Tesla Machine Learning Engineer Interview Guide: Process, Questions, and Tips
Introduction
Tesla Machine Learning Engineer interviews can cover a wide range of topics depending on the product focus, including self-driving systems, AI model deployment, energy forecasting, and manufacturing automation.
Tesla Machine Learning jobs are at the forefront of developing intelligent systems that transform industries. From autonomous driving to energy management and factory automation, machine learning engineers leverage millions of miles of fleet driving data and driver interventions to build robust, scalable end-to-end learning systems for Autopilot, spanning motion planning, perception, and intelligent scheduling.
Tesla Machine Learning Engineer interviews can cover a wide range of topics depending on the product focus, including self-driving systems, AI model deployment, energy forecasting, and manufacturing automation.
Tesla Machine Learning jobs are at the forefront of developing intelligent systems that transform industries. From autonomous driving to energy management and factory automation, machine learning engineers leverage millions of miles of fleet driving data and driver interventions to build robust, scalable end-to-end learning systems for Autopilot, spanning motion planning, perception, and intelligent scheduling.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Machine Learning Engineer Role at Tesla?
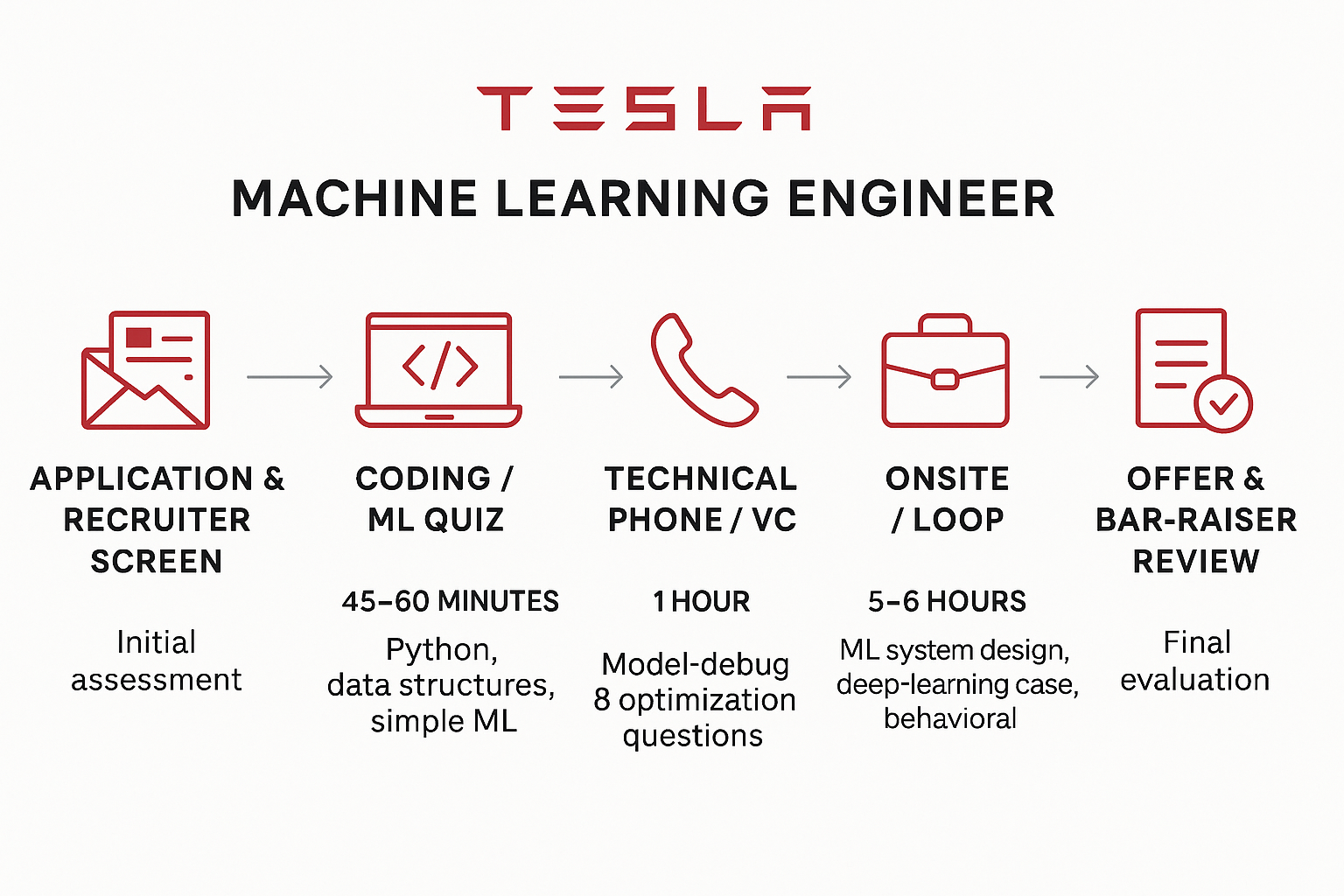
Application & Recruiter Screen
Tesla machine learning engineer interview begins with the online application, where it’s essential to tailor your resume to highlight machine learning, computer vision, or autonomous systems experience. Tesla recruiters are particularly keen on candidates who align with the company’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. If selected, you’ll receive a recruiter screen, typically lasting around 30 minutes. During this call, the recruiter explores your background, work experience, and motivations for applying to Tesla. They often ask behavioral questions like “Why Tesla?” and assess your high-level understanding of machine learning concepts, your technical interests, and how they fit into Tesla’s product areas.
Coding / ML Quiz
Candidates who pass the recruiter screen are given a coding and ML assessment. This is often hosted on platforms like HackerRank, Codility, or a proprietary Tesla system. The coding questions usually focus on medium-level algorithms and data structures—such as arrays, dynamic programming, or tree traversal—implemented in Python. Alongside standard coding problems, some quizzes include simple machine learning tasks like feature engineering, implementing basic ML algorithms (e.g., logistic regression or k-means), or evaluating model performance. This stage tests both your programming fluency and your ability to apply ML concepts quickly and accurately.
Technical Phone / VC
Next is a technical phone or video interview with an ML engineer or team member. This round typically lasts 45–60 minutes and includes a mix of live coding, ML fundamentals, and problem-solving. You may be asked to debug a piece of ML code, explain the steps in improving model performance, or walk through tradeoffs like bias-variance, underfitting, and overfitting. Questions may also probe your knowledge of deep learning architectures (e.g., transformers, BatchNorm), optimization techniques (SGD, Adam), and error analysis. Interviewers are interested not only in your technical accuracy but also in your ability to reason and communicate clearly under pressure.
Onsite / Loop
The onsite (also known as the loop) is a full-day series of 3 to 5 interviews with engineers, team leads, and hiring managers. One round typically focuses on ML system design, where you’ll be asked to design an end-to-end system—such as an object detection pipeline for self-driving vehicles—evaluating scalability, data pipeline structure, deployment constraints, and hardware considerations. Another round may center on a deep learning case study where you’re expected to propose architecture choices and metrics based on a real-world scenario. A behavioral or presentation-based interview usually asks you to walk through a past project, emphasizing your problem-solving approach, collaboration style, and technical decisions. The hiring manager round often dives deeper into your role in past projects, challenges faced, and your potential contribution to Tesla’s team.
Offer & Bar-Raiser Review
If you perform well throughout the loop, your interviewers submit feedback within 24 hours. Tesla places strong emphasis on rapid decision-making and alignment on company values. Interviewers rate your technical performance, communication, and cultural fit independently before a hiring committee or “bar-raiser” makes the final decision. The bar-raiser, often a senior engineer or manager from a different team, ensures consistent hiring standards across departments and evaluates whether you raise the average level of the current team. This final review especially values ownership, execution, and innovative thinking—qualities Tesla prizes across all roles.
Behind the Scenes
Tesla’s interview system emphasizes rapid feedback loops, typically requiring all interviewers to submit evaluations within 24 hours. This practice ensures momentum and helps Tesla move quickly on strong candidates. Additionally, internal discussions place considerable weight on mission alignment; they are looking for engineers who are not only technically capable but also deeply motivated by Tesla’s vision of a sustainable future. Passion for Tesla’s work often becomes a deciding factor, particularly in borderline cases.
Differences by Level
For senior or staff-level machine learning roles, the process includes an additional round focused on ML system architecture. These candidates are expected to demonstrate a deeper understanding of inference systems at scale, distributed training strategies, and designing systems that integrate closely with Tesla’s proprietary hardware such as the Dojo supercomputer. The expectation is not only technical depth but also an ability to drive strategy and mentor junior engineers while contributing to Tesla’s broader machine learning roadmap.
What Questions Are Asked in a Tesla Machine Learning Engineer Interview?
Here are some of the Tesla Machine Learning Engineer interview questions that may recur through your interview stages:
Coding / Technical Questions
In Tesla’s machine learning interviews, technical coding questions often test your grasp of fundamental ML algorithms, numerical stability, and real-time system constraints.
1. Build a model to bid on a new unseen keyword using historical data
Begin by exploring historical keyword features like click-through rates, cost-per-click, and competition level. Use a supervised learning model such as gradient boosting or random forest to predict expected revenue or conversion rate. Consider feature engineering with time-series trends. This is relevant for Tesla ML engineers optimizing ad or bidding systems in online platforms.
2. Determine if 1 million Seattle ride trips sufficiently represent all Lyft data
Use statistical sampling techniques and exploratory data analysis to test representativeness, such as comparing means, variances, or feature distributions between samples and the population. Dimensionality reduction techniques like PCA could help visualize coverage. This builds your ability to assess training data quality, which is critical in ML pipelines.
3. Build a fraud detection model and text messaging alert system
Implement classification models like logistic regression or random forest to detect anomalies in transactions. Incorporate precision-recall trade-offs and use imbalanced data techniques like SMOTE. Pair this with rule-based logic for automated messaging. Fraud and anomaly detection are vital in autonomous systems where Tesla operates.
4. Explain why measuring bias is important in prediction models
Bias in prediction models can lead to systematic under- or over-prediction, especially when training data isn’t representative. Analyze bias using tools like residual plots or calibration curves. Bias detection is especially important in domains like autonomous driving where predictions affect physical outcomes.
5. Decide how to handle missing square footage data in housing models
Apply imputation strategies such as mean, median, or model-based imputation, depending on the data’s missingness mechanism. Consider building a predictive model for square footage using correlated features. Handling missing data robustly is fundamental to ensuring model reliability.
6. Determine how to provide rejection reasons for a classification model
Use interpretable models like decision trees or integrate post-hoc explanation methods such as SHAP or LIME. You can return the most influential features leading to rejection. Model interpretability is essential when deploying ML models in consumer-facing products.
7. Identify methods to increase recall in product search algorithms
Consider lowering classification thresholds, using ensemble models, or leveraging query expansion and synonym mapping. You may also redesign the feature space for better generalization. Optimizing recall directly affects user experience in product or service search functionality—relevant to Tesla’s UX.
8. Implement batch normalization from scratch
Start by understanding the forward and backward passes of batch normalization as introduced in deep learning frameworks. Implement the normalization using basic NumPy operations, paying attention to numerical stability and train/inference mode differences. Test your implementation using toy data and compare results with PyTorch or TensorFlow. This question tests your core understanding of model training internals, which is critical for Tesla’s deep learning applications.
9. Optimize inference latency in a machine learning pipeline
Explore optimization strategies such as model quantization, pruning, and conversion to ONNX or TensorRT formats. Profile the model using tools like NVIDIA Nsight or TensorBoard to find bottlenecks. Consider batching, input preprocessing, and hardware acceleration techniques. This question assesses your ability to deploy performant ML models, directly applicable to Tesla’s real-time inference systems.
ML System-Design Questions
Tesla’s ML system-design questions evaluate how you architect scalable, real-time machine learning pipelines that integrate with hardware and software systems. For example, you may be asked to design a vision pipeline for real-time lane detection; discuss data gathering, model versioning, and scalability.
10. Design a classifier to predict the optimal moment to insert a commercial break in a video
Structure this system to include video segmentation, scene analysis, and user engagement modeling. Use computer vision models and temporal features to identify natural breakpoints in the content. Build a pipeline that supports retraining and A/B testing to optimize revenue impact. While the use case is different, the system architecture mirrors Tesla’s real-time perception challenges.
11. Describe the process of building a restaurant recommendation engine
Design the pipeline using collaborative filtering or deep learning-based recommenders with inputs like location, cuisine, and user preferences. Incorporate feedback loops for personalization and online learning. Think about cold start problems and system scaling for millions of users. This tests your understanding of recommendation system architecture under production constraints.
12. Design a recommendation algorithm for Netflix’s type-ahead search bar
Incorporate user history, query embedding, and prefix matching with real-time ranking. Use approximate nearest neighbor search to keep latency low and build caching strategies. Architect the system to update frequently with trending data. The speed and precision required align with Tesla’s need for real-time decision-making in embedded systems.
13. Create a recommendation engine for rental listings on a platform like Airbnb
Use both user-item interaction data and listing metadata to build hybrid recommendation models. Incorporate location-based ranking and seasonal trends. Design infrastructure for model retraining and A/B testing. Though not vision-based, the scaling and ranking components apply to Tesla’s digital UX systems.
14. Design a podcast search engine with transcript support
Build pipelines for audio transcription, NLP-based indexing, and semantic search. Choose a storage format that allows efficient full-text search across episodes. Consider latency, data freshness, and result relevance. Tesla’s use of multimodal data (e.g. audio, camera) requires similar search and retrieval architecture.
15. Design a machine learning system to minimize wrong order deliveries in food delivery
Identify root causes using historical data and train classification models for error prediction. Integrate a real-time feedback mechanism and dashboard for operators. Make sure the system scales to multiple delivery zones. System design for reducing operational errors is applicable to Tesla’s logistic and supply systems.
16. Design a YouTube video recommendation algorithm for the homepage
Blend collaborative filtering, deep learning, and content-based approaches to personalize recommendations. Optimize for user engagement, diversity, and freshness while controlling for filter bubbles. Ensure the system is modular and can support frequent mod
Behavioral / Culture-Fit Questions
Tesla values candidates who take ownership of their work and can make decisions under pressure and in urgent situations. Always use the STAR method to frame your experiences in alignment with Tesla’s values.
17. Tell me about a time you had to work on a high-stakes technical project under a tight deadline
Describe the context, your specific responsibilities, and how you prioritized tasks under time pressure. Emphasize your communication with cross-functional teams and how you ensured quality didn’t suffer. Reflect on what you learned from the experience. Tesla values individuals who can thrive in fast-paced, high-impact environments.
18. How do you handle disagreements on model or system design with senior engineers or researchers?
Explain your approach to presenting evidence, listening actively, and adapting your point of view. Provide a real example where data and humility helped resolve a conflict. Emphasize your ability to balance assertiveness with collaboration. This reflects Tesla’s emphasis on high-integrity decision-making and teamwork.
19. Describe a time when you learned a new skill quickly to solve a problem
Set up the scenario where you lacked a specific skill or tool required to finish a task. Show how you taught yourself under pressure and integrated that knowledge into a working solution. Share the impact on the project and your team. Tesla looks for fast learners who take initiative and ownership.
20. What motivates you to work at Tesla, and how does your personal mission align with ours?
Show deep understanding of Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Connect your personal values and career goals to that mission. Discuss specific Tesla projects or innovations that inspire you. Mission alignment is core to Tesla’s hiring culture.
21. Tell me about a time you failed, and how you handled it
Provide a concise but honest story of failure, highlighting what went wrong and what you learned. Emphasize resilience, accountability, and how you implemented changes after the incident. Reflect on how it made you better in your role. Tesla embraces those who learn from mistakes and push forward.
22. How do you manage stress and uncertainty in high-pressure environments?
Discuss techniques or habits you use to stay grounded when timelines are tight or stakes are high. Share an example that demonstrates composure and clear thinking. Focus on decision-making and maintaining momentum. Tesla values candidates who remain effective in dynamic, ambiguous situations.
23. Describe how you’ve contributed to a culture of continuous improvement
Share how you identified areas for process or performance improvement within a team. Explain how you led or contributed to changes that improved outcomes. Highlight collaboration, measurement, and iteration. Tesla thrives on iterative learning and systems optimization.
How to Prepare for a Machine Learning Engineer Role at Tesla
Preparing for a machine learning engineer role at Tesla requires a blend of deep technical knowledge, strong system design skills, product intuition, and clear communication, all tailored to the company’s mission-driven and high-performance environment.
Master Core ML & Deep Learning
To succeed, you’ll need thorough mastery of deep learning fundamentals, including CNNs, DQNs, transformers, as well as practical skills in optimizing inference and deployment performance. Not only focus on the theory, you also need to deep dive into application with Tesla’s product. As machine learning theory can be overwhelmed, reviewing cheatsheet before interivews are widely recommended for refreshing core concepts and code.
Practise ML System-Design
Tesla interviewers commonly probe end‑to‑end system thinking. You’ll need to craft scalable ML designs covering data pipelines, feature stores, A/B testing safeguards, and inference infrastructure. The Tesla ML interview frequently includes system-design questions like “design a pipeline for tackling biased datasets” or “how would you serve models on edge devices?”. Study architecture trade-offs like consistency vs. latency, versioning, and production robustness. Tesla also values hands-on knowledge of system-level behaviors in cluster environments—think CUDA, GPU‑CPU optimization, and latency throughputs.
Study Tesla’s Mission & Metrics
Beyond technical proficiency, Tesla emphasizes candidates’ alignment with its mission and familiarity with key AI performance metrics, such as energy efficiency, autonomous functionality, and system safety. To build strong product intuition and stay informed about Tesla’s current technological focus, you can study recent AI Day presentations and understand metrics like Dojo’s training throughput and inference latency. Practicing scenario-based questions like “designing a solution for predicting vehicle range” or “enhancing object detection in autonomous driving” can help you effectively articulate technical concepts within real-world applications.
Mock Interviews & Feedback
Tesla machine learning jobs demand a high level of technical expertise combined with strong verbal communication skills. Mock interviews with peer feedback are a critical part of effective preparation. Verbalizing your approach to machine learning pipelines and system design will help you builds clarity and confidence. Make it a habit to whiteboard the entire ML lifecycle, from data ingestion and preprocessing, through model training and evaluation, to deployment and real-time monitoring. This end-to-end thinking ensures you can articulate scalable, production-ready solutions clearly and efficiently.
Conclusion
Landing a machine learning engineer role at Tesla requires more than just technical skill—it demands a strong alignment with Tesla’s mission to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy, as well as the ability to communicate clearly and think systemically. Structured preparation, from mastering core ML concepts to practicing system design and mock interviews, is key to performing well across Tesla’s rigorous interview stages.
For a complete view of the Tesla hiring journey, be sure to check out our Tesla Interview Process Guide and explore role-specific insights on our Data Scientist and Data Engineer preparation pages.
