AI Engineer Resume & Portfolio Guide for 2026 (With Examples)
Introduction
Breaking into AI engineering this year isn’t hard because you lack talent—it’s hard because the market has turned into a stampede. Since 2023, job postings for AI roles have grown 3x, but applications have grown 10x (Indeed & LinkedIn data). The rise of LLMs pulled in everyone: software engineers, data scientists, bootcamp grads, and career-transitioners. Overnight, every resume started claiming “LLM fine-tuning,” “RAG pipelines,” and “model training at scale,” whether the person actually built anything or just followed a YouTube tutorial at 2x speed.
So hiring managers did what any overwhelmed human would do: they became ruthless.
Here’s the part candidates hate hearing: most AI resumes fail in under 10 seconds. Recruiters spend an average of 7.4 seconds on a first pass (Ladders), and ATS filters quietly reject thousands more before a human even looks.
Why? Because:
- Everyone lists the same buzzwords
- Projects look like recycled Kaggle notebooks
- Bullets describe tasks, not impact
- Nothing shows real engineering or ownership
If you’re sending applications into the void, unsure what counts as a real project, or confused about what hiring managers actually care about, you’re exactly who this guide is for.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know how to craft an AI resume and portfolio that looks credible, intentional, and unmistakably industry-ready. The kind that clears ATS, grabs a hiring manager’s attention, and shows you’re not just repeating buzzwords. You can actually do the work.
How to Write an AI Engineer Resume?
Your resume is not your autobiography; it’s your positioning document. It tells a hiring manager, in under 10 seconds, who you are, what you can do, and whether you’re worth interviewing.
A strong AI resume is usually one page (two if you’re experienced), but every section needs to earn its place.
1. Contact Information
Purpose:
This is how a recruiter decides whether to check your online presence. If these links aren’t easy to find or don’t exist, you’ve already lowered your chances.
Include:
- Full name
- Phone
- Professional email
- GitHub (non-negotiable for AI/ML roles)
- Portfolio website
How to stand out:
- Put LinkedIn and GitHub at the very top, as they get the most clicks.
- Make sure both look polished. A strong GitHub can override weak experience.
- Add a custom portfolio link showcasing your best 2–3 AI projects.
2. Professional Summary or Objective
Purpose:
This is your 3-sentence pitch. Recruiters use it to assess whether your experience aligns with the role without digging into the bullets.
Strong summary example:
AI Engineer with 3 years of experience building NLP and classification models using Python, PyTorch, and AWS. Designed and deployed end-to-end ML pipelines, reducing model latency by 30%. Passionate about scalable systems, LLM fine-tuning, and MLOps automation.
Weak summary example:
Passionate about AI, deep learning, and solving problems with data.
How to stand out:
- State your specialization: NLP, LLMs, CV, or MLOps.
- Add one meaningful metric (latency reduction, accuracy boost, cost savings).
- Mention a technical focus area relevant to the role you want.
A good summary makes the recruiter think: “Okay, this person knows their stuff.”
3. Technical Skills Matrix (Not a Dumping Ground)
Purpose:
This is your keyword alignment section. ATS and humans both use it to check if your toolkit matches the job requirements.
Break it into:
- Languages (Python, SQL, etc.)
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning (PyTorch, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn)
- LLMs & GenAI (Transformers, RAG, prompt engineering)
- MLOps (Docker, Kubernetes, CI/CD, MLflow, FastAPI)
- Cloud (AWS/GCP/Azure)
- Tools (Airflow, Spark, Git)
How to stand out:
- Only list tools you can defend in an interview.
- Prioritize the skills the job description repeats.
- Keep it structured. Recruiters should be able to skim this in 3 seconds.
- Add one niche skill relevant to your specialization (example: LangChain, ONNX, HuggingFace Hub, Vector DBs).
A clean skills matrix tells a recruiter: “This candidate knows where their strengths are.”
4. Work Experience
Purpose:
This shows whether you’ve solved real problems in real environments and not just in notebooks.
Even early-career candidates can include:
- Internships
- Research projects
- Freelance work
- University labs
- Contract gigs
- Personal end-to-end projects
Your bullets must show:
- Ownership
- Impact
- Quantified outcomes
- Practical application of ML/AI
- Understanding of production constraints
How to stand out:
- Use C-A-R: Context → Action → Result
- Quantify every bullet (“improved accuracy by 13%,” “cut latency by 120ms”).
- Highlight cross-functional work (PMs, engineers, designers).
- Show decisions (“chose BERT over LSTM because…”).
- Mention deployment because it’s a differentiator.
Good work experience communicates maturity.
Good bullets communicate competence.
5. Projects (Critical for AI Roles)
Purpose:
This is where early-career candidates prove they can do the job even without experience.
Projects show how you think, how you build, and whether your skills translate to real-world settings.
Projects must:
- Solve real problems
- Use messy, real-world datasets
- Show end-to-end engineering
- Include model decisions
- Show metrics
- Be well-documented
- Ideally include deployment
How to stand out:
- Choose business-relevant projects (e.g., churn prediction, support ticket routing, RAG search).
- Add clean READMEs with diagrams.
- Deploy at least one project via Streamlit, FastAPI, or HuggingFace Spaces.
- Write why you chose the model and not just what you used.
A hiring manager can tell in 5 seconds whether you built something real or just followed a tutorial.
6. Education
Purpose:
This validates your academic foundation, but it’s not the main reason you get hired.
Include:
- Degree
- Institution
- Graduation year
- Relevant coursework (ML, DL, NLP, Systems, Stats)
- Thesis/capstone (if technical)
How to stand out:
- Highlight technical coursework aligned with the job.
- Add a one-line thesis or capstone description.
- Skip GPA unless it’s great.
Education doesn’t make or break your resume, but smartly chosen details can reinforce your profile.
7. Certifications/Awards
Purpose:
Certifications can establish credibility and commitment to learning, especially when you don’t have industry experience.
Only include certifications that matter in AI roles:
- AWS ML Specialty
- Google Professional ML or DE
- TensorFlow Developer
- DeepLearning.AI (NLP, GenAI, LLMOps)
How to stand out:
- Pick certifications aligned with the job you want (MLOps? AWS ML Specialty).
- Avoid listing 12 random online courses.
- Add only those that make a hiring manager trust your technical depth.
Quality > quantity every time.
What Accounts for a Strong vs Weak AI Resume
| Section | Strong Resume | Weak Resume |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Info | Clickable GitHub + portfolio up top | Email buried at the bottom |
| Summary | Specific, metric-backed, role-aligned | “AI enthusiast seeking opportunities” |
| Skills | Categorized, relevant, matched to JD | Long, random tool dump |
| Experience | Measurable impact, real ownership | Tasks and responsibilities |
| Projects | End-to-end, deployed, documented | Kaggle clones + messy repos |
| Education | Relevant coursework | Irrelevant details, clutter |
| Certifications | Industry-recognized | Udemy course backlog |
| Format | Clean, scannable | Canva chaos |
If you’re not getting interviews, fix this first. If you’ve been applying for weeks and hearing nothing back, the bottleneck is usually AI skills alignment. You’re highlighting tools companies don’t care about or ignoring the ones they evaluate heavily. Before you rewrite anything, spend 5 minutes on the Interview Query questions page. Interview Query has 30,000+ real AI/ML interview questions sorted by company, skill, and topic.
Use it to instantly understand:
- What skills companies actually test
- Which keywords matter
- What gaps you need to fill
- How to tailor your summary + skills to real interview patterns
It’s the fastest way to turn a generic resume into a role-ready one.
Tailoring Your AI Resume for FAANG vs Startups
This is one of the biggest misses candidates make.
FAANG companies and startups don’t evaluate resumes the same way. They look for different signals, different project scopes, and different engineering depth.
| Category | FAANG Priorities | Startup Priorities |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Production-level engineering, scalability, optimization | End-to-end ownership, speed, shipping features |
| Engineering Depth | - Distributed training - Large-scale data pipelines - System optimization & inference speed -Throughput & latency improvements |
- Full-stack ML development - Quick prototypes & MVPs - Scrappy, iterative builds |
| ML/LLM Expectations | - Rigorous evaluation (F1, BLEU, perplexity) - Ablation studies - Model trade-off reasoning |
- RAG pipelines - LoRA/QLoRA fine-tuning - Practical LLM integrations |
| Infrastructure Skills | - CUDA, C++ - DeepSpeed, Ray - Kubernetes, Docker - SageMaker, Vertex AI |
- FastAPI/Flask microservices - Streamlit/Gradio demos - Lightweight MLOps |
| Breadth vs Depth | Depth—high specialization | Breadth—ML + MLOps + data engineering |
| Ownership Signals | Clear ownership of complex, large-scale problems | Fast iteration, scrappy execution, quick decision-making |
| Keywords They Screen For | Distributed training Model optimization LLM evaluation Cloud-native ML Large-scale pipelines |
RAG LLM fine-tuning API integrations LangChain Vector databases |
How to Beat ATS Without Looking Like You Stuffed Keywords
Most AI resumes don’t get rejected because candidates lack skill, they get rejected because the resume doesn’t speak the job description’s language. ATS filters are blunt: if your resume doesn’t match the keywords, it never reaches a human.
ATS systems scan for:
- Job titles
- Technical skills
- Tools
- Role-specific nouns
- Action verbs and impact language
It’s mechanical, but predictable, which means you can optimize for it without sounding robotic.
1. Pull keywords directly from the job description
Highlight every tool, framework, and requirement repeated across the posting.
2. Weave those keywords naturally into your summary, skills matrix, and experience bullets
If the JD mentions “PyTorch” and “MLflow” repeatedly, make sure those show up in relevant places.
3. Use clean, standard section headings
“Work Experience,” “Skills,” “Education”, etc. don’t get cute with titles. ATS isn’t creative.
4. Match the job title when appropriate
Use phrases like “AI Engineer,” “Machine Learning Engineer,” or “MLOps Engineer” to improve relevance.
Example of Natural Keyword Alignment (Good)
Built a PyTorch-based classification model and deployed it using AWS Lambda + API Gateway, reducing inference latency by 40%.
Straightforward. Technical. Keyword-rich. Human.
Example of Keyword Dumping (Bad)
Used PyTorch TensorFlow AWS Python Docker Cloud Data Models etc.
Readable by no one, ATS or human.
If you’re unsure which keywords your resume is missing. Instead of guessing what to include, browse Interview Query’s company interview page:
Each company page breaks down:
- Real interview processes
- Skills they repeatedly test
- Topic patterns
- Role-specific expectations
This makes it easy to pinpoint the exact keywords top companies like Meta, Google, Databricks, Snowflake, and NVIDIA look for, and align your AI resume accordingly.
AI Resume Templates & Visual Examples
A lot of candidates struggle because they don’t know what an actual AI resume should look like.
Below are copy-ready resume templates designed specifically for AI/ML/LLM/MLOps roles. They’re structured for ATS, optimized for clarity, and built around real hiring patterns at FAANG companies and fast-moving startups.
These templates are intentionally minimal, technical, and impact-first — the exact structure hiring managers prefer.
Template 1: One-Page AI/ML Engineer Resume (General)
FULL NAME
Location • Email • Phone • LinkedIn • GitHub • Portfolio
SUMMARY
AI/ML Engineer with X years of experience building NLP/LLM/ML models and deploying
production pipelines. Improved {metric}. Strong in Python, PyTorch, AWS, and MLOps.
SKILLS
Languages: Python, SQL
ML/DL: PyTorch, TensorFlow, Scikit-learn
GenAI: Transformers, RAG, LoRA, Embeddings
MLOps: Docker, Kubernetes, MLflow, FastAPI
Cloud: AWS (SageMaker, Lambda), GCP (Vertex AI)
Tools: Airflow, Spark, Git
EXPERIENCE
AI Engineer — Company
• Built {model} improving {metric}.
• Deployed via {method}, reducing latency by {value}.
• Automated {process}, saving {time/cost}.
PROJECTS
Project Name — GitHub / Demo Link
• Built {use case} using {stack}.
• Achieved {metric}.
• Deployed using {tool}.
EDUCATION
Degree — Institution
Relevant coursework: ML, DL, NLP, Systems, Stats
Template 2: LLM/GenAI Engineer Resume (FAANG-Ready)
FULL NAME
Location • Email • Phone • LinkedIn • GitHub • Portfolio
SUMMARY
LLM Engineer specializing in distributed training, finetuning, and evaluation of
large-scale language models. Experience with Transformers, Ray, DeepSpeed, CUDA,
and cloud-native ML systems.
FAANG-FOCUSED SKILLS
LLMs: Transformers, QLoRA, RAG, evaluation
Distributed Systems: Ray, DeepSpeed, CUDA
MLOps: Kubernetes, Docker, Terraform, MLflow
Cloud: AWS, GCP
EXPERIENCE
Machine Learning Engineer — Company
• Fine-tuned 7B model with QLoRA, reducing hallucinations by 35%.
• Built retrieval pipeline increasing recall by 22%.
• Implemented distributed training using Ray, improving throughput 40%.
PROJECTS
LLM Project — GitHub / Demo
• Built RAG pipeline with FAISS/Chroma.
• Evaluated using ROUGE, BLEU, perplexity.
• Deployed via FastAPI on AWS.
Template 3: Startup-Ready AI Engineer Resume (Full-Stack + Fast Execution)
FULL NAME
Location • Email • Phone • LinkedIn • GitHub • Portfolio
SUMMARY
Full-stack AI Engineer with experience shipping LLM-powered features end-to-end.
Strong in rapid prototyping, RAG, API integrations, FastAPI, and Streamlit.
STARTUP-FOCUSED SKILLS
GenAI: RAG, LoRA, embeddings, prompt engineering
Backend: FastAPI, Flask
Front-end demos: Streamlit, Gradio
Infra: Docker, GitHub Actions
Databases: Postgres, Chroma, Pinecone
EXPERIENCE
AI Engineer — Startup
• Built LLM-based summarization tool reducing manual review time 60%.
• Deployed full RAG pipeline (FastAPI + Chroma).
• Shipped 3 customer-facing features in 6 weeks.
PROJECTS
Demo Project — GitHub / Live Link
• Built MVP in 10 days using {stack}.
• Reduced cost/latency by {metric}.
• Created Streamlit demo with clear UX.
AI Resume Example
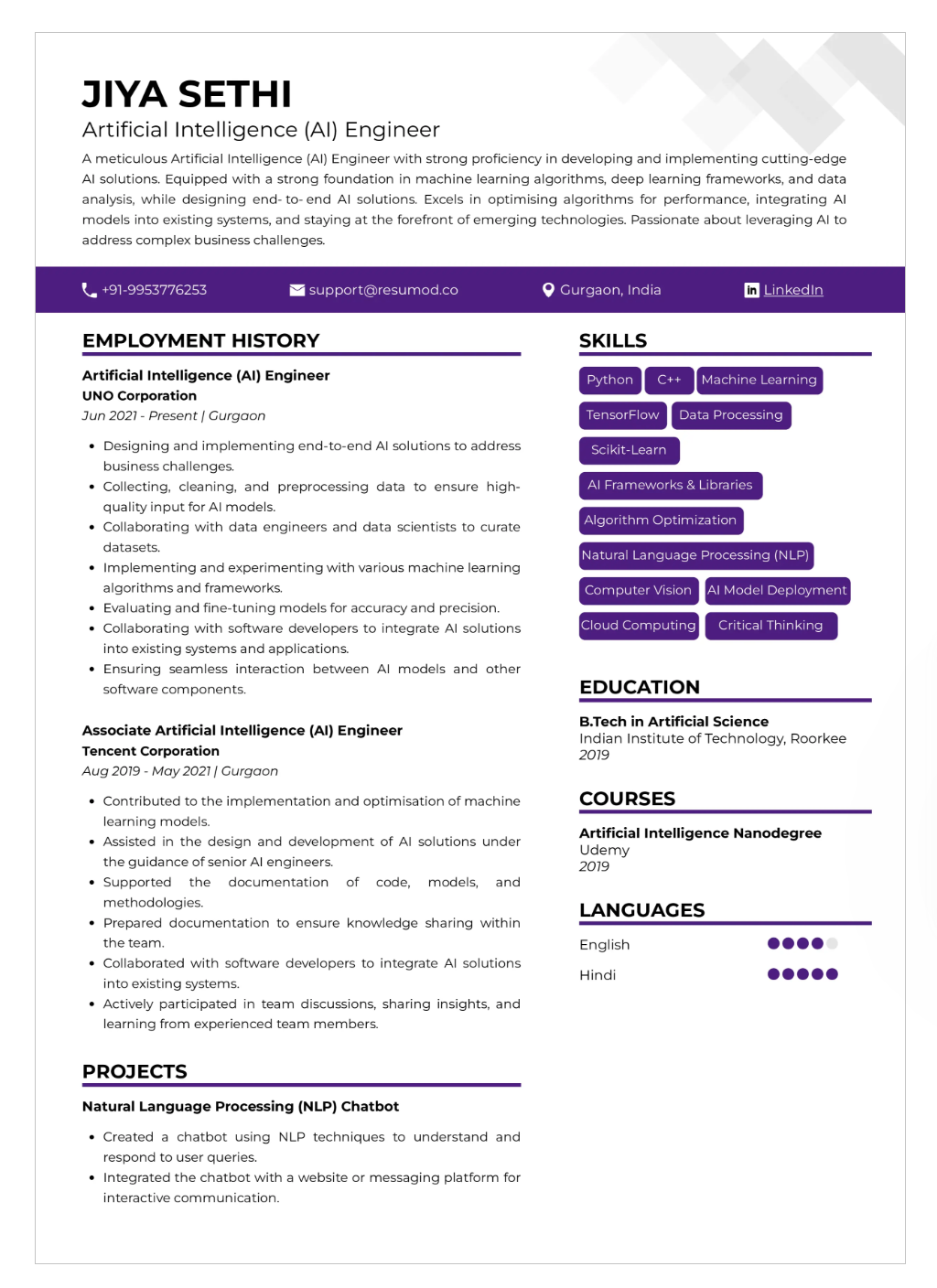
Source: Resumod
Why Jiya Sethi’s resume is good
The Jiya Sethi resume works because it’s clean, structured, and instantly credible. The summary is tight and technical, the skills matrix is grouped logically (not a messy tool dump), and the layout is completely ATS-safe. There’s no fluff—just the exact languages, frameworks, and cloud tools an AI/ML recruiter scans for in the first five seconds.
What really makes it strong is the way the experience and projects are written. Every bullet shows impact through metrics and real model improvements, not vague tasks. It reflects an actual ML lifecycle—data, modeling, evaluation, deployment—which signals competence without over-explaining. Combined with a polished GitHub presence, the resume reads like someone who can build real systems, not just complete tutorials.
If you need real interview practice before the real interview, use Interview Query’s AI Interviewer. It simulates actual ML/AI interviews, drills you on follow-up questions, tests your reasoning, and helps you refine your explanations.
This is the safest place to “fail privately” and fix your blind spots before you face a human hiring manager.
AI Resume + Portfolio Mistakes That Kill Your Chances
These red flags are what hiring managers instantly reject. If you fix these, you will outperform 80% of junior applicants immediately.
| Mistake | Fix |
|---|---|
| Listing tools you can’t explain | Only list skills you can defend in interviews |
| Kaggle clone projects | Build real-world, end-to-end projects |
| No quantification | Add metrics for accuracy, latency, time saved |
| Messy GitHub | Clean structure, detailed READMEs |
| Long paragraphs, weak bullets | Use C-A-R (Context → Action → Result) |
| Too much fluff | Focus on outcomes, not processes |
| Not tailoring | Customize summary + top bullets to each role |
| No deployment experience | Add at least 1 Streamlit/FastAPI deployment |
| Overloading the skills section | Structure into categories |
| Missing LLM/GenAI experience | Include at least one LLM project |
FAQs on Creating an AI Resume
1. How do I optimize my AI engineer resume for ATS?
Use clean, standard section headers, mirror the exact keywords from the job description, and avoid graphics-heavy templates. Keep formatting simple (one column, no icons) so ATS can parse your text without breaking.
2. What portfolio format is best for AI engineers?
A personal website or Notion portfolio is ideal, but at minimum you need a well-organized GitHub with clean folders, clear READMEs, and at least one deployed project.
3. How do I make my GitHub projects stand out?
Prioritize real-world, end-to-end projects. Add runnable code, environment files, diagrams, explanations of model choices, and pin your top repositories so hiring managers don’t have to dig.
4. What are the most important AI skills to highlight?
Python, PyTorch, TensorFlow, LLMs/GenAI (Transformers, RAG, LoRA), cloud platforms (AWS/GCP), and MLOps tools (Docker, Kubernetes, MLflow, FastAPI). These signal an industry-ready stack.
5. Should I include publications or blog posts?
Yes—especially if they involve ML/AI research, experiments, or engineering deep dives. They demonstrate strong reasoning, communication, and technical credibility.
6. How can entry-level candidates stand out?
Build 3–5 solid, end-to-end projects, document them thoroughly, quantify your results (accuracy, latency, cost savings), and deploy at least one. A polished GitHub can beat limited experience.
7. How do I tailor my resume for different AI roles?
Match your summary, skills, and top bullets to the role type—NLP/LLM, CV, MLOps, or general ML. Highlight the most relevant projects first and use role-specific terminology from the job description.
8. What’s the biggest mistake AI candidates make?
Listing tools or models they can’t explain. It’s the fastest way to get filtered out in technical interviews. Only include skills you can confidently defend with examples.
9. Should I include LLM prompt engineering as a skill?
Only if you can pair it with real implementation work. Prompt engineering alone isn’t enough anymore—hiring managers want to see it tied to RAG pipelines, fine-tuning, evaluation, or actual product features. Otherwise, it reads as surface-level.
10. How long should an AI resume be in 2026?
One page for most candidates, two pages only if you have 5+ years of experience or substantial research, publications, or multiple shipped AI systems. Recruiters won’t read beyond what fits on one screen.
11. Do hackathons or Kaggle scores still matter?
They help, but only as supporting evidence. Hackathons show speed and creativity; Kaggle shows experimentation and modeling skill. But neither replaces real-world, end-to-end projects or deployed systems—which matter far more for AI roles.
Get interview-ready with Interview Query
If you’re preparing to get an AI job this year, start with the resources that reflect real hiring expectations. Use Interview Query’s:
- 30,000+ interview questions
- AI mock interviews
- Company-specific interview guides
- Deep-dive blogs on ML/AI hiring trends
These tools help you align your resume, projects, and interview prep with exactly what companies look for.

