Wharton Study Says 74% of Companies Get Positive Returns from GenAI
GenAI Delivers Real Returns
As artificial intelligence continues to transform business operations, AI spending is soaring. Gartner forecasts global AI spending will reach nearly $1.5 trillion in 2025 and exceed $2 trillion in 2026, with investments expanding beyond tech giants to include Chinese companies and new AI cloud providers.
Yet not all value is created equal. An MIT study on AI and business use from August 2025 found that only 5% of enterprises successfully made AI pilots useful in delivering efficiency and improving the bottom line.
New research from the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School presents a more optimistic picture. The report, building on studies from 2023 and 2024, reveals that 74% of enterprises measuring ROI from generative AI are already seeing positive returns. While results vary across industries and company sizes, the findings show genAI has moved from experimentation to measurable business impact.
From Metrics to Measurement: GenAI Adoption Matures
The Wharton report, entitled Accountable Acceleration: Gen AI Fast-Tracks into the Enteprrise, reveals a crucial shift from tracking usage to measuring ROI. This trend reflects genAI’s evolution from exploration and experimentation in 2023-2024 to more disciplined adoption in 2025.
Usage has thus reached mainstream levels: 82% use genAI weekly, while 46% integrate it daily into repeatable tasks—a 17 percentage point year-over-year increase. IT, Purchasing/Procurement, and Marketing/Sales are the industries leading adoption rates.

More significantly, business leaders now report greater familiarity with AI adoption, with nearly three-quarters (72%) tracking structured ROI metrics including profitability, throughput, and performance.
Long-term optimism remains strong, as 88% expect budget increases in the next 12 months. It’s important to note that investments are also shifting from one-off pilots to performance-justified budgets. Growing allocation to internal R&D points to businesses seeking more customized AI-powered solutions.
The ROI Reality: Who’s Winning and Why
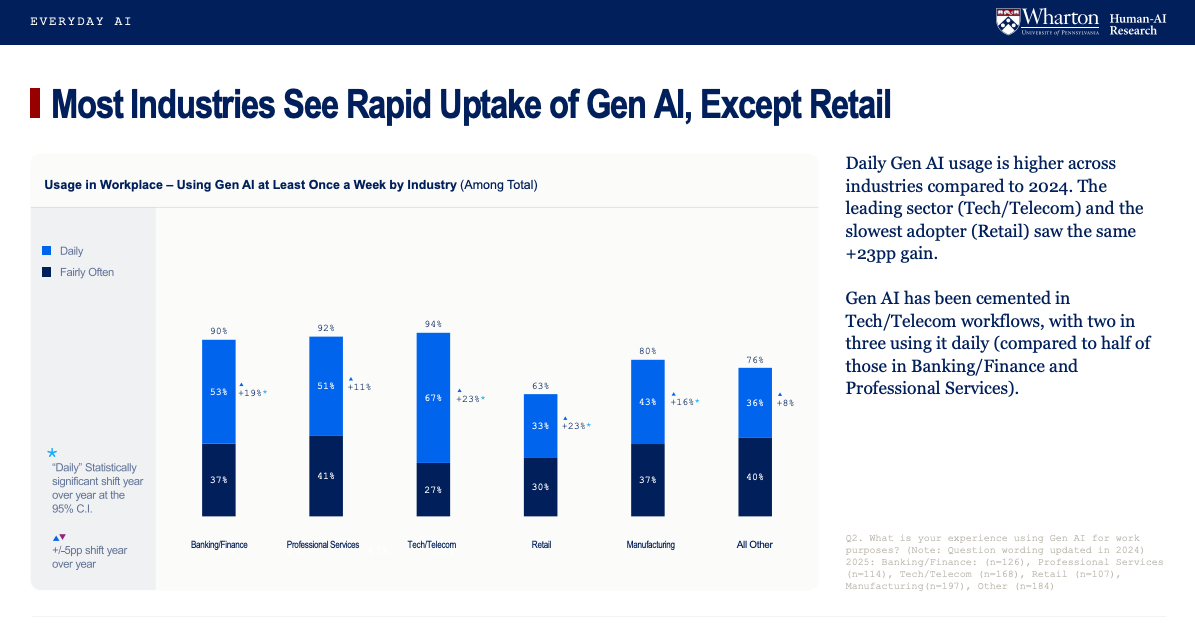
The report reveals clear winners in turning AI hype into value. Tech/Telecom leads with 88% positive ROI, while Banking/Finance and Professional Services follow at 83%.
These industries report ≥90% weekly genAI use, with success rooted in harnessing AI for practical productivity utility in core workflows: data analysis (73%), document/meeting summarization (70%), and document editing/writing (68%).
Moreover, employee productivity remains the top measured benefit for the third consecutive year, followed by quality improvements, enhanced customer experience, and optimized business operations.
In contrast, Retail (54%) and Manufacturing (75%) face slower returns. These “laggards”—concentrated among those using genAI weekly or less—encounter organizational restrictions, skepticism, and slower integration, highlighting the widening divide between leaders successfully embedding AI and those risking falling behind.
The People Challenge: Where Success and Struggle Meet
Despite positive ROI numbers, human capital factors remain the decisive constraint. While 89% view genAI as skill-enhancing, 43% worry about declining skill proficiency.
Training investment is also softening despite growing need, and organizations remain split between internal training and external hiring—neither approach fully resourced.
The biggest barriers are recruiting advanced genAI talent (49%), delivering effective training (46%), managing morale (43%), and navigating change management (41%).
The report suggests 2026 could mark an inflection point from acceleration to performance at scale. Those pulling ahead share common traits: leadership commitment, disciplined ROI measurement, and deliberate alignment of talent, training, and trust with their investments.
As genAI proves its value, success increasingly depends not on the technology itself, but on how well organizations prepare their people to use it. Leaders must also equip themselves with the capacity to regularly monitor their investments and resulting performance to identify room for improvement.
