eBay Interview Process, Behavioral Questions & Salary Guide
Introduction
Whether you’re applying for a role in software engineering, product management, or analytics, understanding the eBay interview questions and broader eBay interview process is the first step to landing an offer. eBay remains one of the world’s most impactful marketplace platforms, and its interviews reflect both technical depth and customer-centric thinking.
This guide curates the most common eBay interview topics across roles, outlines what to expect at each interview stage, and links directly to role-specific preparation guides. Whether you’re a first-time applicant or returning candidate, use this as your roadmap to navigate the entire eBay hiring journey.
Why Work at eBay?
eBay company culture revolves around enabling “economic opportunity for all,” and this mission is more than a tagline—it’s baked into every team, role, and decision. Teams work on meaningful problems that directly empower small businesses, entrepreneurs, and buyers globally.
- Mission-Driven Commerce – eBay’s core focus on inclusivity and open access makes it one of the few tech companies actively championing economic democratization.
- Seller-First & Customer-First Values – Product and engineering decisions are evaluated based on how they build trust and fairness across the marketplace.
- Global Scale, Real-World Impact – With hundreds of millions of active buyers and over a billion live listings, your work has massive downstream effects.
- Hybrid & Remote Flexibility – eBay offers generous WFH options, location-agnostic roles, and wellness programs tailored to a post-pandemic workforce.
- Inclusive Hiring Practices – The company publicly shares its DEI reports and continues to invest in programs that increase representation across technical and leadership roles.
What’s eBay’s Interview Process Like?
The eBay hiring process is structured, fast-moving, and tailored to the function you’re applying to—whether technical or strategic. While details vary across roles and levels, most candidates follow a consistent progression through five main stages.
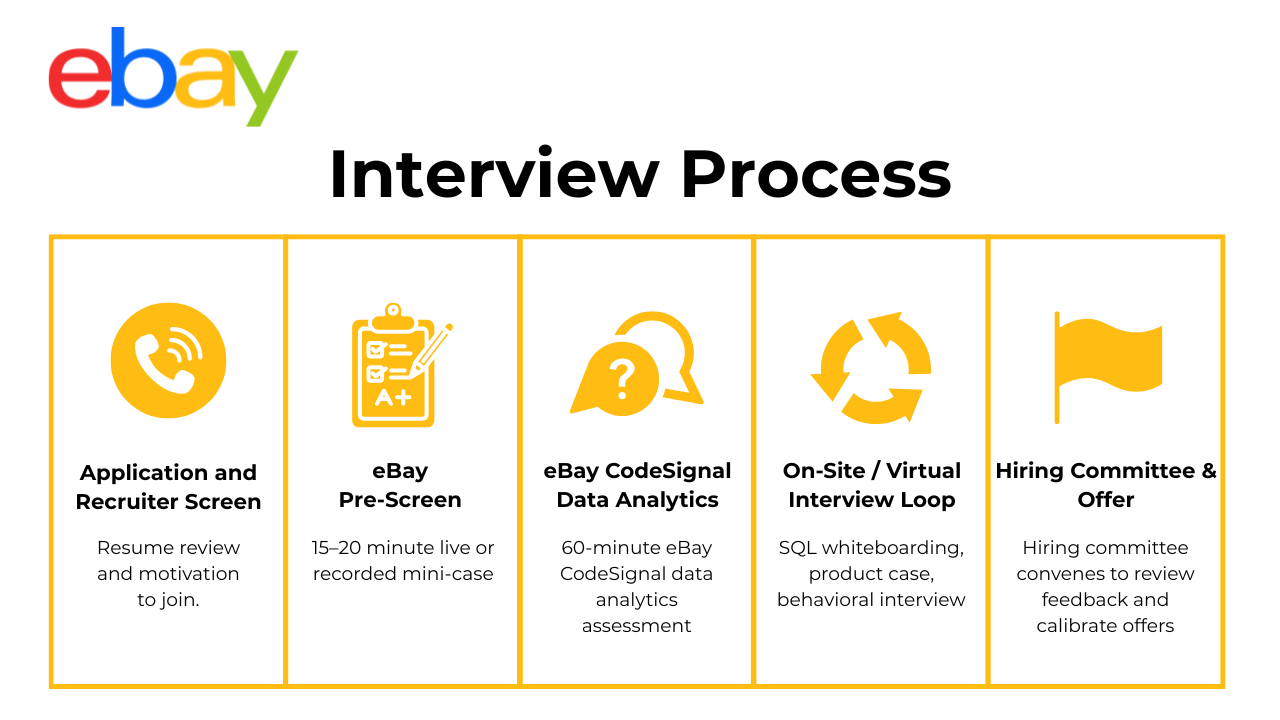
Recruiter Screen & Resume Alignment
This first conversation is with a recruiter who will evaluate resume alignment, clarify the scope of the role, and discuss compensation expectations. You may be asked about your background, domain familiarity (e.g., e-commerce, marketplace dynamics), and why you’re interested in eBay specifically. The recruiter may also preview the upcoming steps, including timelines and team fit.
eBay Online Assessment (OA)
The eBay online assessment is commonly used for technical roles and serves as a skills screening checkpoint. Delivered via platforms like CodeSignal or HackerRank, it typically includes algorithmic coding, SQL challenges, or logic-based modeling questions, depending on the role. Timing usually ranges from 45 to 90 minutes. These assessments are auto-scored and used to shortlist candidates for the next phase.
You can find detailed OA walkthroughs in our Software Engineer and Data Analyst guides.
Technical / Functional Rounds
This is where the role-specific depth comes into play. Engineers might be asked to solve whiteboard problems, debug code live, or walk through system design interview questions. For data and analytics candidates, this round may involve SQL challenges, experiment design, or case-based problem solving. The nature of the questions differs for software engineers versus data scientists, but the focus is consistent: clarity of thought, problem-solving, and real-world execution.
Behavioral & Values Fit
In these rounds, interviewers dig into your collaboration style, decision-making under ambiguity, and alignment with eBay’s culture. You’ll face common eBay behavioral interview questions, such as how you navigated a disagreement with a cross-functional team, owned a production issue, or advocated for a user need. Expect to reflect on trade-offs, difficult calls, and how you made decisions with limited data.
Hiring-Manager & Executive Loop
The final stage usually involves a deeper conversation with your prospective eBay hiring manager. This isn’t just a formality—it’s a strategic discussion about team dynamics, long-term growth, and ownership. You might be asked about career trajectory, how you collaborate with PMs or engineers, and what excites you most about the role. For senior candidates, this loop may also include director-level or executive reviewers for final approval.
Most Common eBay Interview Questions
The most frequently asked eBay interview questions cut across both functional knowledge and company-aligned values. Below are the top themes to prepare for:
Role-Specific Interview Guides
Jump directly to your target role for prep:
- eBay Software Engineer Interview Guide
- eBay Data Scientist Interview Guide
- eBay Machine Learning Engineer Interview Guide
- eBay Data Analyst Interview Guide
- eBay Product Manager Interview Guide
Mission & Values Questions
Candidates often describe their eBay interview experience as values-driven. Interviewers look for responses that tie back to eBay’s core mission: enabling economic opportunity and marketplace fairness. Be ready to explain how your work supports underserved users, improves seller trust, or supports ethical tech development.
Why do you want to work with us?
Interviewers look for a response that weaves your personal story into eBay’s north star of “economic opportunity for all.” A strong answer references concrete initiatives— for example, Authenticity Guarantee or Promoted Listings Advanced—to show you’ve done your homework. You should then connect those programs to your own experience building trustworthy data systems or seller-empowering products. Finally, close with a future-facing statement on how your skills will amplify marketplace fairness at global scale. Demonstrating mission alignment is often the deciding tiebreaker among technically equivalent candidates.
-
Prep-time errors cascade into courier wait costs and customer satisfaction; systematic under-prediction for certain cuisines or neighborhoods unfairly penalizes those merchants and riders. A values-driven answer discusses fairness audits—stratified residual plots, demographic parity checks—and remediation tactics like group-aware loss weighting. Explain how transparent dashboards foster trust among restaurant partners, mirroring eBay’s obligation to treat power sellers and hobbyists equitably. Mention that unbiased ETAs also reduce driver idle fuel, aligning with sustainability goals. The interviewer wants to hear you place ethical modeling on equal footing with raw accuracy.
How would you build an automated system to detect prohibited firearm listings on a marketplace?
Start with policy comprehension—know the exact legal and ToS boundaries. Propose a two-stage filter: an NLP model scanning titles/descriptions and a vision model flagging firearm imagery, fused through a high-precision rules engine. Stress the need for low false-positives so legitimate sellers aren’t wrongly punished, and outline an appeal workflow to maintain marketplace trust. Continuous re-training on adversarial examples keeps the system resilient. Framing the solution around user safety and fairness shows alignment with eBay’s mission.
-
Advocate using post-hoc explainability (e.g., SHAP) to surface the top contributing factors per prediction while filtering out protected attributes. Describe how explanations empower applicants to improve and reduce complaint volume—paralleling how eBay educates suspended sellers. Clarify legal compliance (ECOA, GDPR) and the importance of consistent reasoning across demographics. Demonstrating this empathy reinforces the value of transparent, ethical technology in marketplace ecosystems.
What are effective ways to make data more accessible to non-technical stakeholders?
Reference semantic layers that translate column names into business language, Looker dashboards with natural-language insight cards, and Slack bots that answer simple metric queries. Emphasize role-based access so small sellers see only their own data while larger merchants view aggregated benchmarks—supporting eBay’s inclusive ethos. Describe how democratizing insights shortens decision loops and empowers under-served users to grow revenue. Highlight tooling that attaches data-quality badges, reinforcing trust in every chart.
How would you ensure search-ranking algorithms surface small-seller listings as fairly as those from power sellers?
Propose a seller-equity metric—share of impressions to the bottom 80 % of sellers—and bake it into the objective alongside GMV. Use counterfactual logging to estimate revenue impact if equity drops and deploy guardrails that trigger rollbacks. Discuss calibrating diversity constraints or re-ranking layers that inject under-represented sellers without harming buyer relevance. Such a holistic approach embodies eBay’s commitment to leveling the playing field.
Design a program that helps entrepreneurs in low-bandwidth regions participate in eBay’s marketplace.
Outline lightweight listing tools (SMS or USSD), image-compression pipelines that tolerate 2G networks, and regional pickup hubs partnering with local carriers. Suggest metrics like “first-item-listed rate” and cohort GMV to track success. Address training—video tutorials in local languages—and fraud deterrence that respects varying ID systems. Showing how you tailor technology to infrastructure gaps ties directly to enabling global economic opportunity.
What safeguards would you add to an AI-driven listing-suspension system to prevent demographic bias?
Describe pre-launch bias testing on labeled review outcomes segmented by seller location, tenure, and category. Implement real-time fairness monitors comparing suspension rates across cohorts and a human-in-the-loop appeal queue. Require model cards documenting training data provenance and known limitations. By embedding ethics and transparency, you protect both underserved sellers and eBay’s brand trust.
Technical Depth Questions
These range from LeetCode-style problems to SQL aggregations and ML model trade-offs. You may encounter coding interview questions such as “Implement sessionization logic on streaming data,” or model-evaluation challenges requiring deep familiarity with metrics like AUC, precision, or NDCG. Expect system-level awareness even during code walkthroughs.
-
A performant answer explains why
ORDER BY RANDOM()is off-limits (full-table sort) and offers two production patterns: pick a random integer ≤max_idon an indexed, gap-free surrogate key, or query from a nightly reservoir table already holding 1 M random IDs. Mention object-store back-pressure and how to guarantee uniformity if the key space has holes. Discuss trade-offs between MySQL’sRAND()*max_id, PostgresTABLESAMPLE SYSTEM, and RedshiftBERNOULLI, noting their bias caveats. Tie the technique to eBay use cases such as low-impact QA sampling on the listing catalog. Retrieve the last transaction for each day—id, timestamp, amount—ordered chronologically.
Showcase
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY DATE(created_at) ORDER BY created_at DESC)and filter onrow_number = 1. Explain why date truncation in the partition clause is safer than string casting and how a descending index on(created_at)eliminates sort spill. Note that finance pipelines append-only, so late inserts require backfill logic. Accurate day-end snapshots feed eBay’s revenue reconciliation and fraud-alert models.How would you interpret logistic-regression coefficients for categorical and boolean variables?
Emphasize that
exp(β)yields an odds ratio: a boolean flag’s coefficient compares odds when the flag flips from 0→1, while each one-hot dummy’s coefficient is relative to the reference category. Warn about sparse categories inflating variance and how regularization or hierarchical pooling mitigates that. Show how odds ratios translate into feature importance for product teams—e.g., “Free returns increases likelihood of purchase 1.4×.” Correct interpretation underpins trustworthy seller-conversion dashboards.Compare Lasso and Ridge regression—when would you choose each?
State that Lasso’s L1 penalty induces exact zeroes, creating sparse, interpretable models, while Ridge’s L2 shrinks but rarely zeros coefficients, stabilizing estimates under multicollinearity. Discuss bias-variance implications and cross-validated α tuning. Point out that eBay’s high-dimensional text features often benefit from ElasticNet blending. Finally, mention how coefficient shrinkage speeds downstream online inference by trimming weight vectors.
-
The logistic (sigmoid) maps a scalar logit to (0, 1) for binary probability, while softmax converts a vector of logits into a k-class probability distribution summing to 1. Sigmoid uses a single decision boundary; softmax learns (k-1) simultaneous boundaries optimized by cross-entropy loss. Discuss numerical stability (log-sum-exp) and calibration. Cite eBay workloads: softmax for multi-category item classification, sigmoid for binary fraud detection.
-
Use a window frame
ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW, multiply each lag by its weight insideSUM, and filter rows whereROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY product ORDER BY sale_date) > 2. Explain why materializing daily aggregates in a staging table prevents re-scanning raw events. Weighted smoothing helps inventory managers spot real demand shifts instead of day-to-day noise. Implement sessionization on a streaming click-stream where events may arrive up to five minutes late.
Describe keyed windowing in Flink or Spark Structured Streaming using event-time, with a five-minute watermark to tolerate lateness. Outline state size management via TTL and a fallback merge when late events cross session boundaries. Provide a compact definition of session (30 min inactivity gap) and discuss emitting change-feed updates versus final results. Mastery here demonstrates deep familiarity with real-time analytics constraints at eBay scale.
Given prediction scores and ground-truth labels for 100 M impressions, compute AUC at scale while keeping memory under 4 GB.
Propose external sorting of (score, label) blocks, then a single scan accumulating true-positive and false-positive counts to approximate the ROC curve. Explain why Histogram-bin approximation (e.g., 10 k bins) trades minimal accuracy for big memory savings. Mention using Spark’s
binaryClassificationMetricsbut validating numeric stability with 64-bit counters. Efficient large-scale AUC computation is essential for daily recommender retraining.Design a feature-flag SDK that evaluates flags in ≤2 ms p95 on the buyer-facing checkout path.
Outline a hierarchical cache: in-process LRU keyed by flag-ID → user-segment hash, backed by an edge-local Redis cluster, and an asynchronous config poller that hot-reloads rules every 30 s. Describe a protobuf rule format, percent-rollout hashing, and a circuit breaker that defaults to “control” if latency exceeds budget. Include an analytics fire-and-forget path to log exposure events. Interviewers look for system-level thinking even in “simple” utilities.
System-Design & Architecture
At scale, performance is everything. In eBay system design interview questions, you may be asked to architect a feature-flag service, scalable recommendation system, or real-time clickstream ingestion pipeline. These questions test your ability to think through constraints, latency, and operational complexity.
Deep dive: eBay Software Engineer Guide
-
A strong answer separates streaming ETL (Kafka → Flink) from batch backfills, lands features in an online store, and trains incremental XGBoost models every hour. Predictions are served through a low-latency REST layer fronted by Redis, with object‐storage checkpoints for reproducibility. Data-drift detectors fire alerts when KS-scores dip below 0.05, triggering an automated retrain job in Airflow. Finally, blue-green deployment ensures zero-downtime swaps while Prometheus dashboards track p95 latency and forecast MAE.
-
Decouple binary data from metadata: videos live in object storage (S3/GCS) under deterministic keys, while a
videos_metatable stores title, uploader, timestamps, and a checksum. Create compound indexes on(uploader_id, upload_ts DESC)and a full-text GIN index ontitle. Hot thumbnails are cached in a CDN; cold blobs tier to infrequent-access buckets via lifecycle rules. This separation keeps metadata lookups millisecond-fast and blob retrieval bandwidth-efficient—an approach directly applicable to eBay’s image-hosting pipeline. Design a real-time feature store that serves 99-percentile look-ups under 5 ms for 300 M sellers while keeping feature freshness < 15 minutes.
Partition “hot” features in a sharded Redis cluster for sub-millisecond access and persist “cold” history in Iceberg on S3. A Flink job does incremental feature computation and dual-writes to both layers, tagging each record with a version hash so training and serving stay consistent. Employ a gRPC side-car in model pods for typed look-ups, plus a TTL-based invalidation scheme. CloudWatch alarms catch latency spikes, and a shadow read path compares Redis to S3 nightly to guard against silent corruption.
Sketch an automated model rollback framework that activates when live GMV-prediction error exceeds 2× baseline.
Stream inference outputs and ground-truths into a monitoring service that computes rolling MAE; if the alert threshold trips, Kubernetes flips traffic to the previous model image via weighted services. Each rollback emits a GitOps event that snapshots bad inputs for root-cause notebooks and kicks off a post-mortem template. Canary pools and shadow evaluation ensure the backup model is warm, and a governance gate prevents auto-rollforward until two green windows pass—protecting the marketplace from cascading revenue loss.
Build a real-time anomaly-detection pipeline that flags sudden drops in search click-through rate across thousands of query clusters.
Consume click-impression streams with Kafka, aggregate CTR per cluster every minute in Flink, and compare to a seasonality-adjusted EWMA baseline stored in Redis. Trigger an alert when z-score < –3 for three consecutive windows, de-duplicated via a Redis set-NX to avoid alert storms. Exposed alerts include cluster identifiers and top offending listings, enabling on-call engineers to triage ranking bugs quickly. Historical replay back-tests the detector, tuning sensitivity while maintaining < 5 min detection latency.
Design a multi-tenant ride-sharing schema that supports fast surge-pricing analytics.
Core tables include
riders,drivers,vehicles, and a widetripsfact keyed by (trip_id,pickup_geohash,requested_ts). Partitiontripsby request-date and cluster onpickup_geohashso surge heat-maps need only range-scan hot partitions. Append-only writes preserve immutable audit trails, while a materialized view pre-aggregates five-minute pickup counts for real-time surge computation. Foreign-key constraints are deferred to preserve ingest speed but enforced in nightly consistency checks.Design a low-latency feature-flag service capable of handling 50 K requests / s at p95 ≤ 2 ms.
Store flag rules in a strongly consistent KV store (etcd), hydrate in-process caches in each edge pod via watch APIs, and fall back to a region-local Redis for cold misses. Evaluate rules using a deterministic hash of
user_idfor percent rollouts, and log exposures asynchronously to Kafka for later analysis. A circuit breaker defaults to “control” if rule evaluation surpasses 1 ms, ensuring checkout flow resilience. Deploy via blue-green to catch misconfigurations before they impact all users.
Data & Analytics Mindset
In roles spanning analytics, ML, or product, you’ll be expected to reason about metrics, design experiments, and debug fluctuations in marketplace performance. Interviewers want to see how you define success, isolate variables, and quantify trade-offs. This mindset is central in both data and product roles.
Explore prep: eBay Data Analyst Guide | eBay Product Manager Guide
-
A complete answer defines a funnel—requests, accepted trips, completed trips—and then derives key ratios like request-to-fulfillment latency and active-buyers-to-active-drivers. You should explain how you’d slice by geo-time buckets, plot heat maps, and set control-chart thresholds that trigger supply nudges when median wait exceeds a 95-percentile SLA. Describe the feedback loop: alert Ops, bump surge pricing, or push driver re-activation notifications. Interviewers want to see structured thinking that ties raw events to actionable, real-time levers—a core skill for marketplaces like eBay anytime GMV volatility appears.
-
Good candidates form hypotheses—new-user dilution, content-type shifts, or UI friction—then propose cohort curves (comments per new vs. existing user), content mix dashboards, and funnel drop-off analyses (view → comment start → submit). They’ll also check logging changes and spam-filter rules to rule out instrumentation artifacts. Finally, they’ll quantify impact (e.g., post-comment ratio down X %) and outline experiments (UI tweaks, notification tests) to confirm causality. The interviewer is judging your ability to isolate drivers amid multiple moving parts.
Does an A/B test with 50 K users in Variant A and 200 K in Variant B bias toward the smaller group?
The correct reasoning is that unequal samples do not bias the estimate if randomization holds—only the standard error differs. You should show the pooled-variance formula, compute minimal-detectable-effect (MDE) for each arm, and discuss power asymmetry. Mention CUPED or regression adjustment to tighten intervals rather than re-balancing mid-test (which would actually create bias). Demonstrating statistical rigor—beyond rote rules of thumb—signals you can safeguard eBay experiments against false conclusions.
Your manager ran an experiment with 20 variants and one looks “significant.” Anything fishy?
Point out multiple-comparison inflation: at α = 0.05 you expect one false positive among 20 arms. Recommend Holm–Bonferroni or Benjamini–Hochberg corrections, or hierarchical Bayes that controls family-wise error. You might suggest a two-stage test—screen all variants, then re-test winners—or a bandit that adapts traffic while controlling FDR. The goal is to show you recognize p-hacking risks and can enforce statistical discipline in a pressure-filled, high-variant environment.
-
Explain cluster randomization: treat an ego network (seed user plus direct followers) as the unit, or use graph partitioning to minimize edge cuts. Quantify potential interference and plan sample-size inflation for intra-cluster correlation. Propose measuring both direct (ego) and indirect (alter) engagement to estimate total treatment effect. Acknowledging spill-over shows you can adapt classic A/B design to social-network topologies—useful when eBay tests buyer-seller messaging features.
-
The solution joins
ab_teststosubscriptions, applies variant-specificCASElogic (e.g., trial must stay subscribed 7 days), and aggregates withAVG(converted)per arm. Discuss data-quality pitfalls: double-counting users who switch variants, handling NULL cancel dates, and late-arriving subscription events. Show that precise metric definitions—and guarding them with unit tests—are foundational to credible experiment readouts. Diagnose a sudden 8 % overnight drop in checkout conversion—what is your step-by-step investigation plan?
Begin with an attribution matrix: traffic source, device, geographic region, payment method, experiment flags. Use guardrail dashboards to see if page-load times, payment-gateway errors, or deal traffic shifted. Run diff queries on yesterday vs. today for key funnel steps, then drill into event-level logs to trace common failure patterns. Outline a war-room protocol: revert recent launches, deploy synthetic transactions, and quantify revenue at risk. This scenario tests your fire-drill composure and structured analytical triage.
Design a KPI framework for eBay’s “Guaranteed Fit” program—how do you measure success and spot regressions?
Propose a north-star metric (return-rate delta vs. non-GF items) backed by supporting metrics: buyer NPS, seller defect rate, and time-to-refund. Define eligibility filters, then build pre-launch baselines by category and seller tier. After rollout, monitor difference-in-differences charts and set alert thresholds (e.g., return spike > 2 σ). Include a cost model that weighs reimbursement spend against reduced customer-service tickets. This question probes your ability to translate product vision into quantifiable, actionable metrics.
Tips When Preparing for an eBay Interview
Interviewing at eBay is as much about alignment with values as it is about technical depth. Whether you’re preparing for an OA, a system design round, or behavioral panels, these strategies will help you approach the eBay interview process with confidence.
Interviewing at eBay is as much about alignment with values as it is about technical depth. Whether you’re preparing for an OA, a system design round, or behavioral panels, these strategies will help you approach the eBay interview process with confidence.
Study Real OA Formats
Practicing for the eBay online assessment under timed conditions is essential. Use platforms like CodeSignal or HackerRank to simulate the actual OA structure and question types—whether it’s coding, SQL, or analytical logic.
Mirror eBay Core Values
Make sure your answers reflect eBay’s mission of creating “economic opportunity for all.” Referencing past projects where you prioritized user equity, platform fairness, or long-term sustainability can help reinforce your alignment with the company’s ethos.
Leverage Marketplace Case Studies
Prepare for interviews by applying your skills to buyer-seller scenarios. This might include pricing algorithms, search ranking fairness, or fraud mitigation. These real-world themes are central across product, data, and engineering teams.
Practice Story-Based Behavioral Answers
Use the STAR method when preparing for eBay behavioral interview questions. Focus on stories that show ownership, adaptability, and impact—especially moments where you influenced decisions or resolved ambiguity.
Map Role-Specific Competencies
Each eBay role has its own expectations. Engineers focus on performance and scale, while PMs prioritize product intuition and trade-offs. Use our tailored guides to prepare accordingly:
Salaries at eBay
Average Base Salary
Average Total Compensation
If you’re researching eBay salary benchmarks, understanding the full compensation package is essential—especially as eBay offers competitive equity, performance bonuses, and flexible benefits.
Median total comp varies significantly by function and level. For those targeting managerial roles, the eBay manager salary typically includes leadership scope bonuses and mid-term stock grants. At the executive level, eBay director salary packages include larger equity refreshers and performance-based multipliers.
Conclusion
Mastering the eBay interview process is more than passing technical rounds—it’s about showcasing your understanding of the marketplace, your alignment with eBay’s values, and your ability to build products and systems that scale responsibly.
To go deeper, explore our role-specific prep guides, each packed with real questions, frameworks, and success strategies:
- eBay Software Engineer Guide
- eBay Data Scientist Guide
- eBay ML Engineer Guide
- eBay Product Manager Guide
- eBay Data Analyst Guide
Ready to practice? Try a Mock Interview, test your skills with the AI Interviewer, or follow a targeted Learning Path. And don’t miss Simran Singh’s success story—after over 4,000 applications, she finally landed her dream job through structured prep on Interview Query.
FAQs
How long does the full eBay hiring process typically take?
The eBay recruitment process can span two to four weeks from recruiter screen to final offer, though senior or niche roles may take longer depending on team alignment and level calibration.
What’s the difference between the recruiter screen and hiring-manager round at eBay?
Your recruiter ensures resume fit and handles logistics; your eBay hiring manager evaluates long-term alignment, ownership skills, and how well you’d integrate into their specific team structure.
Are eBay’s online assessments the same for every role?
Not exactly. The eBay online assessment varies by position—software engineers may face algorithmic coding, while analysts or scientists encounter SQL, stats, or logic-based case studies.
How much do eBay managers and directors really earn?
The typical eBay manager salary ranges from $170K–$230K total comp. For leadership roles, the eBay director salary often exceeds $300K, especially when stock and bonus incentives are included.
What do candidates say the interview experience feels like?
Most candidates describe the eBay interview experience as values-oriented, transparent, and role-specific. Interviewers often ask thoughtful follow-ups and care about both how you solve problems and how you collaborate across teams.
