eBay Business Analyst Interview Guide: Process, Sample Questions & Salary Expectations
Introduction
Breaking into a Business Analyst role at eBay means stepping into one of the world’s most dynamic ecommerce platforms, where data isn’t just a resource—it’s the strategy. Whether you’re analyzing GMV trends or optimizing buyer conversion funnels, you’ll be contributing directly to a product used by millions. This guide walks you through eBay’s interview process, question themes, and preparation advice so you can stand out as a candidate.
Role Overview & Culture
Business Analysts at eBay sit at the heart of data-driven decision-making. Day to day, they work with massive volumes of marketplace data to define KPIs, build dashboards, and generate insights that influence teams across Product, Engineering, Finance, and Marketing. Analysts often partner with cross-functional stakeholders to diagnose changes in user behavior, build forecasting models, or measure the impact of new feature rollouts.
What sets eBay apart is its culture of autonomy and experimentation. The company empowers analysts to take ownership of their work and encourages hypothesis-driven thinking. Whether you’re proposing a new dashboard or launching a deep-dive investigation into seller churn, you’ll find space to lead and iterate. Customer-first values are embedded in every decision, and data is the language used to challenge assumptions and unlock growth.
Why This Role at eBay?
A Business Analyst role at eBay is more than a technical position—it’s a chance to make real business impact at scale. With billions of transactions to draw from and a platform that serves both buyers and sellers globally, the analytics possibilities are vast. Analysts gain exposure to a range of domains—from marketing performance to product experimentation—offering rapid learning and professional development.
The role also offers a clear career trajectory, with many starting as Analysts and moving into Senior or Lead roles focused on strategic initiatives and team management. Compensation is competitive, and the work itself is dynamic, measurable, and high-impact. Here’s what to expect from the eBay Business Analyst interview process.
What Is the Interview Process Like for a Business Analyst Role at eBay?
The interview process for Business Analysts at eBay is structured to evaluate both technical skill and business judgment. It typically unfolds in four main stages.
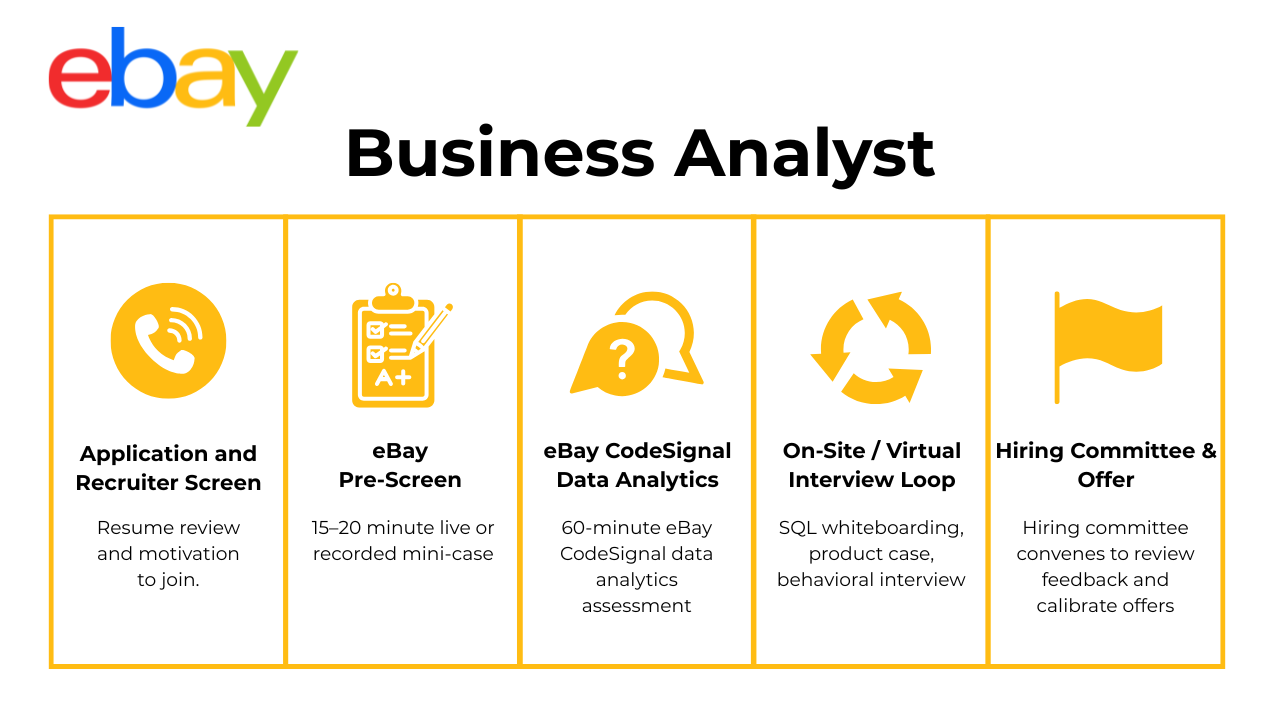
Application & Recruiter Screen
After submitting your application, the first step is a recruiter screen. This conversation focuses on your background, your interest in the role, and your alignment with eBay’s expectations. The recruiter may ask about your experience with SQL, dashboards, or working cross-functionally, and will also touch on basic logistics like location preferences, compensation expectations, and timeline. While not technical, this stage is your chance to clearly communicate how your analytics experience has driven business outcomes.
Technical Screen
The next phase involves a technical assessment, usually delivered as a 30-minute SQL and/or Excel challenge. The SQL questions may involve calculating GMV by category, filtering user events over a time window, or identifying the top sellers in a given timeframe. You’ll be expected to use subqueries, joins, and window functions efficiently, with clean, readable logic. In some cases, you may also receive a mini product case (e.g., diagnosing a metric drop), testing your ability to structure analysis and think critically under time pressure.
Virtual or On-Site Interview Loop
Candidates who pass the technical screen move on to the final interview loop. This stage consists of multiple rounds: a deep-dive SQL/analytics round, a product metrics case, a behavioral panel, and a hiring manager conversation. The SQL round may ask you to manipulate raw data on the fly and explain your choices. The product case could involve investigating a decline in conversion or understanding user segmentation. In the behavioral panel, interviewers will assess how you’ve worked with cross-functional partners, resolved ambiguity, or handled prioritization conflicts. Lastly, the hiring manager will focus on team fit, long-term growth, and your ability to lead analytical initiatives independently.
Feedback & Offer
Once interviews conclude, the team conducts a 24-hour debrief. All interviewers submit written feedback, which is then reviewed by a hiring committee. This ensures that hiring decisions are both fair and calibrated across roles. If successful, you’ll receive an offer along with information about your leveling, compensation, and next steps. For Senior Analyst candidates, there may be an additional round focused on stakeholder influence and leadership, particularly around owning the analytics roadmap for a product area.
What Questions Are Asked in an eBay Business Analyst Interview?
eBay’s interview questions are carefully designed to evaluate your technical fluency, analytical thinking, and business communication skills. Expect a mix of SQL, product case, and behavioral questions across the process.
SQL / Data Manipulation Questions
SQL is a major focus in the technical screening and live interviews. You’ll be asked to write queries that simulate real-world eBay scenarios—such as pulling buyer counts and GMV by category over the last 90 days or identifying user drop-off points in a funnel. The evaluation focuses on your ability to join multiple tables, use window functions appropriately, and write clean, performant code. Interviewers also look for your ability to explain your logic and suggest improvements or edge case handling when needed.
-
A ranked approach with
DENSE_RANK()orROW_NUMBER()partitioned by department ensures ties are handled. Filtering forrank = 2yields the correct value without relying onLIMIT 1,1, which breaks under duplicates. Discussing a composite index on(department, salary)and edge cases like null salaries demonstrates thoroughness. -
You need to join transactions to customer demographics, filter for users who placed ≥ 1 order, and compute
SUM(amount) / COUNT(DISTINCT order_id)grouped by gender. Mentioning null-gender exclusion, outlier checks (e.g., refunds), and presentation formatting shows business polish. A window function alternative can reduce sub-query complexity. -
Combine tables with
UNION ALL, thenGROUP BY ingredientandSUM(mass)to total quantities. Discuss unit standardization (grams vs. ounces) before summing and whyUNION ALLpreserves duplicates needed for a correct tally. Explaining how this mirrors merging heterogeneous data sources strengthens the business-analysis perspective. -
Each record contains
user_id,start_date, andend_datefor completed subscriptions. Self-join the table on identicaluser_idwherea.start_date < b.end_dateandb.start_date < a.end_dateanda.id <> b.id; any hit marks that user as overlapping. Returning all users with ahas_overlapflag involvesDISTINCT user_idfrom the join and a left join back to the full user list. Candidates should note that usingLAG()/LEAD()overstart_dateavoids an O(n²) join on large data sets. How would you surface the five product pairs most frequently bought together by the same customer?
Aggregate each user’s distinct products into sets, explode them into unordered pairs via a self-join or
ARRAYunnest, group by(least(p1,p2), greatest(p1,p2)), count co-occurrences, and pick the top five withp2alphabetically first for ties. Efficient implementations pre-deduplicate(user_id, product_id)to cut pair generation size and may leverage approximate counts or partitioned tables for billion-row scale. Discussion of bloom filters, partition pruning, and batch processing shows senior-level thinking.Which January-2020 sign-ups moved more than $100 of successful volume in their first 30 days?
Join
users(filtered to January-2020 signups) withpaymentstwice—once as sender, once as recipient—keepingpayment_state = 'success'andpayment_datewithin 30 days of signup, sum amounts per user, and count those above $100. A union of the two roles preserves sign, and windowing byuser_idplus a date filter ensures correctness. Good answers highlight indexes on(user_id, payment_date)and justify unions over OR conditions for planner efficiency.-
First gather comment totals per
user_id, then aggregate counts of users pernum_comments, order the buckets, and compute a running fractionSUM(users)/total_usersusing a window function such asSUM(count) OVER (ORDER BY num_comments). If comment counts are sparse, generating a series with a left join fills gaps for smoother plots. The answer should mention whyCUME_DIST()orPERCENT_RANK()can also be used and the importance of indexing the comments table onuser_id. -
The cleanest tactic unions the per-year tables into a CTE tagged with a
yearcolumn, then leverages conditional aggregation:SUM(CASE WHEN year=2021 THEN total_sales END) AS sales_2021, etc. If the database supports dynamic SQL, a generated pivot scales to future years automatically. Good answers highlight the maintenance burden of one-table-per-year schemes and recommend folding data into a single partitioned fact table to simplify analytics and indexing. -
A window function approach uses
SUM(sales * weight)over a three-row frame:0.5 * salesfor the current row,0.3 * LAG(sales,1), and0.2 * LAG(sales,2). Filtering withWHERE LAG(sales,2) IS NOT NULLensures that only rows with two predecessors are output. Explanations should mention choosingORDER BY sale_datein thePARTITION BY product_idclause, discuss handling gaps in dates, and note that materializing daily sales in a pre-aggregated table avoids expensive on-the-fly computations.
Product & Metrics Case Questions
These questions are designed to test your product sense, diagnostic skills, and strategic thinking. A common format is a scenario where a key metric—like GMV or conversion rate—has declined, and you need to diagnose why. You’ll be expected to develop hypotheses, propose user segmentation strategies, and lay out an experiment or next-step analysis plan. Strong answers involve structured thinking, clear prioritization, and a business-first approach to data storytelling.
-
Translate this to eBay by framing “rides” as any on-demand marketplace listing. You’d monitor search-to-purchase conversion, request-to-fulfillment latency, and the ratio of active buyers to active sellers at five-minute granularity. A surge in unfulfilled requests or a growing queue length signals high demand and low supply; you can codify “too much demand” when median wait time breaches a 95th-percentile SLA. Alert thresholds should be data-driven—fit a control-chart to historical latency and trigger when the z-score exceeds, say, 3. Finally, visualize these KPIs in a real-time dashboard so business analysts and ops teams can throttle promotions or nudge sellers to list more inventory.
Given $100 ARPU, 10 % monthly churn, and 3.5-month tenure, how do you derive average lifetime value?
Lifetime value (LTV) for a subscription equals monthly revenue × expected customer lifetime. With 10 % churn, expected lifetime is 1⁄0.10=101 / 0.10 = 101⁄0.10=10 months, but the 3.5-month empirical tenure overrides the pure churn-based estimate. Therefore LTV ≈ $100 × 3.5 = $350. Explain why reconciling churn-implied lifetime with observed tenure prevents overestimation, and how sensitivity analyses (e.g., churn ±2 pp) inform eBay’s retention goals. Round out the answer by noting CAC subtraction for net LTV and cohort segmentation to refine the average.
-
Design an observational study: collect baseline “friend count” and control for confounders like signup channel and historical engagement using propensity-score matching. Then run a logistic-regression or survival model to estimate the marginal effect of each additional friend on six-month retention, reporting confidence intervals. Validate parallel-trends assumptions by plotting pre-intervention activity curves of matched cohorts. If feasible, propose an A/B nudge (suggest-friends feature) to randomize friend-count growth for causal proof. This end-to-end plan shows experimental rigor and statistical sensitivity—key skills for an eBay business analyst.
-
Begin with churn curves (Kaplan–Meier) split by plan, highlighting hazard spikes around renewal dates. Compute plan-level LTV and payback periods; pair these with cohort heat maps to expose seasonality. Train a time-to-event model with covariates like watch hours and payment method to predict churn risk 30 days out. Present findings in a Tableau dashboard that lets eBay execs slice by geography or acquisition channel. Emphasize actionable levers—e.g., annual subscribers showing early warning signals could receive tailored win-back offers.
-
Define a quality score blending median first-response time, conversation resolution rate, and post-chat satisfaction (thumbs-up or NPS). Use NLP sentiment analysis on chat text to flag negative interactions and compute seller-level complaint rates. Establish control limits by benchmarking against top-quartile sellers, then surface outliers in a weekly seller-health report. Run A/B tests on canned-reply templates to quantify causal lifts in satisfaction. This metric framework lets eBay prioritize tooling investments and seller education programs.
-
Calculate cohort survival: January cohort loses 10 % by February, then 8 % (80 % of 10 %) by March, retaining 82 %. February cohort loses 10 % × 0.8 = 8 % by March. Assuming uniform acquisitions, weight cohort sizes equally: expected March churn ≈ (8 % + 8 %) / 2 = 8 %. Clarify assumptions—uniform daily signups and independent churn decay—and note that seasonality or promo spikes would adjust weights. This demonstrates cohort arithmetic and sensitivity thinking coveted in e-commerce analytics.
A 5 % spike in ride cancellations appeared last week—how would you investigate?
Slice the spike by city, time of day, device OS, and driver tier to localize anomalies. Check recent app releases, pricing changes, and service-level incidents (e.g., payment gateway downtime). Build a logistic model of cancellation probability with interaction terms to quantify lift factors. Correlate weather and traffic API data to rule out exogenous shocks. Present a root-cause tree that ranks likely drivers, enabling eBay’s operations team to deploy targeted fixes or rollbacks.
With 90 days of ride data, how would you estimate a new driver’s lifetime and value?
Fit a parametric survival model (Weibull) on driver churn, incorporating covariates like acceptance rate, earnings variance, and trip density. Expected lifetime is the inverse cumulative hazard at 50 % survival; lifetime value equals expected lifetime × average net revenue per driver-day minus incentive costs. Back-test predictions on historical cohorts to gauge calibration. Use the model to score incoming drivers and tailor retention bonuses aggressively where LTV justifies spend. This showcases predictive modeling and profitability framing.
-
First confirm statistical significance by comparing conversion proportions with a chi-square test adjusted for sample size. Then decompose the gap: funnel attribution (signup source, device), pricing localization, and feature adoption. Build a multivariate logistic model with interaction terms for country to see if geography still matters after controls. Conduct cohort analyses on engagement (DAU/MAU, time-to-first-value) to detect behavioral differences. Finally, survey users or interview local teams for qualitative insights—closing the loop between data and product context, a hallmark of eBay business analysis.
Behavioral & Storytelling Questions
Finally, eBay places strong emphasis on your ability to communicate with stakeholders and operate in cross-functional settings. You’ll face questions about persuading non-technical partners, balancing trade-offs under pressure, or learning from an analysis that didn’t go as planned. Use the STAR format to organize your stories, but focus on impact—what business decision was made, what changed, and how your analysis contributed. The best answers show not only your communication skill, but also your judgment and ownership.
Describe a data project you worked on. What were some of the challenges you faced?
Interviewers want a concise STAR story that highlights eBay-relevant hurdles—messy seller-level data, shifting product taxonomies, or conflicting KPI definitions. Emphasize how you scoped the problem, partnered with engineers to unblock pipelines, and quantified impact (e.g., reduced dashboard latency by 40 %). Discuss one soft hurdle (stakeholder alignment) and one technical hurdle (data sparsity) to show range.
What are some effective ways to make data more accessible to non-technical people?
Focus on self-serve dashboards with clear business language, guided insights, and hover-tooltips instead of SQL. Mention layered Tableau/Looker views that roll from GMV down to seller-granular metrics and the use of annotated alerts for marketplace anomalies. Show you keep stakeholders engaged by embedding data stories into weekly business reviews.
What would your current manager say about you? What constructive criticisms might they give?
Pick two strengths that map to eBay’s analyst culture—e.g., “translating technical findings into revenue actions” and “tenacity with incomplete datasets.” Balance with a growth area such as “delegating deep-dive work instead of owning every query,” then outline the steps you’ve taken (mentoring junior analysts, documenting SQL snippets). Authenticity and a clear improvement plan beat generic answers.
Talk about a time you had trouble communicating with stakeholders. How did you overcome it?
Choose an example where category managers and engineering had conflicting definitions of “active listing.” Explain how misalignment stalled a pricing experiment and how you resolved it by facilitating a data taxonomy workshop, prototyping a shared metric, and gaining sign-off—all within one sprint. Close with quantified upside (e.g., 8 % faster A/B iterations).
Why do you want to work with us?
Craft a response tying your passion for two-sided marketplaces and circular commerce to eBay’s recommerce strategy. Reference specific initiatives such as Guaranteed Fit or Authenticity Guarantee to show homework. End by linking your analytical skill set—cohort-based GMV forecasting, buyer retention modeling—to the company’s growth priorities.
How do you prioritize multiple deadlines, and how do you stay organized?
Explain your two-step system: first quantify business impact (GMV uplift, CSAT risk) and effort, then slot tasks in a Kanban board with weekly stakeholder check-ins. Mention using SQL linting, version control, and scheduled Airflow DAGs to keep data work reproducible. Demonstrating a repeatable framework reassures hiring managers you can juggle eBay’s fast-moving roadmap.
Describe a time you used data to influence a product roadmap decision at scale.
Interviewers want evidence you can convert insight into action. Outline the business context, the analysis you ran (e.g., elasticity modeling of listing-fee changes), and the specific roadmap shift that followed. Highlight how you communicated findings to cross-functional leaders and measured post-launch impact.
Tell me about a situation where you challenged an existing KPI because it misrepresented performance. What happened next?
Show courage paired with diplomacy—perhaps you noticed GMV was rising but take-rate was falling. Walk through how you validated the concern, proposed an adjusted KPI, and secured executive adoption. Stress quantitative rigor and stakeholder education.
How do you handle ambiguous data requests when requirements are underspecified?
Explain a repeatable technique: clarifying the underlying business decision, drafting a quick mock-dashboard to elicit feedback, and iterating before deep analysis. Emphasize written scoping docs and agreement on definitions up front, which prevent rework and build trust.
How to Prepare for a Business Analyst Role at eBay
Success in the eBay Business Analyst interview comes down to balance: sharp technical execution, clear product thinking, and the ability to explain data in business terms. Because eBay’s questions are closely tied to its marketplace model, strong candidates not only practice case mechanics—they also study eBay’s core metrics and buyer-seller dynamics. Here’s how to prepare holistically.
Know eBay’s Core Metrics
Start by familiarizing yourself with the KPIs that drive eBay’s platform. Gross Merchandise Volume (GMV) is the most commonly referenced, but you’ll also need to understand take-rate, active buyer growth, listing impressions, seller churn, and conversion rate. Many product and SQL questions tie back to one or more of these metrics—so knowing how they connect (and what might cause them to rise or fall) gives you a big advantage.
Practise the Mix
A good preparation strategy allocates your time across three core areas: SQL and Excel (about 50%), product metrics case studies (30%), and behavioral interviews (20%). For SQL, focus on writing complex queries with window functions, CTEs, and multi-table joins. For product cases, practice frameworks like hypothesis trees and segmentation analysis. Behavioral answers should highlight collaboration, prioritization, and stakeholder impact.
Mock Presentations
Analysts at eBay often present insights to leadership, so building your storytelling muscle is key. Practice putting together a 10-slide deck that walks through a real analysis: the problem, data overview, insights, and business recommendations. You’ll want to be able to summarize a complex topic clearly and concisely for a non-technical audience—especially in the hiring manager round.
Think Out Loud
Interviewers want to see how you approach ambiguity, so make your thought process explicit. Whether you’re solving a SQL prompt or working through a metrics case, voice your assumptions, acknowledge trade-offs, and proactively suggest next steps or data limitations. This shows maturity and analytical judgment—and helps interviewers follow your logic.
FAQs
What Is the Average Senior Business Analyst Salary at eBay?
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
The compensation package for Senior Business Analysts at eBay typically includes a competitive base salary, performance bonus, and equity grants. Candidates in the Bay Area may see a higher range due to regional cost-of-living adjustments, while remote roles often align more closely with national benchmarks.
How Much Does an eBay Business Analyst Salary Package Typically Include?
A typical compensation package for an entry- to mid-level Business Analyst at eBay includes base pay, annual performance bonus, and restricted stock units (RSUs). In recent years, equity has played a larger role in total comp—especially for roles tied to product and strategy.
Is There a Difference Between “Business Analyst eBay Salary” in US vs. EU?
Yes, compensation varies by region. U.S.-based analysts tend to receive higher base salaries and equity grants, particularly in California. EU salaries—especially in Germany and the UK—tend to be lower on a dollar-converted basis, but benefits such as paid vacation and social insurance are more comprehensive.
Are There Current Job Postings for Business Analyst Roles at eBay?
Explore openings on the Interview Query job board, and set a custom job alert to stay notified when new eBay Business Analyst roles go live.
Conclusion
Preparing for a Business Analyst role at eBay requires more than just technical chops. You’ll need to demonstrate strong SQL skills, fluency in marketplace metrics, and an ability to translate data into business action. Make sure you’ve practiced real-world product cases, honed your behavioral stories, and built confidence in your ability to present insights clearly.
To continue preparing, visit our eBay Interview hub and check out related guides for Data Analysts and Product Managers. Want to test your skills? Try a Mock Interview, challenge yourself with our AI Interviewer, or follow a role-specific Learning Path tailored to eBay-style questions.
For inspiration, read Asef Wafa’s success story on how he transitioned into analytics at a top tech company—it’s a great reminder that preparation pays off. Let us know how your interview goes. We’re rooting for you.
