Pure Storage Interview Questions & Hiring Process (2025 Guide)
Introduction
Pure Storage interview questions are designed to test more than just technical skill—they reflect the company’s sharp focus on innovation, scale, and end-to-end ownership. As a pioneer in flash-based data platforms, Pure delivers high-performance infrastructure to enterprises managing petabytes of mission-critical data.
The Pure Storage interview process stands out for its depth: it emphasizes not only algorithmic fluency but also system design intuition, product thinking, and the ability to thrive in fast-paced, customer-first teams. Whether you’re applying for a data scientist, software engineer, or new grad role, each round is structured to surface real-world readiness.
In this article, we’ll walk through everything you need to know to prepare: the structure of the Pure Storage interview process, the types of questions you can expect across different roles, and proven strategies to approach them. Whether you’re targeting a data scientist, software engineer, or new grad role, you’ll find practical insights, sample questions, and role-specific guides to help you feel confident at every stage.
Why Work at Pure Storage?
The Pure Storage company culture blends high ownership with deep collaboration, offering engineers and analysts the freedom to drive impact—no matter where they’re based.
Core Values & Mission
The Pure Storage core values center on two pillars: customer first and innovate & deliver. That means solving for real-world needs at scale and doing it fast. Teams are empowered to experiment and iterate, with a bias toward shipping code and learning through impact. Whether you’re building machine learning pipelines or refining a UX flow, the mission is clear: make data storage radically better.
Culture & Work‑Life Balance
At its core, Pure Storage’s company culture values autonomy, transparency, and trust. The workplace is remote-flexible, with a recharge leave policy that encourages real downtime. Across roles, employees are encouraged to “own it”—from designing scalable systems to driving their own career path. Flat structure, async-friendly workflows, and frequent hackathons all reflect the culture’s fast-moving DNA.
Life at Bellevue & Prague Offices
Pure Storage Bellevue offers a hybrid setup with strong cross-team visibility and access to product leadership—ideal for engineers working on core services and platform features. Meanwhile, the Pure Storage salary benchmark in Prague is competitive within the EU tech market, offering top-tier benefits and equity packages aligned with those in Silicon Valley counterparts. Both hubs offer strong internal mobility, global mentorship, and vibrant team cultures rooted in local flavor.
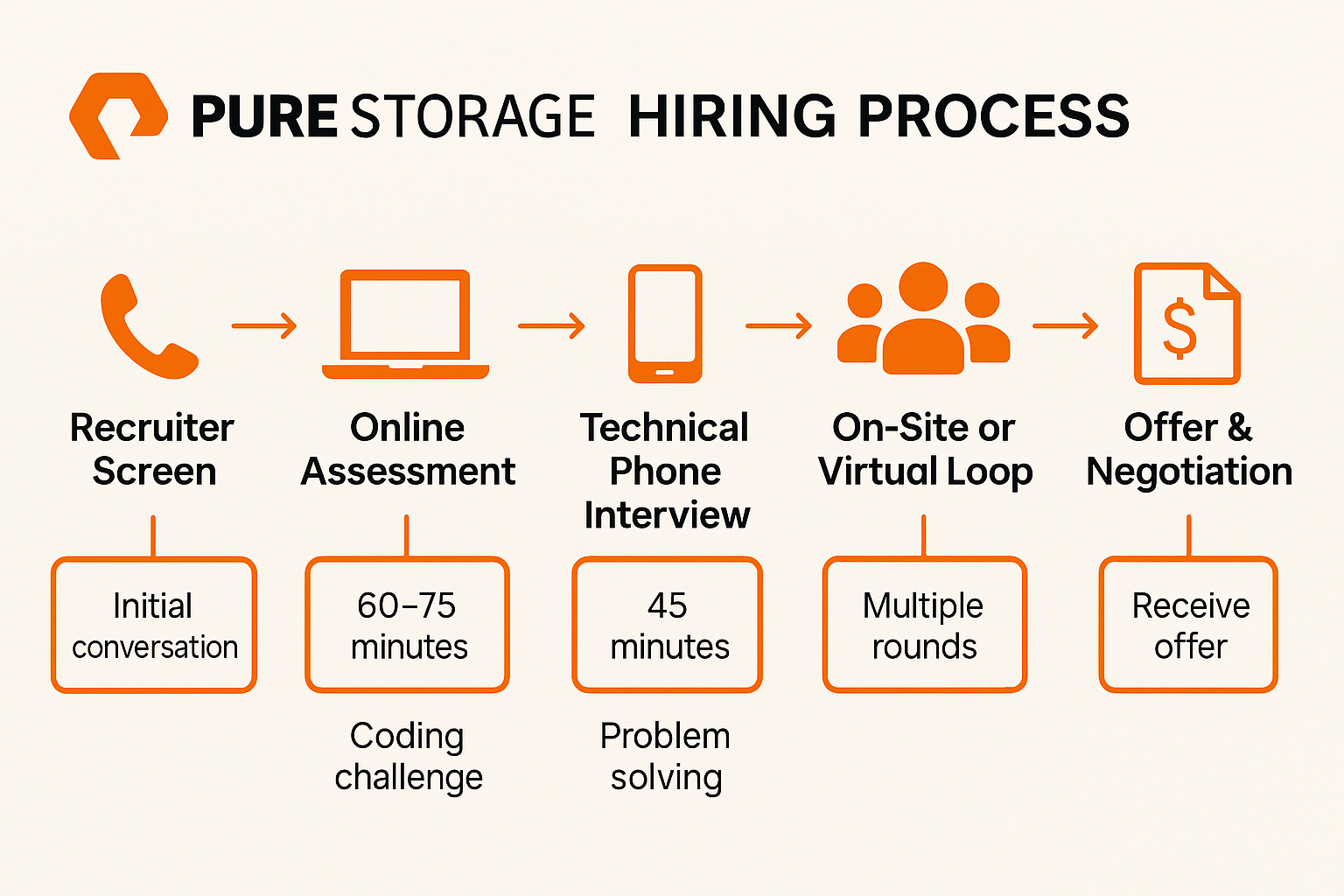
What’s Pure Storage’s Interview Process Like?
The Pure Storage hiring process is structured and candidate-friendly, designed to assess both technical depth and cultural alignment. Here’s a typical flow:
- Recruiter screen
- Online Assessment (OA)
- Technical phone interview
- On-site or virtual loop
- Offer & negotiation
Each stage filters for ownership, problem-solving, and the ability to thrive in a fast-paced, high-accountability environment.
Online Assessment (Coding Challenge)
The Pure Storage online assessment, also referred to as the OA 2025, is typically hosted on platforms like HackerRank or Codility. It includes two coding questions and several CS fundamentals MCQs. Expect a 60–75 minute timed session, with pass thresholds around 85–90% correctness. See our full Pure Storage software engineer interview guide for frequently asked interview questions and preparation tips.
Tip: Focus on accuracy. Most candidates stumble by rushing; hitting 90% correctness is key to passing.
Technical Phone Screen
Based on real Pure Storage interview experience, this 45-minute call includes 1–2 Leetcode-style problems (often hash maps or string parsing) and a few light behavioral questions to gauge ownership, collaboration, and clarity of communication.
Tip: Narrate your thought process while coding. Interviewers care as much about how you solve as the final solution.
On‑Site Loop
The Pure Storage interview process on-site typically includes three to four rounds:
- Whiteboard coding: Problem-solving under time and space constraints
- System design: Scenarios based on distributed systems or internal tooling
- Culture fit panel: Evaluates alignment with values like “own it” and “customer first”
Each round emphasizes not just correctness, but clarity, collaboration, and thought process.
Tip: In system design, highlight tradeoffs clearly. Interviewers want to see pragmatic engineering judgment, not just textbook answers.
Offer & Negotiation
Final offers include a competitive base salary, performance bonus, and equity (RSUs). Candidates also receive structured Pure Storage assessment feedback, especially if they fall just short—making re-applications more transparent. Compensation bands are calibrated across levels and locations, and recruiters often provide flexibility for strong candidates with multiple offers.
Tip: Bring data to the negotiation. Use salary benchmarks from sites like Glassdoor and be ready to share ranges. Having researched salary bands and equity norms gives you leverage for better terms.
Most Asked Pure Storage Interview Questions
Online Assessment Questions
This section highlights typical Pure Storage OA questions found in their coding challenge rounds. These problems test core algorithmic skills, SQL fluency, and string manipulation, similar to what you’d encounter on platforms like HackerRank or Leetcode. You can practice more similar questions on Interview Query dashboard.
Select a random number from a stream with equal probability
Use reservoir sampling to ensure each incoming number has an equal probability of selection. Keep a single candidate and update its probability at each step. This algorithm is both elegant and efficient for large datasets. It’s a common type of Pure Storage OA question to assess data stream fluency in coding challenges.
Tip: Derive (and state) why replacing with probability
1/ikeeps uniformity, showing correctness matters as much as code.Find the missing number from an array spanning 0 to N
Compute the expected total using arithmetic progression, then subtract the actual total. Alternatively, use XOR to cancel out matching elements. It gauges your ability to identify O(n) solutions under time pressure.
Tip: Prefer XOR to avoid overflow on large
Nand to hit O(1) space.Write a function that takes a sentence and returns all bigrams
Tokenize the sentence and loop through word pairs to collect bigrams. Return them in a list or dictionary with frequencies. This question tests your handling of sequences and iteration. Expect this level of string-based logic in a Pure Storage coding challenge.
Tip: Normalize (lowercase, strip punctuation) and decide upfront whether duplicates should be counted.
Stem words in a sentence using the shortest root in a dictionary
Use a trie structure to match prefixes efficiently during word replacement. For each word in the sentence, replace it with the shortest matching root. This type of question challenges your ability to implement scalable string matching. It appears often in Leetcode pure storage mock sets.
Tip: If time is tight, a sorted-prefix set with early break works; mention trie as the optimal follow-up.
Write a SQL query to count users who made additional purchases after an upsell
Identify users who received upsells, then join with subsequent purchases to check conversions. Use date filters and grouping to ensure you’re counting valid follow-ups. This SQL prompt measures your grasp of customer lifecycle analysis. It fits the Pure Storage OA questions’ focus on product data fluency.
Tip: Use a strict
purchase_time > upsell_timepredicate to avoid same-timestamp double counts, and dedupe users before counting.-
This problem requires arranging words into lines of fixed width while ensuring proper spacing between them. The greedy approach works best: fill as many words as possible into a line without exceeding the width, then distribute spaces evenly across gaps. Edge cases like the last line or lines with a single word often require special handling (e.g., left alignment instead of full justification). Interviewers are checking not just correctness but also how you reason about spacing rules.
Tip: Clarify rules for last-line spacing. Interviewers check edge-case handling.
-
You’re given two arrays where one is identical to the other except for a single element that is missing, and the goal is to identify that element. A straightforward method is to compute the sum of both arrays and subtract them to find the missing value. For larger or repeated numbers, a hash map is more robust, as it tracks frequency counts and ensures correctness even with duplicates. This problem tests both mathematical insight and your ability to choose the right data structure under constraints.
Tip: State time/space tradeoffs. Hash maps scale better when numbers repeat.
Write a function to return string shift
The task is to determine if one string can be rotated to become another. A neat trick is to concatenate the first string with itself and then check if the second string is a substring of this new string, which ensures all possible rotations are covered. This approach runs in O(n) time compared to repeatedly rotating, which is inefficient. Candidates should explain both the intuition and complexity to show mastery of string operations.
Tip: Mention complexity explicitly. O(n) string search wins over repeated rotations.
Technical Depth: System Design & Concurrency
Expect high-level architecture prompts and performance-driven questions in a system-design interview setting. These Pure Storage assessment themes often focus on designing reliable, concurrent systems that scale under user demand and engineering complexity.
Describe the process of building a restaurant recommendation engine
Consider collaborative filtering, user history, and location-based personalization. Structure your answer with clear service boundaries and fallback rules. Address data pipelines, latency, and model retraining. This reflects the scale and relevance of Pure Storage assessment questions.
Tip: Always explain how your design adapts as data volume and user requests grow, since scalability is central to Pure Storage’s work.
You can solve this question on Interview Query Dashboard. You will get step-by-step solutions, hints, and discussion threads. Instead of just practicing raw prompts, Interview Query walks you through how top candidates think, covering scalability, reliability, and customer impact. So you can build answers that stand out in interviews.
Design a type-ahead search experience like Netflix’s
Cover trie structures, ranking strategies, and caching for fast autocomplete. Talk about UI responsiveness and backend throughput. Include how you’d handle stale suggestions. This is a staple system-design interview prompt in consumer-facing applications.
Tip: Balance performance with accuracy by discussing both backend latency reduction and the freshness of results.
Create a recommendation engine for rental listings
Blend session data, content similarity, and click-through patterns. Discuss cold-start problems, batching vs real-time scoring, and modular APIs. Optimize for ranking freshness. This is a great example of Pure Storage concurrency questions at scale.
Tip: Address the cold-start problem clearly because it shows you understand both user experience and technical tradeoffs.
How would you design a distributed logging system for debugging live services?
Describe producers (app logs), consumers (debug viewers), and a buffer system like Kafka. Talk about message ordering, fault tolerance, and how to allow concurrent querying. Concurrency issues include race conditions and log duplication. These are common in Pure Storage system design interview loops.
Tip: Show how you maintain consistency and fault tolerance because Pure Storage emphasizes reliability in distributed systems.
Design a rate limiter for API usage across users and services
Propose a token bucket or leaky bucket algorithm and describe how you’d implement it in Redis. Address concurrency by using atomic increments or Lua scripts. Talk about enforcing fairness across users. This reflects infrastructure judgment relevant to Pure Storage assessments.
Tip: Highlight fairness across users and services since Pure Storage values designs that balance performance with equitable access.
Build a dashboard with real-time metrics across multiple services
Use pub-sub for streaming metrics and WebSockets for updates. Discuss load balancing and fault isolation for each component. Address concurrent writes and how to buffer them safely. These questions test your system thinking in fast-changing environments.
Tip: Emphasize how you prevent bottlenecks and ensure low-latency updates because visibility is critical in production systems.
Behavioral & STAR‑Method Interview Questions
In this section, we group Pure Storage interview questions and answers around core company values like ownership, curiosity, and collaboration. Use the STAR method to structure impactful stories that show how you operate in real-world team and product contexts.
Tell me about a time you solved a problem for users that wasn’t assigned to you.
Start with the context of the user pain point you identified. Describe the initiative you took without formal direction. Share the result in terms of adoption or impact. This aligns with Pure Storage’s value of customer obsession and proactive ownership.
Example: While interning, I noticed customers repeatedly asking for a product setup guide. I created a simple tutorial on my own, which reduced support tickets by 15% and was later added to the official onboarding.
Tip: Highlight proactive ownership. Pure values people who step in before being asked.
Describe a project you took full responsibility for end-to-end.
Frame the problem, scope, and your decision to lead it independently. Discuss the technical decisions and stakeholder communication involved. Conclude with measurable results and learnings. This story shows initiative and accountability, core traits Pure Storage looks for.
Example: I led a churn prediction project, defining scope, building the model, and presenting findings. The project delivered strong results and was adopted for ongoing reporting.
Tip: Emphasize independence and accountability. Pure wants engineers who own outcomes.
Share a situation where you taught yourself a new tool to unblock a team.
Focus on the team dependency and urgency, then describe how you self-learned the tool. Highlight how your solution helped the team progress. Include any feedback or longer-term benefits. This emphasizes curiosity and a bias for action.
Example: When my team needed a dashboard but no one knew Tableau, I learned it in a week, built the report, and documented the process, which unblocked deliverables on time.
Tip: Show resourcefulness. Pure values engineers who self-teach to move fast.
Walk through a time you made a decision under ambiguity.
Explain what information was missing and how you gathered just enough to proceed. Emphasize how you mitigated risk and communicated rationale. Share how things turned out and what you’d do differently. Pure Storage looks for engineers who move forward with imperfect information.
Example: When customer lifetime value data was missing, I built a proxy metric using available transactions, validated it, and used it to guide a pricing change that increased conversions.
Tip: Stress decision-making under uncertainty. Pure rewards progress over perfection.
Tell me about a time you had to influence someone without authority.
Set the stage with a cross-functional challenge or misalignment. Describe how you built trust or used data to make your case. Share the outcome and what you learned about persuasion. This taps into collaboration and leadership, even without formal titles.
Example: I convinced engineering to add a new API by showing how it would cut reporting time by 40%. They prioritized it after I presented the cost-benefit analysis.
Tip: Pure looks for collaboration. You’ll need to demonstrate influence through impact and communication.
For in-depth question banks tailored to your discipline, check out our comprehensive guides:
- Software Engineer → Pure Storage Software Engineer Interview Guide
- Data Scientist → Pure Storage Data Scientist Interview Guide
- ML Engineer → Pure Storage ML Engineer Interview Guide
- Business Analyst → Pure Storage Business Analyst Interview Guide
Tips When Preparing for a Pure Storage Interview
Preparing for a Pure Storage interview isn’t just about solving LeetCode problems. The company looks for candidates who can bridge technical depth with system-level thinking, product judgment, and cultural alignment. Here’s how to approach preparation from multiple angles.
Go Beyond Coding: Practice Real-World Tradeoffs
Pure Storage is an infrastructure company, so interviewers want to hear not only what solution you chose but why. In a system design prompt (say, designing a distributed logging system), explicitly call out tradeoffs between throughput, latency, and cost. This separates you from candidates who just implement the “textbook” approach.
Tip: Practice narrating design tradeoffs out loud with a timer, 35 minutes per mock round. On Interview Query, the system design dashboard gives you sample prompts and model answers to benchmark your reasoning.
Anchor Behavioral Stories in “Customer First”
Pure’s culture prizes ownership and customer obsession. Generic STAR stories won’t cut it—you need stories that end with a clear user or business impact. Instead of saying “I fixed a data pipeline issue,” frame it as “I reduced reporting latency by 40%, which allowed our product team to launch features two weeks earlier.”
Tip: Write 3-4 STAR examples tied to outcomes like performance gains, scale improvements, or customer adoption. Rehearse them until you can tell each story in under two minutes.
Simulate Pressure With Mock Interviews
Most candidates underestimate how pressure shifts their performance. You’ll face 45–60 minute blocks where you must think, code, and communicate simultaneously. Replicate this pressure before the actual interview.
Tip: Do at least three timed mock interviews that cover both algorithms and SQL. Interview Query’s AI mock interviews recreate this format, offering instant feedback on both code correctness and clarity.
Learn Pure Storage’s Core Product Areas
Unlike a consumer app, Pure builds storage systems used in mission-critical enterprise environments. Knowing basic flash storage concepts (latency, concurrency, fault tolerance) and how they affect product design will help you stand out.
Tip: Before your interview, skim Pure’s blogs or engineering posts. Be ready to answer: “How would you design for petabyte-scale workloads?” or “How do you ensure reliability under hardware failure?”
Salaries at Pure Storage
Most data science positions fall under different position titles depending on the actual role.
From the graph we can see that on average the Product Manager role pays the most with a $200,115 base salary while the Data Analyst role on average pays the least with a $116,667 base salary.
FAQs
Is Pure Storage a product‑based company?
Yes. Pure Storage is a product-based company focused on building enterprise-grade flash storage solutions and cloud data platforms.
What are Pure Storage’s core values?
Pure Storage’s core values include Customer First, Innovate & Deliver, and Own It, pillars that shape both product strategy and team culture. These values guide how employees collaborate, make decisions, and prioritize customer outcomes.
What does the Pure Storage online assessment cover?
The online assessment typically includes two coding questions (in Python, Java, or C++) and multiple-choice questions on algorithms, systems programming, and core CS fundamentals. The session is 60–75 minutes long, with a pass-through rate around 85–90%, making accuracy just as important as speed.
How long is the Pure Storage hiring process?
The typical timeline ranges from two to four weeks, depending on role level, scheduling, and team availability for panel reviews. More senior roles or processes with cross-functional loops may take longer due to scheduling and additional decision rounds.
Where can I find real Pure Storage interview experiences?
You can explore Glassdoor and subreddit threads where candidates share unfiltered insights, timelines, and sample questions from their Pure Storage interview rounds.
What do Pure Storage Data Science interviews cover?
Data science interviews at Pure Storage test both technical depth and product sense. Expect SQL and statistics questions, machine learning fundamentals, and case-style prompts about optimizing storage or performance. Candidates are also evaluated on how they frame business impact, not just models.
What skills are required to work at Pure Storage?
Key skills include strong programming ability (Python, Java, or C++), systems knowledge (concurrency, distributed computing), and proficiency in SQL or data analysis. Beyond technical ability, Pure Storage places high value on ownership, product thinking, and collaborative communication.
Are Pure Storage interviews hard?
Yes. Pure Storage interviews are considered challenging because they combine coding and system design depth with behavioral alignment. Candidates who prepare across algorithms, SQL, and STAR-based storytelling tend to do well, especially when they show how their work scales to real-world enterprise impact.
Conclusion
Pure Storage sets a high bar, not just for technical excellence, but for ownership, product thinking, and cultural alignment. Whether you’re aiming for a data, software, or new grad role, the interview process is designed to surface impact-driven candidates who can thrive in fast-paced, customer-first teams.
Ready to tackle your Pure Storage interview? Start with our Pure Storage Interview Questions to practice real coding, SQL, and system design problems.
Then explore our Pure Storage interview guide for structured prep strategies:
- Software Engineer → Pure Storage Software Engineer Interview Guide
- Data Scientist → Pure Storage Data Scientist Interview Guide
- ML Engineer → Pure Storage ML Engineer Interview Guide
- Business Analyst → Pure Storage Business Analyst Interview Guide
Finally, if you are ready for real-time practice, schedule a 1-on-1 mock interview for tailored feedback.
