake, Redshift, Synapse - Clustering, partitioning, materialized views - Query federation and storage optimization |
| SQL Dialect Differences | How you adapt queries between different database systems. | - Syntax and function variations - JSON handling and semi-structured data - Indexing and performance tuning syntax |
Tip: Advanced SQL interview success comes from showing that you can scale logic across systems, from local Postgres instances to Spark clusters and serverless BigQuery jobs. Be ready to discuss trade-offs between performance, cost, and maintainability in any environment.
Example Questions and Answers
How would you optimize a SparkSQL join between two massive Parquet tables?
This question tests your understanding of distributed query optimization. Start by filtering early to reduce data size, use broadcast joins when one table is small, and align partition keys to avoid shuffles. Ensuring both tables are in Parquet format also reduces I/O. This shows you can reason about query performance in distributed systems and not treat SparkSQL like a single-node database.
Tip: Mention analyzing the physical plan with
EXPLAINor usingspark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThresholdto tune join strategy, it shows real production-level awareness.How would you query JSON event data in BigQuery to calculate daily active users efficiently?
Here, interviewers test your ability to handle semi-structured data in a cloud SQL environment. Use
JSON_EXTRACT_SCALAR()to parse user IDs, cast timestamps withDATE()functions, andCOUNT(DISTINCT user_id)grouped by day. Partition tables byevent_dateand select only necessary fields to reduce cost. This demonstrates your ability to balance compute efficiency with functional correctness in a serverless warehouse.Tip: Emphasize that optimizing storage and partition pruning in BigQuery can drastically lower cost, which is a key insight for real-world data teams.
How would you convert a PostgreSQL query using
json_col->>'user_id'to run in BigQuery and Snowflake?This question tests SQL portability. In BigQuery, use
JSON_EXTRACT_SCALAR(json_col, '$.user_id'), and in Snowflake, usejson_col:user_id::stringto extract the same value. This demonstrates that you can migrate logic seamlessly between warehouses while accounting for type casting and JSON path syntax differences. Understanding dialect nuances is crucial for teams managing multi-cloud or migration projects.Tip: Always test JSON extraction logic on a small dataset first, since syntax inconsistencies across dialects can cause silent query errors or null results.
Additional SQL Dialect Insights
Beyond PostgreSQL, BigQuery, and Snowflake, data engineers are often expected to navigate multiple SQL dialects in real-world environments. The table below highlights key focus areas and quirks interviewers commonly test across major database systems.
| Database | Common Interview Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| MySQL | - Uses LIMIT OFFSET for pagination, which performs poorly on large datasets. - Expect questions on indexed pagination, query caching, and optimizing slow joins with subqueries. -Advanced questions may test quirks in |
| SQL Server | - Uses TOP() instead of LIMIT. - Performance tuning with indexes, CTEs, and - Common topics include concurrency handling, deadlocks, and large ETL pipeline strategies. |
| Oracle SQL / PL/SQL | - Row limiting with ROWNUM or FETCH FIRST N ROWS. - Must understand ordering and filtering quirks with - PL/SQL introduces procedural elements ( - Common scenarios include stored procedures, nested blocks, and transaction rollback. |
| PostgreSQL | - Strong in analytics and warehousing. - Heavy use of advanced window functions ( - Interviewers may test JSON handling, arrays, CTEs, and recursive queries for semi-structured data. |
| BigQuery | - Serverless and pay-per-query model—focus on query cost optimization. - Expect questions on partitioning, clustering, and storage vs. compute separation. - Common scenarios include querying nested JSON, using |
| Snowflake | - Emphasizes virtual warehouses and scaling compute separately from storage. - Expect questions on micro-partitioning, - Interviewers often test semi-structured data handling with |
Tip: When discussing SQL dialects in interviews, highlight that you understand why these differences exist. Whether due to architecture (distributed vs. single-node), cost model (compute-based vs. serverless), or syntax design. Showing adaptability across engines demonstrates production-level versatility, not just query fluency.
Behavioral Data Engineering Interview Questions
Even the most technically skilled data engineers need strong soft skills to thrive on a team. That’s why behavioral questions are a standard part of SQL and data engineering interviews since they reveal how you think, communicate, and collaborate under real-world conditions.
Strong behavioral answers connect technical depth with human clarity, showing that you’re not just a great coder, but also a reliable partner in building data systems that work.
Read more: Top 32 Data Science Behavioral Interview Questions
Tip: Frame your answers using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result). It keeps your responses clear, structured, and focused on measurable outcomes, which is something interviewers in technical roles really appreciate.
-
This question assesses your communication and empathy in a cross-functional environment.
- Situation: In a data migration project, conflicting definitions of “active customer” between the sales and product teams led to misaligned SQL reports.
- Task: I needed to clarify business logic while ensuring both teams trusted the data.
- Action: I scheduled a review session, created sample outputs, and built a shared data glossary to standardize terms.
- Result: The final dashboard aligned with both teams’ expectations, reducing back-and-forth revisions by 60%.
Tip: Show that you listen, document, and validate since clear communication is key in bridging business and technical teams.
How would you convey insights and the methods you use to a non-technical audience?
Interviewers want to see if you can translate technical depth into actionable insights.
- Situation: While presenting query optimization results to marketing leads, I realized the discussion was getting too technical.
- Task: My goal was to communicate why performance gains mattered to campaign reporting.
- Action: I replaced technical jargon with relatable visuals, showing before-and-after load times and how faster pipelines enabled daily insights instead of weekly ones.
- Result: Leadership approved increased data processing frequency, improving campaign agility.
Tip: Focus on storytelling and connect SQL or ETL improvements to business value, not just metrics.
What do you tell an interviewer when they ask you what your strengths and weaknesses are?
This question tests your self-awareness and growth mindset.
- Situation: In my previous role, I was known for my SQL debugging and query optimization skills, often resolving performance issues in shared pipelines.
- Task: I used that strength to mentor junior engineers and document best practices. For weaknesses, I acknowledged that I initially hesitated to delegate technical tasks.
- Action: I worked on building trust through code reviews and collaborative sprints.
- Result: Our team’s delivery time improved, and I became more effective at scaling both my impact and others’.
Tip: Choose strengths that match the job and weaknesses that show active improvement, because honesty with progress demonstrates maturity.
Describe a time when you had to resolve a data quality or ETL pipeline issue under pressure.
Here, interviewers test your problem-solving and composure.
- Situation: A key revenue dashboard failed hours before an executive review due to duplicate records in the sales ETL pipeline.
- Task: I needed to identify and fix the issue quickly without disrupting other data loads.
- Action: I used SQL CTEs to isolate duplicates, applied a
ROW_NUMBER()deduplication fix, and added a validation query to catch anomalies in the future. - Result: The dashboard was restored within two hours, and the postmortem led to a permanent automated quality check.
Tip: Emphasize calm, structured troubleshooting and the steps you took to prevent recurrence, it reflects reliability in production environments.
Tell me about a time you collaborated with another team to improve data reporting or performance.
This question highlights teamwork and ownership.
- Situation: Our analytics team struggled with slow dashboard refreshes due to unoptimized queries.
- Task: I collaborated with the BI team to diagnose bottlenecks.
- Action: We rewrote heavy joins into CTEs, added indexes on join keys, and used pre-aggregated views for dashboards.
- Result: Query time decreased by 70%, and the solution became a shared company best practice.
Tip: Stress your ability to take initiative, collaborate across functions, and turn one fix into a scalable improvement for the team.
Common SQL Interview Mistakes & Troubleshooting
Even experienced data engineers can stumble in SQL interviews, not because they lack knowledge, but because they miss small details that reveal bigger gaps in understanding.
These mistakes often come down to rushing, unclear reasoning, or skipping validation steps, all of which can cost valuable points in an interview.
Read more: Common SQL Interview Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Here are some of the most common pitfalls, and how to avoid them.
| Mistake | Why It Hurts | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Jumping straight into code without clarifying requirements | You risk solving the wrong problem or missing edge cases. | Restate the question in your own words before writing any query. Confirm what output and conditions are expected. |
| Ignoring data quality issues | Missing nulls, duplicates, or incorrect types can lead to wrong results. | Always start by checking for missing or inconsistent values with quick validation queries. |
| Overcomplicating simple problems | Adds confusion and makes debugging harder. | Keep it simple and use clean, readable SQL that communicates intent clearly. |
Relying on SELECT * in interviews |
It’s inefficient and shows lack of precision. | Explicitly select only the necessary columns, it demonstrates focus and understanding of schema. |
| Forgetting to test edge cases | Your query might fail with empty tables, nulls, or unexpected inputs. | Always test with sample or boundary data before finalizing your answer. |
| Not explaining your thought process | Interviewers can’t follow your logic even if the answer is right. | Narrate your reasoning step-by-step as you build your query. |
| Neglecting query optimization | Produces slow or resource-heavy solutions. | Use indexes wisely, minimize nested subqueries, and check query plans if available. |
| Getting stuck in syntax details | Focus shifts away from problem-solving. | Use pseudocode or describe logic verbally if syntax slips, the goal is clarity, not perfection. |
Tip: Think aloud while coding. When you explain what each part of your query is doing, even if you make a small mistake, interviewers see how you think, not just what you know. That’s often the deciding factor between good and great candidates.
Salary Negotiation and Career Growth Tips for Data Engineers
Acing your SQL and technical interviews is only half the battle, the next challenge is negotiating your offer and planning long-term growth. Data engineering roles vary widely by company size, location, and tech stack, so understanding your market value and career trajectory is key to making smart decisions.
Read more: Data Analyst Salary: What to Expect and How to Maximize Earnings
Here’s how to navigate both the short-term offer stage and your long-term growth path with confidence.
Before the Offer: Do Your Homework
Preparation makes negotiation easier. Before your final rounds, research compensation ranges for your target role using tools like Levels.fyi, Glassdoor, or Interview Query’s salary reports.
Look at base pay, bonuses, stock options, and benefits to form a realistic benchmark.
Focus on:
- The company’s data stack and expected workload (e.g., big data vs. analytics-heavy role)
- Cost-of-living and location-based pay ranges (especially for hybrid/remote setups)
- Comparable roles like “Data Engineer II” at one company may equal “Senior Data Engineer” elsewhere
Tip: If asked for salary expectations early, give a range slightly above your minimum target. For example:
“Based on my research and experience, I’m targeting between $120K–$135K depending on scope and benefits.”
During Negotiation: Lead With Value, Not Numbers
When you get the offer, focus on what you bring to the team, not just what you expect to earn. Emphasize your technical depth (SQL, ETL design, cloud data experience), project results, and communication skills. This shifts the conversation from “how much” to “why you’re worth it.”
Practical tactics:
- Ask clarifying questions about performance-based raises or bonus cycles.
- Negotiate each component separately (base, sign-on, equity) instead of one total figure.
- Express excitement for the role and keep your tone collaborative, not combative.
Tip: Silence can be powerful. After you make a counteroffer, pause. Let the recruiter respond, most will come back with a better number or extra perks.
Long-Term Growth: Invest in Your Skill Stack
Career growth for data engineers isn’t just about titles, it’s about staying technically relevant. The best engineers continually evolve their stack across data modeling, orchestration, and machine learning integration.
Keep advancing by:
- Learning data orchestration tools (Airflow, dbt, Dagster)
- Deepening your cloud expertise (AWS, GCP, or Azure certifications)
- Building cross-functional skills in analytics, DevOps, or ML pipelines
- Contributing to open-source or internal documentation to build visibility
Tip: Treat every role as a stepping stone. Use each project to strengthen one of three pillars: architecture, automation, or analytics. That’s how data engineers grow from writing SQL to shaping data strategy.
SQL Interview Preparation Checklist
Preparing for SQL interviews as a data engineer is about building consistency, confidence, and structure into your study routine. A good prep plan keeps you organized and ensures you’re reviewing the right topics at the right time.
This unified roadmap and checklist helps you track your preparation week by week, combining technical goals, focus areas, and actionable readiness checks so you can stay organized from start to finish.
Read more: How to Prepare for a Data Engineer Interview
| Timeline | Focus Area | Key Goals | Readiness Checks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2–3 Weeks Before | Foundations | Review joins, subqueries, aggregates, indexes, normalization, and ACID. Practice 3–5 problems daily. | ☐ Solid on SQL basics and syntax. ☐ Completed 15–20 practice queries. ☐ Explored at least one cloud SQL platform. |
| 1–2 Weeks Before | Hands-on SQL | Solve scenario-based and ETL problems. Review CTEs, window functions, and performance tuning. | ☐ Built one SQL pipeline or ETL mini-project. ☐ Comfortable with window functions, and optimization. |
| 1 Week Before | Mocks & Refinement | Take mock interviews, identify weak areas, and refine problem-solving approach. | ☐ Finished 2–3 mock sessions. ☐ Can explain trade-offs in query design. |
| 3–4 Days Before | Concept & Project Review | Summarize key SQL functions, revisit schema design, and review major projects. | ☐ Reviewed all key SQL topics. ☐ Practiced behavioral (STAR) answers out loud. ☐ Ready to discuss one project end-to-end. |
| Day Before | Setup & Mindset | Prep your setup, review notes briefly, and rest. | ☐ Tested environment. ☐ Ready with 2–3 questions for interviewer. ☐ Confident and focused. |
| Interview Day | Execution | Read carefully, explain logic aloud, and validate results. | ☐ Stay calm and structured. ☐ Communicate clearly. |
Tip: Treat this checklist like a progress board, and tick off each box as you move through the stages. By interview week, you’ll have built both the technical foundation and the communication confidence that top data teams look for.
FAQs: SQL Interview Questions for Data Engineers
What are the most common SQL interview questions for data engineers?
Most SQL interviews test your ability to query, transform, and interpret data efficiently. Expect questions on joins, aggregations, window functions, subqueries, and indexing, along with scenario-based tasks like optimizing slow queries, building ETL transformations, or modeling tables for analytics.
How should I prepare for SQL coding problems in interviews?
Practice hands-on coding daily using real datasets or mock challenges. Focus on understanding logic and readability rather than memorizing syntax. Platforms like Interview Query or LeetCode are great for realistic SQL problems that mimic data engineering scenarios.
What is the difference between normalization forms in SQL?
Normalization organizes data into separate, non-redundant tables to improve consistency and reduce anomalies. The key forms—1NF, 2NF, and 3NF, progressively remove duplicate and dependent data, making updates and queries more efficient in relational systems.
How do data engineers use SQL for ETL and pipeline creation?
SQL powers every step of ETL: extracting raw data, transforming it through joins, filters, and aggregations, and loading it into structured warehouse tables. It’s the backbone of most pipelines, whether you’re managing batch processes or real-time data flows.
What advanced SQL topics should I study for big data or cloud interviews?
Focus on distributed SQL concepts like partitioning, sharding, and query optimization in systems such as Hive, SparkSQL, BigQuery, and Snowflake. Understanding how SQL operates in parallel environments and how to minimize compute costs is key for cloud roles.
How do I showcase my SQL and data engineering skills in an interview?
Bring up real project examples — describe how you designed tables, optimized queries, or automated ETL workflows. Use metrics where possible, like reducing query time or improving load performance, to show measurable impact.
What are common mistakes to avoid during SQL interviews?
Avoid rushing into code, skipping clarifications, or ignoring edge cases. Always validate your assumptions, explain your reasoning, and check your results. Interviewers care more about your process than perfect syntax.
How can I negotiate a better salary as a data engineer?
Do your research before the offer stage and know your worth based on skills, experience, and market rates. Lead the conversation with your value such as highlight specific contributions, scalability wins, or system improvements that justify a stronger offer.
What are some behavioral interview questions for data engineering roles?
Behavioral questions often explore teamwork, communication, and problem-solving under pressure. Expect prompts like “Tell me about a time you optimized a slow query” or “How did you handle a failed data load?”, your goal is to show clarity, ownership, and collaboration.
Conclusion: Master SQL, Master the Data Engineer Interview
SQL remains the core skill that separates good data engineers from great ones. It’s the language that connects data to insight, and mastering it shows you can think critically, design efficiently, and scale intelligently. Whether you’re just starting out or refining your advanced querying skills, consistent practice and clear reasoning will make all the difference. Use this guide as your roadmap, and walk into your next SQL interview ready to show not just what you know, but how you think like a true data engineer.
Helpful Interview Query Resources
Want to master SQL interview questions? Start with our SQL Question Bank to drill real-world scenario questions used in top interviews.
Master CASE WHEN logic or GROUP BY filters with our step-by-step SQL Learning Path to go from basic joins to advanced optimization.
Then, simulate the real pressure using Mock Interviews.


