Google Business Intelligence Interview: Inside the SQL, Case, and Dashboarding Rounds
Introduction
At Google, data is more than information. It is the foundation of every decision. Business intelligence (BI) analysts and developers transform massive datasets into actionable insights that guide billion-dollar products and global strategies. With the BI market projected to surpass $40 billion by 2030, demand for analysts who can turn raw data into growth decisions continues to surge. Whether it’s improving ad performance, optimizing YouTube recommendations, or tracking Google Cloud revenue, BI teams shape how Google grows.
The Google business intelligence interview tests how well you can analyze, visualize, and communicate complex data. Expect a mix of SQL, data modeling, and problem-solving questions that evaluate your ability to translate analytics into strategy. This guide breaks down everything you need to prepare, including the interview process, sample BI interview questions, preparation strategies, and compensation details.
What does a Google business intelligence analyst do?
A Google business intelligence analyst bridges the gap between data and decision-making. They collect, clean, and model data from multiple sources, then build dashboards and reports that support teams across engineering, product, sales, and marketing.
Day to day, they:
- Build scalable data pipelines and manage BI tools such as Looker, Tableau, or Google Data Studio
- Design and maintain dashboards that track KPIs across user engagement, marketing spend, and product performance
- Collaborate with stakeholders to translate business goals into measurable data models
- Automate reporting workflows to make data accessible and decision-ready
- Drive strategic recommendations using data storytelling and visualization best practices
In essence, business intelligence analysts ensure that Google’s decisions, from global marketing campaigns to product launches, are grounded in accurate, accessible data.
Why this role at Google
Working in business intelligence at Google means operating at the intersection of data, technology, and impact. You will analyze petabytes of information generated by billions of users and apply it to products used worldwide. What makes the role stand out is Google’s emphasis on innovation and learning, where BI analysts and developers collaborate with data engineers, scientists, and product leaders while working with advanced tools like BigQuery, LookML, and predictive analytics. The company’s data culture encourages experimentation, and your insights directly influence how Google prioritizes growth opportunities. If you are passionate about building systems that help the world’s most data-driven company make smarter decisions, this is one of the most rewarding BI roles in tech.
If you’re still exploring other analytics or engineering paths at the company, check out our complete Google interview guide for a breakdown of different roles, teams, and interview structures across Google.
Google Business Intelligence Interview Process
The Google business intelligence interview process is designed to measure both analytical rigor and communication skill. It tests how well candidates can extract meaning from data, translate findings into actionable insights, and collaborate across technical and business teams. The process typically runs for four to six weeks and consists of several stages that progressively deepen in technical and strategic scope.
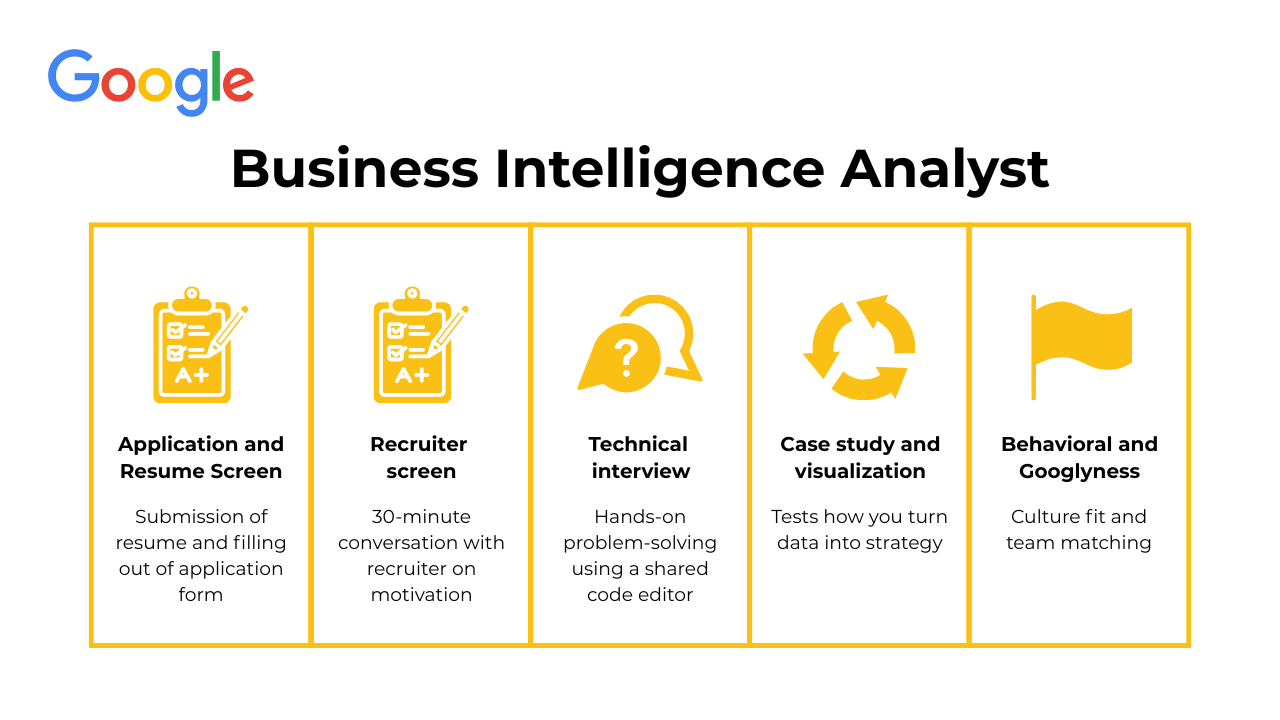
Application and resume screen
Google reviews your resume for data fluency and measurable business impact. Experience with SQL, dashboarding tools (Looker, Tableau), and end-to-end data workflows stands out.
Strengthen your profile by highlighting projects with clear outcomes, such as how you:
- Improved decision-making speed with a dashboard
- Reduced reporting latency with a new data model
- Increased campaign efficiency through insights
Tip: Use strong action verbs such as “built,” “optimized,” and “implemented.” Mention the tools, datasets, and scale you worked with. Recruiters will quickly notice achievements tied to measurable outcomes and collaborative projects.
Recruiter screen
If your resume is shortlisted, you will be invited to a recruiter conversation that usually lasts about 30 minutes. This stage helps Google confirm that your background, interests, and experience align with the business intelligence function. The recruiter will walk you through the timeline, clarify what teams are hiring, and gauge your familiarity with Google’s analytics environment.
You can expect light behavioral questions about past projects and your approach to working with cross-functional teams. The tone is conversational, but recruiters are attentive to how clearly and confidently you explain your work.
Tip: Be ready to summarize your most impactful project in one or two concise sentences. Focus on what you did, how you measured success, and why it mattered to the business. Asking thoughtful questions about the team’s priorities or tools also demonstrates curiosity and initiative.
Technical interview
The technical interview is the most rigorous stage. It tests your ability to query data, model datasets, and think analytically, usually with a current business intelligence analyst, engineer, or data scientist. You will write and debug SQL in a shared document or virtual whiteboard. Typical topics include joins, subqueries, window functions, schema design, query optimization, data integrity, and sometimes ETL logic or performance tuning.
Interviewers look for accuracy, efficiency, and clear reasoning. Explain your steps out loud, and if you make a mistake, correct it transparently and walk through how you fixed it.
Tip: Practice live-coding SQL while narrating your thought process. You can use public datasets or mock schemas to simulate real business problems. Review Google’s ecosystem tools like BigQuery or LookerML, since interviewers often reference them in examples.
Want to practice real case studies with expert interviewers? Try Interview Query’s Mock Interviews for hands-on feedback and interview prep. Book a mock interview →
Case study and visualization round
This round tests how you turn data into strategy. You may explore a scenario like diagnosing a drop in Google Ads revenue or designing a YouTube metrics dashboard.
You will be assessed on:
- How you structure the problem
- The metrics you prioritize
- How you visualize trends for stakeholders
- Your ability to explain trade-offs and decisions
Tip: Start by restating the problem in your own words to ensure understanding, then move step by step from goal to metric to visualization. Use frameworks such as AARRR (Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, Revenue) or a metrics tree to organize your thoughts. End by summarizing insights and explaining how they could inform product or business strategy.
Behavioral and Googlyness interview
The behavioral interview examines how you communicate, collaborate, and handle challenges. Google defines “Googlyness” as a mix of curiosity, humility, teamwork, and creativity under pressure. The interviewer will explore how you respond to uncertainty, resolve conflicts, and build relationships across diverse teams.
Expect open-ended questions that encourage storytelling. You may be asked about a time when you influenced a decision with data, handled competing deadlines, or learned from a project that went wrong. The goal is to understand your thought process and professional maturity, not just your achievements.
Tip: Structure your answers with the STAR framework: Situation, Task, Action, Result. Include metrics or outcomes when possible. Show how you balance analytical reasoning with empathy and communication—both are essential qualities for a business intelligence role at Google.
Hiring committee review and offer
After interviews conclude, each interviewer submits detailed feedback. An independent hiring committee then reviews all assessments to ensure consistency and fairness across candidates. This step is unique to Google and helps maintain high hiring standards.
If the committee approves your profile, you move to the team-matching phase. Different groups, such as Google Cloud, Ads, or YouTube, may express interest based on your skills and experience. You might have short conversations with team leads to confirm fit before receiving your final offer.
Offer components typically include:
- Competitive base salary
- Annual bonus
- Stock units with vesting
- Professional development and benefits
Tip: Once you receive the offer, review all components carefully, including stock vesting schedules and relocation support if applicable. You can also ask your recruiter about growth paths for business intelligence roles, such as transitions into analytics engineering or product data strategy.
Need 1:1 guidance on your interview strategy? Interview Query’s Coaching Program pairs you with mentors to refine your prep and build confidence. Explore coaching options →
Google Business Intelligence Interview Questions
The Google business intelligence interview combines technical rigor with strategic thinking. It is designed to assess how effectively you can work with data, understand business needs, and communicate insights across different audiences. Questions typically span SQL, data modeling, dashboarding, product analytics, and behavioral scenarios.
Interviewers are not just looking for technical precision. They want to see how you interpret results, prioritize metrics, and frame your reasoning in a structured, business-oriented way. Below are the three major categories you can expect during the process.
SQL and data analysis interview questions
This section focuses on your ability to manipulate, query, and analyze large datasets efficiently. Expect to write SQL queries from scratch, optimize existing queries, and interpret database schemas. Questions often simulate real Google scenarios such as analyzing product performance, identifying trends, or troubleshooting data inconsistencies.
Interviewers will look for clean logic, scalability, and awareness of performance trade-offs. You may also encounter questions that test your understanding of joins, window functions, aggregations, and handling missing data.
-
This question tests your understanding of ranking and partitioning logic using window functions. You will need to rank employees by salary within each department and handle cases where there are fewer than three employees. Efficient query structuring and sorting order are key to accuracy.
Tip: Use
RANK()orDENSE_RANK()over department partitions and confirm how to handle ties in salary before writing your query. -
This problem evaluates your ability to identify missing or unmatched records. You’ll need to perform an anti-join or subquery to find neighborhoods without corresponding users. It’s a test of how you handle data completeness and null values.
Tip: Use a
LEFT JOINcombined with aWHERE user_id IS NULLcondition or aNOT EXISTSclause for optimal clarity. -
You’ll need to work with timestamps to isolate the most recent transaction each day. This tests your use of
ROW_NUMBER()or aggregation functions alongside date extraction. Accuracy in ordering and partitioning is essential.Tip: Apply
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY DATE(created_at) ORDER BY created_at DESC)and filter for the first row per partition. -
This question measures your ability to rank user activity per day and manage grouped data with window functions. You must carefully partition by date and order by download counts to generate accurate results.
Tip: Combine
RANK()withPARTITION BY dateand verify whether ties should be included or broken using a secondary key like user ID. -
This question assesses your ability to categorize data conditionally and group it by time periods. You will need to use
CASE WHENstatements to classify departments and aggregate by quarter.Tip: Use date truncation functions like
DATE_TRUNC('quarter', date)and remember to exclude quarters with no transactions. -
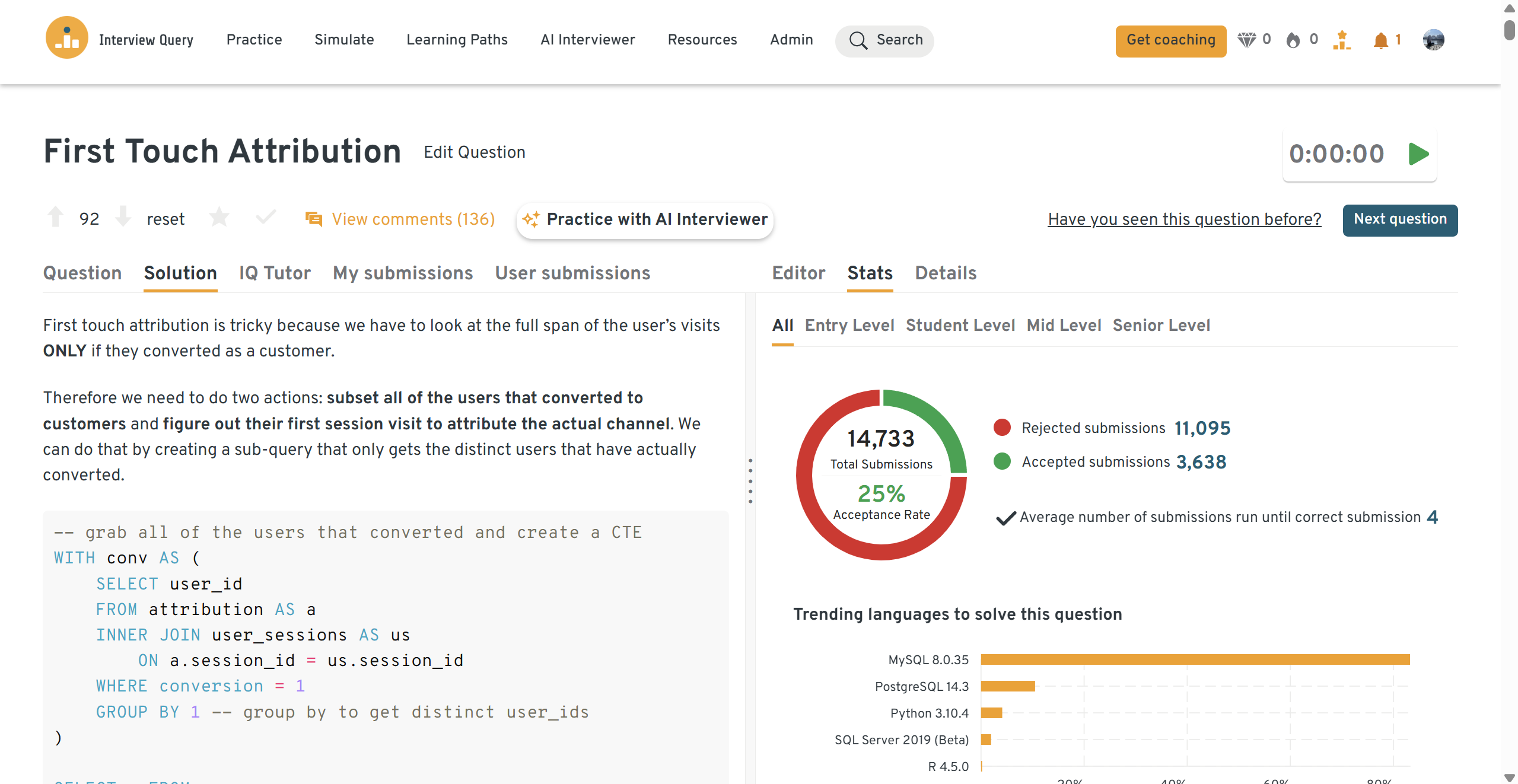
You will join both tables, identify the first channel interaction for each user, and associate it with the conversion. This question tests your understanding of joins, aggregation, and ranking based on chronological order.
Tip: Use
MIN(session_date)per user andJOINit back to the attribution table to pinpoint the correct first-touch channel.You can practice this exact problem on the Interview Query dashboard, shown below. The platform lets you write and test SQL queries, view accepted solutions, and compare your performance with thousands of other learners. Features like AI coaching, submission stats, and language breakdowns help you identify areas to improve and prepare more effectively for data interviews at scale.
Business case and visualization interview questions
This section assesses your ability to think beyond the numbers. You will be given a scenario or dataset and asked to define key metrics, diagnose trends, or design a dashboard. The goal is to evaluate whether you can transform complex data into actionable insights for decision-makers.
Questions may cover KPI design, experiment measurement, or visualization trade-offs. You might also be asked to propose a solution for a hypothetical product issue, such as declining user engagement or inefficient ad performance.
-
This question evaluates your ability to investigate churn and engagement issues using behavioral and cohort analysis. You should describe how you would segment users, identify common drop-off patterns, and design targeted experiments or campaigns to win them back.
Tip: Combine quantitative data (usage logs, subscription data) with qualitative insights (user feedback or surveys) to propose actionable retention strategies.
-
The interviewer wants to see how you balance creativity with data-driven decision-making. You should define success metrics, estimate potential adoption, and assess engineering trade-offs and business impact.
Tip: Start by framing the hypothesis (why this feature matters), then outline an A/B test plan to validate user interest before committing development resources.
You’re analyzing YouTube’s new dashboard that shows creators their real-time performance metrics. How would you evaluate whether the dashboard is successful?
This question focuses on product analytics and visualization effectiveness. You need to measure engagement with the dashboard, understand how creators use it to make decisions, and assess its impact on content performance.
Tip: Track metrics such as dashboard usage frequency, time spent per session, and subsequent video uploads or engagement changes.
Google Ads is planning to introduce a new automated campaign optimization feature. How would you measure its effectiveness?
You should discuss how you’d design an experiment to test the feature’s impact on advertiser ROI, click-through rate, and campaign cost efficiency.
Tip: Define both primary metrics (conversion rate improvement) and guardrail metrics (budget stability) to ensure the feature improves performance without unintended side effects.
Imagine you’re building a cross-departmental dashboard for Google Cloud leadership to track product adoption across industries. How would you design and prioritize the metrics?
This question evaluates your ability to translate business objectives into data visualization. You should describe how you would gather stakeholder requirements, ensure metric consistency, and organize the dashboard for clarity.
Tip: Focus on clear segmentation (by region, industry, or account tier) and add drill-down capabilities for deeper exploration.
You’re given a dataset showing Google Play app downloads by category and region. How would you visualize this data to identify global growth opportunities?
You should describe how you would use geographic heatmaps and trend visualizations to uncover market potential and performance gaps. The goal is to show how visualization aids strategic planning.
Tip: Highlight trends across both time and geography, and recommend actions such as localizing app content or adjusting marketing focus by region.
Google is considering shifting ad spend from YouTube to Shorts. How would you analyze whether this is a good move?
This question combines business case analysis and experiment design. You should outline how you’d compare user engagement, ad performance, and revenue efficiency across both platforms.
Tip: Use an A/B testing or cohort approach to control for audience differences, and evaluate both short-term metrics (CTR, watch time) and long-term retention effects.
Behavioral and cross-functional interview questions
The behavioral portion of the interview explores how you approach teamwork, ambiguity, and influence without authority. Google’s BI teams operate cross-functionally, so you will often be asked about how you collaborate with product managers, engineers, and executives.
Questions typically revolve around stakeholder communication, project prioritization, and conflict resolution. Interviewers assess your interpersonal skills and ability to adapt in a fast-paced, data-driven environment.
Why do you want to work at Google?
This question helps interviewers understand your motivation and whether it aligns with Google’s mission to make information universally accessible and useful. They want to see that you’ve done your research on the company’s data culture and analytics-driven approach to decision-making.
Tip: Connect your personal goals with Google’s impact areas, such as AI, cloud infrastructure, or scalable analytics. Show that you’re motivated by solving problems at a global scale.
Sample Answer: I’ve always admired how Google uses data to make products more intuitive. In my previous role, I built dashboards that helped reduce marketing spend inefficiencies by 18 percent. I want to bring that same data-driven thinking to Google’s business intelligence team to help improve decision-making across global operations.
Describe a time when your analysis directly influenced a business decision.
Google looks for impact-driven analysts who can translate insights into action. This question evaluates how you use data storytelling to drive measurable change.
Tip: Choose an example with quantifiable results that demonstrate business impact or process efficiency.
Sample Answer: I led a project analyzing user churn for a subscription app. My analysis revealed that late payment reminders were driving cancellations. After adjusting the email cadence, churn dropped by 14 percent within two months, directly improving retention revenue.
Tell me about a time you disagreed with a team member on an analytical approach. How did you resolve it?
Interviewers are assessing your ability to manage conflict constructively and maintain professionalism. As a BI analyst, you’ll often collaborate across engineering, marketing, and operations teams.
Tip: Focus on how you balanced logic with empathy and prioritized data-backed reasoning over personal opinion.
Sample Answer: During a pricing analysis, my teammate wanted to use average order value as our main metric, while I believed median price better captured skewed data. I suggested running both analyses. The hybrid model increased pricing accuracy by 11 percent and improved forecast reliability.
How do you communicate complex findings to a non-technical audience?
Google expects BI analysts to simplify complex data into actionable insights. This question gauges your ability to bridge the gap between analytics and business strategy.
Tip: Explain how you tailor your message to the audience, using visuals or examples instead of raw numbers.
Sample Answer: When presenting campaign performance to executives, I replaced SQL-heavy slides with visual dashboards summarizing key KPIs. This helped leadership understand the ROI story quickly and led to faster budget approvals, reducing review time by 30 percent.
Tell me about a time you made a mistake in your analysis. What did you learn?
Google values transparency and accountability. This question tests whether you can take ownership and improve your processes after setbacks.
Tip: Choose an example where the error led to learning or process improvement, not one that caused significant harm.
Sample Answer: I once misclassified ad campaign data due to a missing join condition, which skewed conversion metrics. I immediately identified the issue, corrected the dataset, and implemented validation checks. This process reduced similar data errors by 40 percent in later projects.
Describe a time you had to deliver results under tight deadlines.
Google operates in high-pressure environments, and interviewers want to know how you handle multiple priorities efficiently.
Tip: Highlight how you stayed organized, leveraged automation, or coordinated with others to meet deadlines without sacrificing accuracy.
Sample Answer: During a quarterly reporting cycle, I had 48 hours to consolidate marketing data across five regions. I automated part of the ETL process using SQL scripts, which saved eight hours of manual work and allowed the team to deliver insights ahead of schedule.
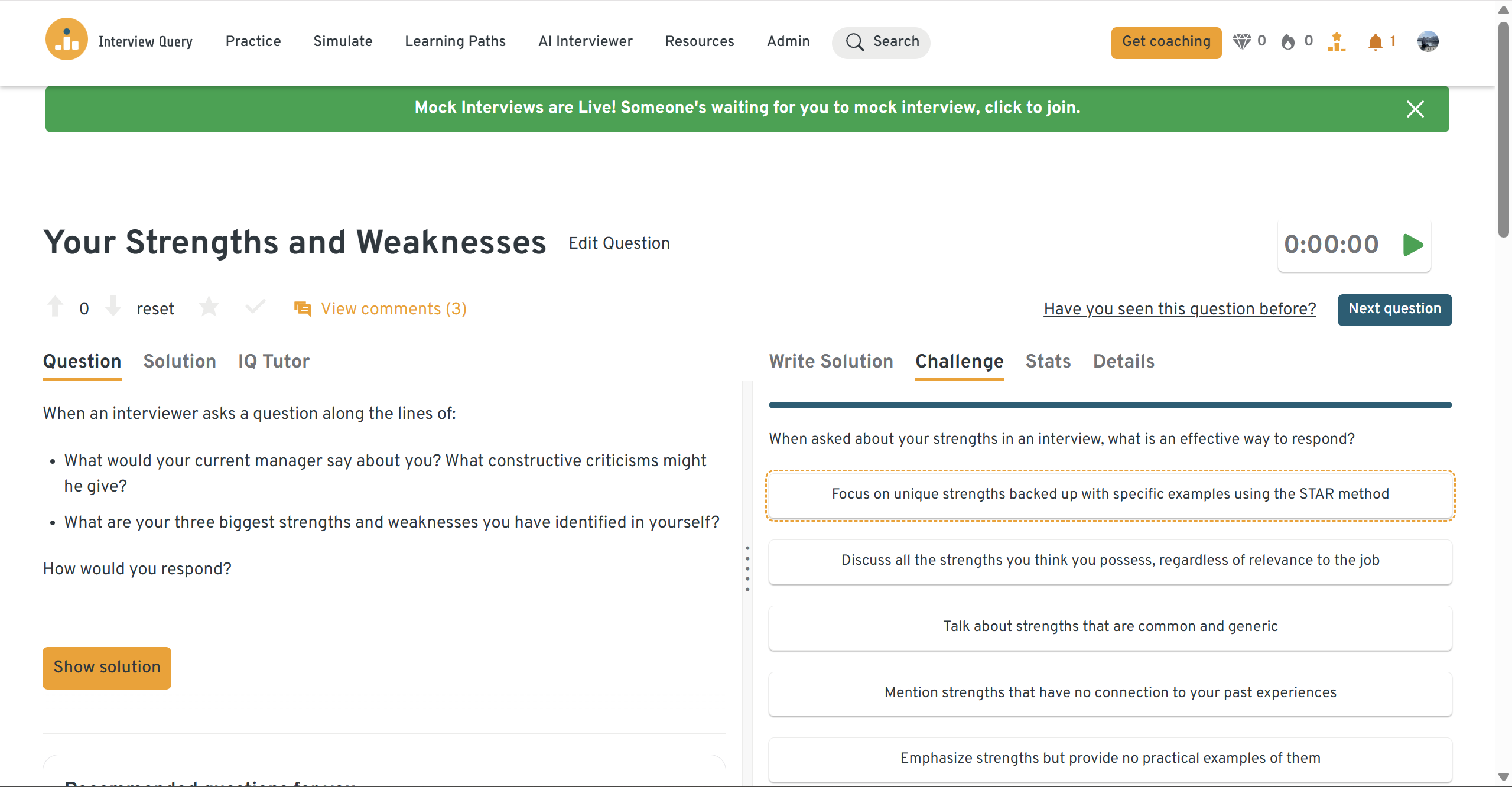
What would your current manager say about you? What constructive criticisms might they give?
This question tests your self-awareness and how you handle feedback. Google values humility and the ability to learn from experience, especially in fast-paced data environments.
Tip: Choose a strength that aligns with BI work (analytical thinking, collaboration, attention to detail) and a development area that shows you’re proactive about improving.
Sample Answer: My manager would say that I’m methodical and reliable when handling complex datasets. A past area for improvement was communicating findings more visually. I took a visualization course and redesigned our reporting templates, which reduced meeting time spent on explaining results by 25 percent.
Head to the Interview Query dashboard to practice this question hands-on. With built-in SQL testing, performance analytics, and AI-guided tips, it’s one of the best ways to sharpen your skills for Meta’s data interviews.
Want more challenges? Test your skills with real-world analytics challenges from top companies on Interview Query. Great for sharpening your problem-solving before interviews. Start solving challenges →
For inspiration, you can also read this success story of a candidate who landed a job at Google during a recession, which walks through how they positioned their experience, handled interviews, and navigated a tough job market.
How to Prepare for a Google Business Intelligence Interview
Succeeding in a Google business intelligence interview means showing that you can turn data into business decisions. The best preparation strategy combines technical depth, analytical structure, and strong storytelling. Here are the most effective ways to prepare.
Master SQL and data manipulation
Google’s BI interviews revolve heavily around SQL. You will be expected to extract, transform, and interpret large datasets with precision. Review joins, subqueries, window functions, and aggregation logic. If you’re just ramping up on SQL or wondering how long it realistically takes to get interview-ready, this guide on how long it takes to learn SQL breaks down timelines, study paths, and practice strategies.
Tip: Practice solving SQL problems in shared documents while explaining your thought process aloud. Interviewers want to see not just accuracy but also clarity in reasoning.
Understand data modeling and ETL workflows
Google prioritizes candidates who know how to structure data for long-term scalability. Be ready to discuss how you would design tables, clean datasets, and automate reporting pipelines.
Tip: Review how Google’s data stack works with BigQuery and LookML. Practice explaining why a certain schema or normalization approach improves data integrity and reporting efficiency.
Get comfortable with visualization tools and dashboard design
BI analysts at Google create dashboards that executives use to make high-impact decisions. Familiarize yourself with Looker, Tableau, or Google Data Studio. Understand how to present complex metrics simply.
Tip: Design mock dashboards using sample datasets. Focus on hierarchy, layout clarity, and how each chart links to a specific business question.
Practice business case analysis
Expect scenarios that test how you connect data to strategy. You might be asked to identify why user engagement dropped or how to measure the success of a new feature.
Tip: Use frameworks like metrics trees or AARRR (Acquisition, Activation, Retention, Referral, Revenue). Start with the goal, identify measurable indicators, and explain what actions you would take based on your findings.
Focus on metrics that drive Google’s products
Interviewers appreciate candidates who show familiarity with Google’s ecosystem. Understand metrics relevant to Ads, Cloud, or YouTube, such as click-through rate, watch time, churn rate, and cost per acquisition.
Tip: When discussing a project, relate it to how Google tracks growth, efficiency, or engagement. Use product-relevant examples like measuring campaign ROI or optimizing conversion funnels.
Develop strong communication and stakeholder management skills
BI analysts translate data insights for engineers, marketers, and executives. You will need to explain technical findings to non-technical teams.
Tip: Practice simplifying complex analyses into two-sentence summaries. End each explanation with a clear business implication, such as “This trend suggests we should reallocate ad spend to mobile users.”
Review statistics and analytical reasoning
While Google BI roles are not as math-heavy as data science positions, a working knowledge of correlation, variance, and significance testing can strengthen your analysis.
Tip: Be prepared to interpret results, explain the difference between correlation and causation, and justify when statistical testing is necessary in a business context.
Conduct mock interviews and get feedback
Simulate real interview settings by walking through SQL challenges or case studies with a peer or mentor. Beyond live mock sessions, you can also rehearse with Interview Query’s AI interview tool, which simulates BI-style questions and gives feedback on your answers.
Tip: Record your mock sessions and evaluate your pacing, clarity, and ability to explain your logic under time pressure.
Review your own projects and quantify your impact
Many candidates struggle to articulate their past work. Prepare stories that highlight measurable outcomes.
Tip: For every project you include, answer three questions: What problem were you solving? What was your approach? What changed because of your work? Use numbers wherever possible.
Stay updated on Google’s business strategy
Knowing where Google is growing, especially in Ads, Cloud, and AI analytics, helps you frame your responses with context.
Tip: Read Google’s quarterly reports or blog posts about product launches. Mentioning relevant trends during the interview shows awareness and business sense.
*Expert advice: Build your confidence through consistent, structured practice. Combine SQL drills, dashboard-building exercises, and storytelling rehearsals. Google rewards clarity, curiosity, and structured thinking, which stand out as much as technical skill.*
If you prefer a structured roadmap, explore Interview Query’s learning paths, which bundle SQL, analytics, and case-study practice into step-by-step curricula designed for data and BI roles.
Average Google Business Intelligence Analyst Salary
Business intelligence analysts at Google are among the highest-paid data professionals, reflecting the technical depth and cross-functional scope of the role. According to Levels.fyi, total annual compensation in the United States averages $276K for an L5 senior business analyst, with the median package around $253K per year. Compensation includes a mix of base salary, stock grants, and annual performance bonuses, which scale with seniority and team placement.
- L5 (Senior Business Analyst): $276K per year ($180K base + $60K stock + $36K bonus)
- L6 (Staff Business Analyst): Estimated $340K–$420K annually, depending on team and location
- L7 (Senior Staff Business Analyst): Estimated $450K+ with higher stock allocation and bonus components
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
Google’s compensation model rewards long-term contribution and impact. Stock units vest over four years, and annual bonuses are tied to both individual performance and company profitability. Analysts are also eligible for relocation assistance, upskilling budgets, and internal mobility programs, making the BI function both financially and professionally rewarding.
FAQs
How many rounds are in the Google business intelligence interview process?
The process typically includes four to five rounds: a recruiter screen, a technical SQL or analytics assessment, one or two business case interviews, and one behavioral or “Googlyness” round. Some candidates may also go through a team-matching phase before receiving an offer.
How long does the entire interview process take?
On average, it takes between four to six weeks from initial recruiter contact to final offer. This can vary depending on how quickly your interviews are scheduled and whether team matching or additional assessments are required.
What technical skills should I focus on most?
You should prioritize SQL, data visualization, and business intelligence fundamentals like data modeling and ETL pipelines. Google looks for candidates who can move seamlessly from raw data to actionable business insights.
Do I need a background in data science to apply?
A data science background isn’t required, but experience in data analytics, business analysis, or reporting is crucial. What matters most is your ability to interpret large datasets and turn them into clear business recommendations.
What visualization tools does Google use most often?
Google primarily uses Looker and Data Studio for internal dashboards and visualization. However, proficiency in tools like Tableau or Power BI is also valuable since visualization principles translate across platforms.
How is this role different from a data analyst position at Google?
Business intelligence analysts focus more on scaling data infrastructure, building automated dashboards, and reporting business KPIs. Data analysts, meanwhile, often conduct experiments, statistical modeling, and deep ad-hoc analysis.
Does Google hire business intelligence analysts directly from outside tech industries?
Yes, many BI hires come from backgrounds in consulting, finance, or traditional business analytics. As long as you can demonstrate strong SQL proficiency, data storytelling, and stakeholder communication, your industry background is secondary.
What kind of business cases are common in the interview?
Expect questions focused on optimizing product metrics, evaluating campaign performance, or improving team efficiency through better data reporting. You may also be asked to walk through how you would design a dashboard or automate a recurring business report.
Is Python required to become a Google business intelligence analyst?
Python isn’t mandatory for most BI roles, but it can help automate ETL processes and enhance data cleaning or visualization workflows. Having a working knowledge of Python or similar scripting languages gives you an edge in technical rounds.
What is the average compensation for a business intelligence analyst at Google?
According to Levels.fyi, total compensation for BI analysts at Google typically ranges between $140K and $250K per year. This includes base salary, annual bonuses, and equity, with higher packages in cities like San Francisco, Seattle, and New York.
Start Your Google Business Intelligence Interview Prep Today
Breaking into a business intelligence role at Google requires more than just technical skill — it demands the ability to connect data with strategy and communicate insights that drive global decisions. By mastering SQL, business case reasoning, and data visualization, you’ll stand out as a candidate who can turn information into impact.
Take the next step by exploring the Google business intelligence interview question set, scheduling a mock interview, and following the data analytics learning path. With consistent practice and structured preparation, you’ll be ready to ace every round and join Google’s world-class analytics team.
If you’re casting a wider net, our company interview guides cover BI, data, and analytics roles at other top tech firms as well.


