Tesla Data Engineer Interview Questions and Guide | Interview Query
Introduction
Tesla is a leading technology company known for its innovations in Autopilot, electric vehicles, and sustainable energy solutions. The company values innovation and speed over perfection, fostering a mission-driven culture that encourages rapid development and calculated risk-taking. Guided by Elon Musk’s “first principles” approach—breaking complex problems down to their fundamentals and rebuilding from the ground up—Tesla empowers employees to think independently and move fast. They look for dedicated, high-performing individuals who can adapt quickly and push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Role Overview & Culture
To prepare for a Tesla data engineer interview, start by understanding the critical responsibilities of the role and its impact on Tesla’s manufacturing and Autopilot systems. As a data engineer at Tesla, you’ll design and maintain scalable data pipelines, process real-time telemetry from vehicle sensors and factories, and support analytics used in performance monitoring and system optimization. Day-to-day tasks involve building infrastructure for large-scale batch and streaming data, collaborating with software and ML teams, and ensuring clean, reliable datasets for decision-making. Tesla data engineer interview questions will test your skills in ETL development, distributed systems, and real-time data processing, as well as your alignment with Tesla’s fast-paced, innovation-driven culture.
Why This Role at Tesla?
Working as a data engineer at Tesla means contributing directly to cutting-edge innovation, especially in the fast-growing and niche field of sustainable energy. Your work has the potential to drive meaningful breakthroughs—not just in technology, but in shaping the future of human progress. At Tesla, employees are given a high degree of ownership and autonomy. With Elon Musk’s ambitious vision at the core, the company actively encourages creative problem-solving and bold risk-taking.
Moreover, Tesla’s compensation for data engineers is generally competitive with industry standards. Total compensation including bonuses, stock options, and other incentives often exceeds $120K, with experienced engineers potentially earning $180K or more.
To land the job, you first need to ace the Tesla data engineer interview using the tips below.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Data Engineer Role at Tesla?
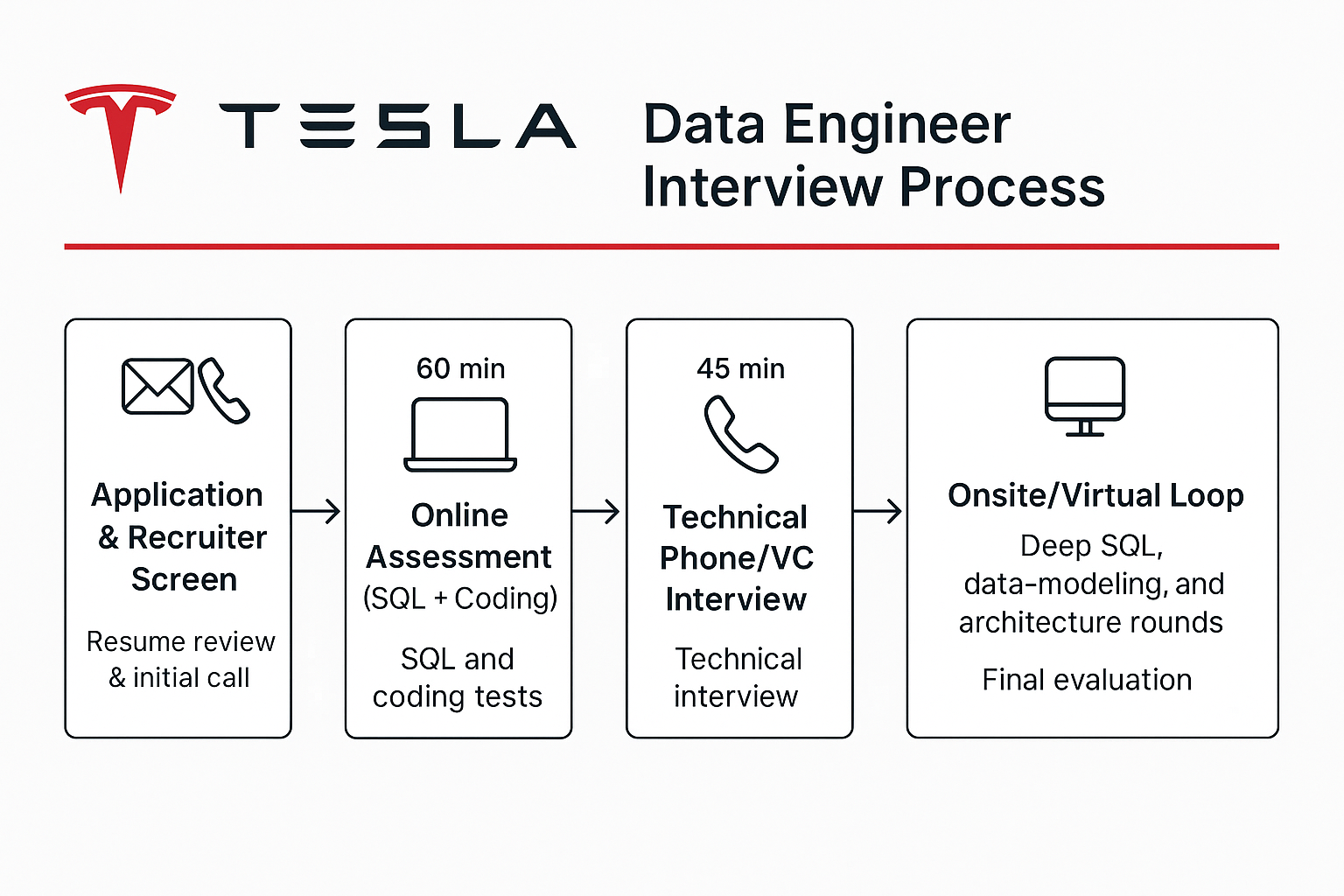
Application & Recruiter Screen
If your background aligns with the role, a recruiter will reach out for a brief screening call. This conversation focuses on your resume, motivation for joining Tesla, and your fit for the team. The recruiter may ask about your experience with data infrastructure, SQL, or real-time telemetry systems. They’ll also give an overview of the process and timeline.
Online Assessment (SQL + Coding)
If you pass the initial screen, you’ll receive an online assessment designed to test your technical fundamentals. This usually includes SQL queries and data manipulation tasks, alongside general coding problems (commonly in Python). The test is time-limited (usually 60 minutes) and simulates real-world scenarios such as analyzing datasets or writing efficient logic. This stage is crucial for showcasing your ability to work with data at scale.
Technical Phone/VC Interview
In this 45-minute video call, you’ll speak with a Tesla engineer or data team member. The focus is on technical depth and problem-solving. You may be asked to solve SQL challenges, discuss database design, or work through logic and Python problems in live coding. Clear communication, structured thinking, and an ability to explain trade-offs in your solutions are key to doing well in this round.
Onsite/Virtual Loop
Tesla data engineer onsite sessions are technically rigorous and typically span 3 to 5 interviews in a single day, each lasting 45–60 minutes. The loop focuses on SQL proficiency, Python scripting, data modeling, systems design, and your understanding of end-to-end data architecture.
You’ll likely encounter live coding rounds on platforms like CoderPad, where you’re asked to solve complex SQL queries using joins, window functions, and real-time data manipulation. Python rounds often focus on logic, efficiency, and ETL-style scripting. A dedicated use-case problem session is also common—this may involve walking through a real-world scenario, such as designing a data pipeline for vehicle telemetry or optimizing analytics infrastructure for factory operations.
Hiring Committee & Offer
After each round of interviews, your interviewers will provide feedback to a cross-functional hiring committee. The committee will then make the final decision. This process typically takes about a week after your final round. The recruiter will follow up with the result—and if all goes well, congratulations, you’ll receive your offer letter!
Behind the Scenes
Tesla only hires high-performing candidates and is constantly competing for top talent. Interviewers are required to submit their feedback within 24 hours, ensuring timely and accurate reflections on the candidate’s performance.
In some interview rounds, senior managers are involved in assessing whether the candidate exceeds Tesla’s high standards, both technically and culturally. This is known as the bar-raiser vote, where the goal is to maintain or elevate the team’s performance bar. Candidates who don’t meet this threshold may be voted out, regardless of other interviewers’ feedback.
Differences by Level
Tesla also tailors its hiring process based on the candidate’s level of seniority. For a data engineer intern interview, the process is typically lighter and may involve a recruiter screen followed by one or two technical rounds focusing on SQL, basic Python, and an understanding of data pipelines. For senior analysts, the interview process typically includes an additional round focused on assessing their ability to generate strategic insights and support high-level decision-making.
What Questions Are Asked in a Tesla Data Engineer Interview?
Here are a few questions that are asked in Tesla Data Engineer interviews:
Coding / Technical Questions
For Tesla SQL interview questions, focus on window functions and advanced joins. Here are some examples:
1. Select the top 3 departments with at least ten employees and the highest average salary
Focus on using GROUP BY, HAVING, and ORDER BY with an aggregate function to identify departments that meet the threshold. You’ll also need to limit the results using TOP or LIMIT depending on SQL flavor. This question evaluates your ability to combine filtering with aggregation in a real-world context. It’s highly relevant for any Tesla data engineer managing compensation, departmental performance, or HR analytics data.
2. Calculate the first touch attribution channel for each user’s signup
You’ll be joining tables that contain event timestamps and marketing channel information. The key is to find the earliest event per user and attribute it correctly. Use ROW_NUMBER() or MIN() along with PARTITION BY. This question simulates marketing funnel tracking, which is crucial in product usage analysis.
3. Write a query to count users who made additional purchases after an initial upsell
This tests your ability to identify behavioral patterns from transaction logs. Use JOINs and possibly subqueries or window functions to isolate upsell events and track later purchases. Pay attention to filtering by user and event sequence. This is relevant to understanding product lifecycle usage or post-sale engagement — scenarios Tesla might encounter in energy products or services.
4. Write a SQL query to calculate the average number of swipes per user per day
Focus on grouping by both user and date, then computing averages across users. Use DATE() functions and aggregation thoughtfully. Think about how you’d design this in a normalized schema. This tests analytical capabilities common in sensor or app behavior analysis, which is useful for Tesla’s vehicle telemetry or user experience analytics.
Here you must use ROW_NUMBER() or RANK() to get the latest salary, then detect ETL errors such as mismatches or duplicates. Watch out for timestamp edge cases or malformed data. This simulates real-world data integrity issues you’d face in ETL pipelines. Very applicable to Tesla’s high-scale data ingestion challenges.
For Python questions, expect topics like data cleaning or batch scheduling, often tied to real-world Tesla use cases.
6. Group a list of sequential timestamps into weekly lists starting from the first timestamp
Approach this with date arithmetic and slicing in Python. You want to iterate through the list while maintaining buckets that restart every 7 days. Pay attention to edge cases like timezone-aware timestamps or gaps. This question is relevant for Tesla’s time-series data processing from vehicles or IoT devices.
7. Write a function that takes a sentence and returns all bigrams as tuples
Use string splitting and list comprehension or zip to generate bigram pairs efficiently. You should also consider punctuation and casing depending on context. This kind of tokenization is helpful in natural language processing or log parsing. Tesla might find this useful in analyzing chatbot interactions or user feedback.
8. Stem words in a sentence using the shortest root words available from a dictionary
Implement a trie structure or prefix matching approach to optimize word replacements. Ensure that you only replace with the shortest possible root word. This simulates NLP preprocessing commonly seen in search or classification tasks. Tesla could apply such logic in parsing technician logs or support tickets.
9. Write a function to return the top N frequent words from a block of text
Count word frequencies using collections.Counter, then sort and retrieve the top N. Consider edge cases such as ties or case sensitivity. You might also want to normalize inputs. This type of analysis is useful for prioritizing issues or feedback in Tesla’s QA processes.
10. Write a function to remove stop words from a sentence
A straightforward dictionary lookup or set membership test will work best here. Preprocess the text by splitting and filtering against the stop word list. Ensure to retain meaningful tokens. Tesla’s data pipelines for NLP or content parsing can benefit from this basic but critical preprocessing step.
System / Data Architecture Questions
For the system design and data architecture questions, candidates are often asked to design real-time data pipelines that reflect Tesla’s scale and complexity. These questions assess your ability to architect scalable and reliable systems, with an emphasis on key trade-offs such as partitioning strategies, schema evolution handling, and decisions between using a data lake versus a data warehouse. Here are some questions to practice on:
11. Design an end-to-end architecture for an international e-commerce warehouse
Consider how to model product data, inventory across countries, and currency conversions. Your architecture should also address latency and consistency tradeoffs. Think about data replication, partitioning, and localization. Tesla faces similar challenges in global supply chain operations and inventory data synchronization.
12. Design a data mart or warehouse for an online retailer’s sales and supply chain analytics
Focus on schema modeling using star or snowflake patterns, with dimension tables for products, customers, and time. Address data ingestion pipelines, ETL scheduling, and support for aggregations. This exercise assesses your understanding of analytical workloads. Tesla may use comparable setups for factory output reporting or parts procurement analytics.
13. Add a column with data to a billion-row table while minimizing downtime
You need to plan for schema evolution in a high-availability system. Strategies might include batched updates, background jobs, or dual writes with toggled reads. It evaluates your thinking around scale, risk mitigation, and system impact. Tesla deals with enormous telemetry data—this mirrors such production challenges.
14. Design a schema to represent client click data and build relevant queries
Plan for high write throughput, indexing strategy, and query patterns for behavior analysis. Normalize the data to balance performance and flexibility, and prepare it for downstream ETL. This is particularly relevant for Tesla’s vehicle usage tracking or app telemetry.
15. Compute the average response time for each user session across distributed systems
Analyze log entries by session and timestamp, possibly requiring deduplication or ordering. Design logic to track user activity and identify slowdowns across distributed services. Think in terms of microservices and observability data pipelines. Tesla’s backend systems across charging, mobile apps, and vehicles would benefit from similar performance analysis.
Behavioral or “Culture Fit” Questions
Try to prepare a few stories that show strong ownership and urgency, and organize them using the STAR method. Keep them flexible so you can easily adapt them to different types of behavioral questions during the interview:
16. Describe your approach to resolving conflict with a colleague
Share a specific time you had a disagreement or interpersonal challenge. Walk through how you stayed respectful, listened actively, and worked toward a constructive outcome. Emphasize teamwork, not winning the argument. Collaboration and low-ego problem-solving are essential in Tesla’s high-performance culture.
17. Describe a challenging communication experience with stakeholders
Think of a situation where you had to explain something technical, complex, or disappointing to business or cross-functional partners. Show how you tailored your message to different audiences and maintained clarity. Discuss how you handled questions, concerns, or resistance. Tesla analysts regularly communicate across engineering, design, and leadership.
18. Tell me about a time you had to adapt quickly to a major change in project scope or timeline
Choose an example where priorities shifted rapidly—maybe due to data changes, executive feedback, or external events. Explain how you adjusted your plan, coordinated with others, and still delivered value. Highlight resilience and flexibility. Tesla operates in a fast-moving environment where change is constant.
19. Describe a time you had to give or receive constructive feedback
Use the STAR method to describe when you offered or received meaningful feedback. Emphasize how you ensured the conversation was respectful and focused on improvement. Reflect on what you learned or how you applied the feedback. Tesla’s culture depends on rapid learning through honest dialogue.
20. Tell me about a time you took initiative outside of your formal responsibilities
Pick a moment when you noticed an opportunity or problem and acted without being asked. Explain your motivation, what actions you took, and the outcome. Highlight creativity, ownership, and measurable impact. Tesla values people who go beyond the job description and solve real problems.
How to Prepare for a Data Engineer Role at Tesla
Data engineering at Tesla demands strong communication, fast problem-solving, and a solid understanding of Tesla’s unique engineering culture. Here’s how to get ready:
Master Core SQL Patterns
Many interview questions focus on SQL efficiency and logic. Be comfortable using window functions, CTEs, and advanced query optimization techniques. Practice with real datasets to improve performance tuning and logic structuring under time pressure.
Mock Interviews
Practice makes perfect. Try to practice pair programming sessions and schema design drills with a peer or mentor.
Think Out Loud & Clarify Assumptions
Tesla interviews often include bar-raiser rounds that test your clarity of thought and communication. Get in the habit of talking through your problem-solving process and verifying requirements up front—this shows both confidence and precision. It also signals to the interviewer that you not only meet the team’s baseline expectations but are likely to contribute meaningfully and elevate team performance.
FAQs
What Is the Average Salary for a Data Engineer Role at Tesla?
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
How long does Tesla take to give feedback?
Tesla typically provides interview feedback within one week of your interview or application status update. While some candidates may hear back in just a few days, others report waiting up to 7 business days for a response, especially after final-round interviews.
Conclusion
To boost your chances on landing an offer, keep practicing with real Tesla data engineer interview questions on Interview Query, where you can sharpen your SQL, data pipeline, and system design skills in a realistic format.
For a deeper dive, you must check out our Tesla Interview Guide, and if you’re looking to strengthen your technical foundation, explore our Data Engineer Learning Path!
